Abstract
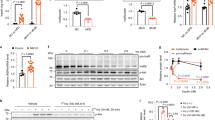
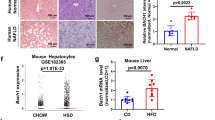
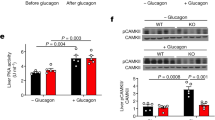
We hypothesized that insulin stimulates phosphorylation of CEACAM1 which in turn leads to upregulation of receptor-mediated insulin endocytosis and degradation in the hepatocyte. We have generated transgenic mice over-expressing in liver a dominant-negative, phosphorylation-defective S503A-CEACAM1 mutant. Supporting our hypothesis, we found that S503A-CEACAM1 transgenic mice developed hyperinsulinemia resulting from impaired insulin clearance. The hyperinsulinemia caused secondary insulin resistance with impaired glucose tolerance and random, but not fasting, hyperglycemia. Transgenic mice developed visceral adiposity with increased amounts of plasma free fatty acids and plasma and hepatic triglycerides. These findings suggest a mechanism through which insulin signaling regulates insulin sensitivity by modulating hepatic insulin clearance.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Backer, J.M. et al. Insulin stimulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity maps to insulin receptor regions required for endogenous substrate phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 1367–1374 (1992).
Baumann, C.A. et al. CAP defines a second signalling pathway required for insulin-stimulated glucose transport. Nature 407, 202–207 (2000).
Mathews, S.T. et al. Alpha2-HSG, a specific inhibitor of insulin receptor autophosphorylation, interacts with the insulin receptor. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 164, 87–98 (2000).
Maddux, B.A. & Goldfine, I.D. Membrane glycoprotein PC-1 inhibition of insulin receptor function occurs via direct interaction with the receptor α-subunit. Diabetes 49, 13–19 (2000).
Najjar, S.M. et al. Insulin-stimulated phosphorylation of recombinant pp120/HA4, an endogenous substrate of the insulin receptor tyrosine kinase. Biochemistry 34, 9341–9349 (1995).
Cheung, P.H. et al. Cell-CAM105 isoforms with different adhesion functions are coexpressed in adult rat tissues and during liver development. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 6139–6146 (1993).
Hsieh, J.-T. et al. Tumor suppressive role of an androgen-regulated epithelial cell adhesion molecule (C-CAM) in prostate carcinoma cell revealed by sense and antisense approaches. Cancer Res. 55, 190–197 (1995).
Luo, W., Wood, C.G., Earley, K., Hung, M.C. & Lin, S.H. Suppression of tumorigenicity of breast cancer cells by an epithelial cell adhesion molecule (C-CAM1): the adhesion and growth suppression are mediated by different domains. Oncogene 14, 1697–1704 (1997).
Rosenberg, M. et al. The expression of mouse biliary glycoprotein, a carcinoembryonic antigen-related gene, is down-regulated in malignant mouse tissues. Cancer Res. 53, 4938–4945 (1993).
Neumaier, M., Paululat, S., Chan, A., Matthaes, P. & Wagener, C. Biliary glycoprotein, a potential human cell adhesion molecule, is down-regulated in colorectal carcinomas. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 90, 10744–10748 (1993).
Li Calzi, S., Choice, C.V. & Najjar, S.M. Differential effect of pp120 on insulin endocytosis by two variant insulin receptor isoforms. Am. J. Physiol. 273, E801–808 (1997).
Formisano, P. et al. Receptor-mediated internalization of insulin. Potential role of pp120/HA4, a substrate of the insulin receptor kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 24073–24077 (1995).
Soni, P., Lakkis, M., Poy, M.N., Fernstrom, M.A. & Najjar, S.M. The differential effects of pp120 (Ceacam 1) on the mitogenic action of insulin and insulin-like growth factor 1 are regulated by the nonconserved tyrosine 1316 in the insulin receptor. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20, 3896–3905 (2000).
Choice, C.V., Howard, M.J., Poy, M.N., Hankin, M.H. & Najjar, S.M. Insulin stimulates pp120 endocytosis in cells co-expressing insulin receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 22194–22200 (1998).
Duckworth, W.C., Bennett, R.G. & Hamel, F.G. Insulin degradation: progress and potential. Endocr. Rev. 19, 608–624 (1998).
