Abstract
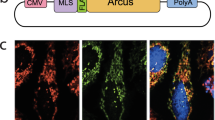
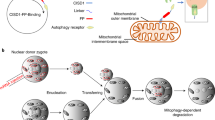
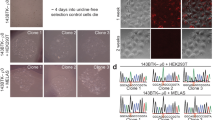
A T→G transversion at nt 8993 in mitochondrial DNA of MTATP6 (encoding ATPase 6 of complex V of the respiratory chain) causes impaired mitochondrial ATP synthesis in two related mitochondrial disorders: neuropathy, ataxia and retinitis pigmentosa1 and maternally inherited Leigh syndrome2. To overcome the biochemical defect, we expressed wildtype ATPase 6 protein allotopically3 from nucleus-transfected constructs encoding an amino-terminal mitochondrial targeting signal appended to a recoded ATPase 6 gene (made compatible with the universal genetic code) that also contained a carboxy-terminal FLAG epitope tag. After transfection of human cells, the precursor polypeptide was expressed, imported into and processed within mitochondria, and incorporated into complex V. Allotopic expression of stably transfected constructs in cytoplasmic hybrids (cybrids) homoplasmic with respect to the 8993T→G mutation showed a significantly improved recovery after growth in selective medium as well as a significant increase in ATP synthesis. This is the first successful demonstration of allotopic expression of an mtDNA-encoded polypeptide in mammalian cells and could form the basis of a genetic approach to treat a number of human mitochondrial disorders.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Holt, I.J., Harding, A.E., Petty, R.K.H. & Morgan-Hughes, J.A. A new mitochondrial disease associated with mitochondrial DNA heteroplasmy. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 46, 428–433 (1990).
Tatuch, Y. et al. Heteroplasmic mtDNA mutation (T→G) at 8993 can cause Leigh's disease when the percentage of abnormal mtDNA is high. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 50, 852–858 (1992).
Law, R.H., Farrell, L.B., Nero, D., Devenish, R.J. & Nagley, P. Studies on the import into mitochondria of yeast ATP synthase subunits 8 and 9 encoded by artificial nuclear genes. FEBS Lett. 236, 501–505 (1988).
DiMauro, S. & Andreu, A.L. Mutations in mtDNA: are we scraping the bottom of the barrel? Brain Pathol. 10, 431–441 (2000).
Anderson, S. et al. Sequence and organization of the human mitochondrial genome. Nature 290, 457–465 (1981).
White, S.L. et al. Genetic counseling and prenatal diagnosis for the mitochondrial DNA mutations at nucleotide 8993. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 65, 474–482 (1999).
de Vries, D.D., van Engelen, B.G.M., Gabreëls, F.J.M., Ruitenbeek, W. & van Oost, B.A. A second missense mutation in the mitochondrial ATPase6 gene in Leigh's syndrome. Ann. Neurol. 34, 410–412 (1993).
Elston, T., Wang, H. & Oster, G. Energy transduction in ATP synthase. Nature 391, 510–513 (1998).
Noji, H. & Yoshida, M. The rotary machine in the cell, ATP synthase. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 1665–1668 (2001).
Rastogi, V.K. & Girvin, M.E. Structural changes linked to proton translocation by subunit c of the ATP synthase. Nature 402, 263–268 (1999).
Hutcheon, M.L., Duncan, T.M., Ngai, H. & Cross, R.L. Energy-driven subunit rotation at the interface between subunit a and the c oligomer in the F0 sector of Escherichia coli ATP synthase. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 98, 8519–8524 (2001).
Garcia, J.J., Ogilvie, I., Robinson, B.H. & Capaldi, R.A. Structure, functioning, and assembly of the ATP synthase in cells from patients with the T8993G mitochondrial DNA mutation. Comparison with the enzyme in Rho0 cells completely lacking mtDNA. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 11075–11081 (2000).
Manfredi, G. et al. Oligomycin induces a decrease in the cellular content of a pathogenic mutation in the human mitochondrial ATPase 6 gene. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 9386–9391 (1999).
Tatuch, Y. & Robinson, B.H. The mitochondrial DNA mutation at 8993 associated with NARP slows the rate of ATP synthesis in isolated lymphoblast mitochondria. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 192, 124–128 (1993).
Vazquez-Memije, M.E. et al. Comparative biochemical studies in fibroblasts from patients with different forms of Leigh syndrome. J. Inher. Metab. Dis. 19, 43–50 (1996).
Chinnery, P.F. et al. Peptide nucleic acid delivery to human mitochondria. Gene Ther. 6, 1919–1928 (1999).
Geromel, V. et al. Mitochondria transfection by oligonucleotides containing a signal peptide and vectorized by cationic liposomes. Antisense Nucleic Acid Drug Dev. 11, 175–180 (2001).
Nakada, K. et al. Inter-mitochondrial complementation: mitochondria-specific system preventing mice from expression of disease phenotypes by mutant mtDNA. Nature Med. 7, 934–939 (2001).
Seibel, M. et al. Processing of artificial peptide-DNA-conjugates by the mitochondrial intermediate peptidase (MIP). Biol. Chem. 380, 961–967 (1999).
Gray, R.E., Law, R.H.P., Devenish, R.J. & Nagley, P. Allotopic expression of mitochondrial ATP synthase genes in nucleus of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Methods Enzymol. 264, 369–389 (1996).
Herlitze, S. & Koenen, M. A general and rapid mutagenesis method using polymerase chain reaction. Gene 91, 143–147 (1990).
Sutherland, L., Davidson, J., Glass, L.L. & Jacobs, H.T. Multisite oligonucleotide-mediated mutagenesis: application to the conversion of a mitochondrial gene to universal genetic code. Biotechniques 18, 458–464 (1995).