Han, E. et al. Differences in tissue-specific and embryonic expression of mouse Ceacam1 and Ceacam2 genes. Biochem. J. 355, 417–423 (2001).
Chen, X., Iqbal, N. & Boden, G. The effects of free fatty acids on gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis in normal subjects. J. Clin. Invest. 103, 365–372 (1999).
Michael, M.D. et al. Loss of insulin signaling in hepatocytes leads to severe insulin resistance and progressive hepatic dysfunction. Mol. Cell 6, 87–97 (2000).
Najjar, S.M., Choice, C.V., Soni, P., Whitman, C.M. & Poy, M.N. Effect of pp120 on receptor-mediated insulin endocytosis is regulated by the juxtamembrane domain of the insulin receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 12923–12928 (1998).
Svedberg, J., Stromblad, G., Wirth, A., Smith, U. & Bjorntorp, P. Fatty acids in the portal vein of the rat regulate hepatic insulin clearance. J. Clin. Invest. 88, 2054–2058 (1991).
Escobar, O. et al. Hepatic insulin clearance increases after weight loss in obese children and adolescents. Am. J. Med. Sci. 317, 282–286 (1999).
Bosello, O. et al. Modifications of abdominal fat and hepatic insulin clearance during severe caloric restriction. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 34, 359–365 (1990).
Peiris, A.N., Mueller, R.A., Smith, G.A., Struve, M.F. & Kissebah, A.H. Splanchnic insulin metabolism in obesity. Influence of body fat distribution. J. Clin. Invest. 78, 1648–1657 (1986).
Svedberg, J., Bjorntorp, P., Smith, U. & Lonnroth, P. Free-fatty acid inhibition of insulin binding, degradation, and action in isolated rat hepatocytes. Diabetes 39, 570–574 (1990).
Hennes, M.M., Shrago, E. & Kissebah, A.H. Receptor and postreceptor effects of free fatty acids (FFA) on hepatocyte insulin dynamics. Int. J. Obes. 14, 831–841 (1990).
Ferrannini, E., Barrett, E.J., Bevilacqua, S. & DeFronzo, R.A. Effect of fatty acids on glucose production and utilization in man. J. Clin. Invest. 72, 1737–1747 (1983).
Kissebah, A.H., Alfarsi, S., Adams, P.W. & Wynn, V. Role of insulin resistance in adipose tissue and liver in the pathogenesis of endogenous hypertriglyceridaemia in man. Diabetologia 12, 563–571 (1976).
Rooney, D.P. & Robertson, R.P. Hepatic insulin resistance after pancreas transplantation in type I diabetes. Diabetes 45, 134–138 (1996).
Diem, P., Abid, M., Redmon, J.B., Sutherland, D.E. & Robertson, R.P. Systemic venous drainage of pancreas allografts as independent cause of hyperinsulinemia in type I diabetic recipients. Diabetes 39, 534–540 (1990).
Bergman, R.N. & Ader, M. Free fatty acids and pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 11, 351–356 (2000).
Bergman, R.N. Non-esterified fatty acids and the liver: why is insulin secreted into the portal vein? Diabetologia 43, 946–952 (2000).
Reaven, G.M. & Chen, Y.D. Role of insulin in regulation of lipoprotein metabolism in diabetes. Diabetes Metab. Rev. 4, 639–652 (1988).
Randle, P.J., Garland, P.B., Newsholme, E.A. & Hales, C.N. The glucose fatty acid cycle in obesity and maturity onset diabetes mellitus. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 131, 324–333 (1965).
Randle, P.J., Priestman, D.A., Mistry, S. & Halsall, A. Mechanisms modifying glucose oxidation in diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 37, S155–161 (1994).
Nestel, P.J., Ishikawa, T. & Goldrick, R.B. Diminished plasma free fatty acid clearance in obese subjects. Metabolism 27, 589–597 (1978).
Koopmans, S.J., Kushwaha, R.S. & DeFronzo, R.A. Chronic physiologic hyperinsulinemia impairs suppression of plasma free fatty acids and increases de novo lipogenesis but does not cause dyslipidemia in conscious normal rats. Metabolism 48, 330–337 (1999).
Kido, Y. et al. Tissue-specific insulin resistance in mice with combined mutations in the insulin receptor, IRS-1, and IRS-2. J. Clin. Invest. 105, 199–205 (2000).
Kim, J.K. et al. Redistribution of substrates to adipose tissue promotes obesity in mice with selective insulin resistance in muscle. J. Clin. Invest. 105, 1791–1797 (2000).
Walsh, A., Ito, Y. & Breslow, J.L. High levels of human apolipoprotein A-I in transgenic mice result in increased plasma levels of small high density lipoprotein (HDL) particles comparable to human HDL. J. Biol. Chem. 264, 6488–6494 (1989).
Bisaha, J.G., Simon, T.C., Gordon, J.I. & Breslow, J.L. Characterization of an enhancer element in the human apolipoprotein C-III gene that regulates human apolipoprotein A-I gene expression in the intestinal epithelium. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 19979–19988 (1995).
Najjar, S.M. et al. pp120/ecto-ATPase, an endogenous substrate of the insulin receptor tyrosine kinase, is expressed as two variably spliced isoforms. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 1201–1206 (1993).
Najjar, S.M. et al. Cloning and characterization of a functional promoter of the rat pp120 gene, encoding a substrate of the insulin receptor tyrosine kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 8809–8817 (1996).
Folch, J., Lees, M. & Sloane-Stanley, G.H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 226, 497–509 (1957).
Mondon, C.E., Olefsky, J.M., Dolkas, C.B. & Reaven, G.M. Removal of insulin by perfused rat liver: effect of concentration. Metabolism 24, 153–160 (1975).
Cinti, S., Eberbach, S., Castellucci, M. & Accili, D. Lack of insulin receptors affects the formation of white adipose tissue in mice. A morphological and ultrastructural analysis. Diabetologia 41, 171–177 (1998).
Ruch, R.J. & Klaunig, J.E. Kinetics of phenobarbital inhibition of intercellular communication in mouse hepatocytes. Cancer Res. 48, 2519–2523 (1988).
Lee, A.D., Gulve, E.A., Chen, M., Schluter, J. & Holloszy, J.O. Effects of Ca2+ ionophore ionomycin on insulin-stimulated and basal glucose transport in muscle. Am. J. Physiol. 268, R997–1002 (1995).
Lee, C.H. et al. Nck associates with the SH2 domain-docking protein IRS-1 in insulin-stimulated cells. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 90, 11713–11717 (1993).
Acknowledgements
We thank D. Accili, S.F. Previs and G.I. Shulman for critical reading of the manuscript and for helpful scientific discussions, and E.M. Rubin and N. Beauchemin for providing the apolipoprotein A-1 promoter cDNA and anti-mouse BGP antibodies, respectively. We thank S. Robson, E. Tietz and S. Lilly for assistance in immunohistochemistry and microscopy, and T. Dai and R. Ruch for assistance in primary hepatocytes. We also thank the Ohio University Edison Biotechnology Institute Collaborative Transgenics, Athens, Ohio for performing DNA microinjections as part of their service grant support (to S.M.N.). This work was chiefly supported by two grants from the National Institutes of Health–National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases (to S.M.N.), and partially by Sigma-Tau Research (to S.M.N.) and the Department of Veterans Affairs (to S.K.E.). M.N.P. was partially supported by the Institutional Pre-doctoral National Research Service Award fellowship from the National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Poy, M., Yang, Y., Rezaei, K. et al. CEACAM1 regulates insulin clearance in liver. Nat Genet 30, 270–276 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng840
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng840
This article is cited by
-
Reflections on the state of diabetes research and prospects for treatment
Diabetology International (2023)
-
The effect of high-intensity interval training and CoQ10 administration on hepatic CEACAM1 and PDGFA proteins in diet-induced obese rats
Sport Sciences for Health (2023)
-
Whey protein sweetened with Stevia rebaudiana increases insulin-degrading enzyme, but not carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 1 expression in the liver from resistance-trained rats
Nutrire (2022)
-
Co-receptor regulation of insulin signaling
Nature Metabolism (2022)
-
Association of circulating CEACAM1 levels and insulin sensitivity in gestational diabetes mellitus
BMC Endocrine Disorders (2020)