Rizzuto, R. et al. A gene specifying subunit VIII of human cytochrome c oxidase is localized to chromosome 11 and is expressed in both muscle and non-muscle tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 264, 10595–10600 (1989).
Rizzuto, R., Simpson, A.W.M., Brini, M. & Pozzan, T. Rapid changes of mitochondrial Ca2+ revealed by specifically targeted recombinant aequorin. Nature 358, 325–327 (1992).
Higuti, T., Kawamura, Y., Kuroiwa, K., Miyazaki, S. & Tsujita, H. Molecular cloning and sequence of two cDNAs for human subunit c of H+-ATP synthase in mitochondria. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1173, 87–90 (1993).
Ryan, M.T., Voos, W. & Pfanner, N. Assaying protein import into mitochondria. Methods Cell Biol. 65, 189–215 (2001).
Branda, S.S. & Isaya, G. Prediction and identification of new natural substrates of the yeast mitochondrial intermediate peptidase. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 27366–27373 (1995).
Breen, G.A.M., Miller, D.M., Holmans, P.L. & Welch, G. Mitochondrial DNA of two independent oligomycin-resistant chinese hamster ovary cell lines contains a single nucleotide change in the ATPase 6 gene. J. Biol. Chem. 261, 11680–11685 (1986).
John, U.P. & Nagley, P. Amino acid substitutions in mitochondrial ATPase subunit 6 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae leading to oligomycin resistance. FEBS Lett. 207, 79–83 (1986).
Strub, A., Lim, J.H., Pfanner, N. & Voos, W. The mitochondrial protein import motor. Biol. Chem. 381, 943–949 (2000).
Galanis, M., Devenish, R.J. & Nagley, P. Duplication of leader sequence for protein targeting to mitochondria leads to increased import efficiency. FEBS Lett. 282, 425–430 (1991).
Altendorf, K., Stalz, W., Greie, J. & Deckers-Hebestreit, G. Structure and function of the F(0) complex of the ATP synthase from Escherichia coli. J. Exp. Biol. 203, 19–28 (2000).
Jäger, H., Birkenhäger, R., Stalz, W.D., Altendorf, K. & Deckers-Hebestreit, G. Topology of subunit a of the Escherichia coli ATP synthase. Eur. J. Biochem. 251, 122–132 (1998).
Schon, E.A., Santra, S., Pallotti, F. & Girvin, M.E. Pathogenesis of primary defects in mitochondrial ATP synthesis. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 12, 441–448 (2001).
Mizushima, S. & Nagata, S. pEF-BOS, a powerful mammalian expression vector. Nucleic Acids Res. 18, 5322 (1990).
Rees, S. et al. Bicistronic vector for the creation of stable mammalian cell lines that predisposes all antibiotic-resistant cells to express recombinant protein. Biotechniques 20, 102–110 (1996).
Zolotukhin, S., Potter, M., Hauswirth, W.W., Guy, J. & Muzyczka, N. A “humanized” green fluorescent protein cDNA adapted for high-level expression in mammalian cells. J. Virol. 70, 4646–4654 (1996).
Hauswirth, W.W., Lewin, A.S., Zolotukhin, S. & Muzyczka, N. Production and purification of recombinant adeno-associated virus. Methods Enzymol. 316, 743–761 (2000).
Isaya, G., Kalousek, F. & Rosenberg, L.E. Sequence analysis of rat mitochondrial intermediate peptidase: similarity to zinc metallopeptidases and to a putative yeast homologue. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 89, 8317–8321 (1992).
Sciacco, M. & Bonilla, E. Cytochemistry and immunocytochemistry of mitochondria in tissue sections. Methods Enzymol. 264, 509–521 (1996).
Pallotti, F. & Lenaz, G. Isolation and subfractionation of mitochondria from animal cells and tissue culture lines. Methods Cell Biol. 65, 1–35 (2001).
Klement, P., Nijtmans, L.G., Van den Bogert, C. & Houstek, J. Analysis of oxidative phosphorylation complexes in cultured human fibroblasts and amniocytes by blue-native-electrophoresis using mitoplasts isolated with the help of digitonin. Anal. Biochem. 231, 218–224 (1995).
Manfredi, G., Spinazzola, A., Checcarelli, N. & Naini, A. Assay of mitochondrial ATP synthesis in animal cells. Methods Cell Biol. 65, 133–145 (2001).
Mariottini, P. et al. Identification of the polypeptides encoded in the unassigned reading frames 2, 4, 4L, and 5 of human mitochondrial DNA. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 83, 1563–1567 (1986).
Acknowledgements
We thank S. Goff and E. Bacharach for advice and H. Du for technical assistance. This work was supported by grants from the US National Institutes of Health (to G.M., E.A.S. and J.G.) and the Muscular Dystrophy Association (to E.A.S. and G.M.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manfredi, G., Fu, J., Ojaimi, J. et al. Rescue of a deficiency in ATP synthesis by transfer of MTATP6, a mitochondrial DNA-encoded gene, to the nucleus. Nat Genet 30, 394–399 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng851
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng851
This article is cited by
-
Optimized allotopic expression of mitochondrial ND6 transgene restored complex I and apoptosis deficiencies caused by LHON-linked ND6 14484T > C mutation
Journal of Biomedical Science (2023)
-
Leber hereditary optic neuropathy—new insights and old challenges
Graefe's Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology (2021)
-
Therapeutic Options in Hereditary Optic Neuropathies
Drugs (2021)
-
Molecular basis of Leigh syndrome: a current look
Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases (2020)
-
Mitochondrial DNA variants in colorectal carcinogenesis: Drivers or passengers?
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2017)