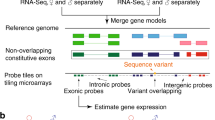
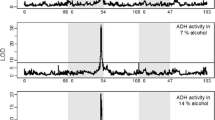
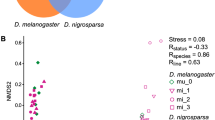
Abstract
Although most genetic association studies are performed with the intention of detecting nucleotide polymorphisms that are correlated with a complex trait, transcript abundance should also be expected to associate with diseases or phenotypes. We performed a scan for such quantitative trait transcripts in adult female heads of the fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) that might explain variation for nicotine resistance. The strongest association was seen for abundance of ornithine aminotransferase transcripts, implicating detoxification and neurotransmitter biosynthesis as mediators of the quantitative response to the drug. Subsequently, genetic analysis and metabolite profiling confirmed a complex role for ornithine and GABA levels in modification of survival time upon chronic nicotine exposure. Differences between populations from North Carolina and California suggest that the resistance mechanism may be an evolved response to environmental exposure.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liotta, L. & Petricoin, E. Molecular profiling of human cancer. Nat. Rev. Genet. 1, 48–56 (2000).
de Koning, D.J. & Haley, C.S. Genetical genomics in humans and model organisms. Trends Genet. 21, 377–381 (2005).
Mackay, T.F. The genetic architecture of quantitative traits. Annu. Rev. Genet. 35, 303–339 (2001).
Cohen, C., Welzl, H. & Battig, K. Effects of nicotine, caffeine and their combination on locomotor activity in rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 40, 121–123 (1991).
Wolf, F.W. & Heberlein, U. Invertebrate models of drug abuse. J. Neurobiol. 54, 161–178 (2003).
Carrillo, R. & Gibson, G. Unusual genetic architecture of natural variation affecting drug resistance in Drosophila melanogaster. Genet. Res. 80, 205–213 (2002).
Jessen, A., Buemann, B., Toubro, S., Skovgaard, I.M. & Astrup, A. The appetite-suppressant effect of nicotine is enhanced by caffeine. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 7, 327–333 (2005).
Palsson, A. & Gibson, G. Association between nucleotide variation in Egfr and wing shape in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 167, 1187–1198 (2004).
Dworkin, I., Palsson, A., Birdsall, K. & Gibson, G. Evidence that Egfr contributes to cryptic genetic variation for photoreceptor determination in natural populations of Drosophila melanogaster. Curr. Biol. 13, 1888–1893 (2003).
Macdonald, S.J., Pastinen, T. & Long, A.D. The effect of polymorphisms in the Enhancer of split gene complex on bristle number variation in a large wild-caught cohort of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 171, 1741–1756 (2005).
De Luca, M. et al. Dopa decarboxylase (Ddc) affects variation in Drosophila longevity. Nat. Genet. 34, 429–433 (2003).
Seiler, N. Ornithine aminotransferase, a potential target for the treatment of hyperammonemias. Curr. Drug Targets 1, 119–153 (2000).
Kelly, A. & Stanley, C.A. Disorders of glutamate metabolism. Ment. Retard. Dev. Disabil. Res. Rev. 7, 287–295 (2001).
Sivilotti, L. & Nistri, A. GABA receptor mechanisms in the central nervous system. Prog. Neurobiol. 36, 35–92 (1991).
Beleboni, R.O. et al. Pharmacological and biochemical aspects of GABAergic neurotransmission: pathological and neuropsychobiological relationships. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 24, 707–728 (2004).
Livak, K.J. & Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)). Methods 25, 402–408 (2001).
Vale, C., Damgaard, I., Sunol, C., Rodriguez-Farre, E. & Schousboe, A. Cytotoxic action of lindane in neocortical GABAergic neurons is primarily mediated by interaction with flunitrazepam-sensitive GABA(A) receptors. J. Neurosci. Res. 52, 276–285 (1998).
Parmar, D. et al. Effect of lindane on hepatic and brain cytochrome P450s and influence of P450 modulation in lindane induced neurotoxicity. Food Chem. Toxicol. 41, 1077–1087 (2003).
Tomfohr, J., Lu, J. & Kepler, T.B. Pathway level analysis of gene expression using singular value decomposition. BMC Bioinformatics 6, 225 (2005).
Thibault, S.T. et al. A complementary transposon toolkit for Drosophila melanogaster using P and piggyBac. Nat. Genet. 36, 283–287 (2004).
Yoneda, Y., Roberts, E. & Dietz, G.W., Jr . A new synaptosomal biosynthetic pathway of glutamate and GABA from ornithine and its negative feedback inhibition by GABA. J. Neurochem. 38, 1686–1694 (1982).
Palsson, A., Rouse, A., Riley-Berger, R., Dworkin, I. & Gibson, G. Nucleotide variation in the Egfr locus of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 167, 1199–1212 (2004).
Yang, H.P. & Nuzhdin, S.V. Fitness costs of Doc expression are insufficient to stabilize its copy number in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol. Biol. Evol. 20, 800–804 (2003).
Jain, A.N. et al. Fully automatic quantification of microarray image data. Genome Res. 12, 325–332 (2002).
Churchill, G.A. Fundamentals of experimental design for cDNA microarrays. Nat. Genet. 32 (Suppl.), 490–495 (2002).
Jin, W. et al. The contributions of sex, genotype and age to transcriptional variance in Drosophila melanogaster. Nat. Genet. 29, 389–395 (2001).
Wolfinger, R.D. et al. Assessing gene significance from cDNA microarray expression data via mixed models. J. Comput. Biol. 8, 625–637 (2001).
Acknowledgements
We thank S. Nuzhdin for providing the California inbred lines and R. Carrillo for initial sampling of nicotine resistance. This paper is dedicated to the memory of R. Rose, who first pointed out the lindane connection in our data. This work was supported by US National Institutes of Health grant P01-GM45344 to G.G.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
G.P.-G. performed all of the data analysis and experimental components, with the exception of the genetic complementation test (P.H.) and metabolite profiling (N.D.). She was assisted by W.-P.H. in the statistical analysis. G.G. conceived the experiment and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Fig. 1
Schematic of OAT function. (PDF 12 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
Regression of nicotine concentration on survival time. (PDF 14 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 3
qRT-PCR of Gad1. (PDF 10 kb)
Supplementary Table 1
Expression on nicotine correlated to survival time. (PDF 15 kb)
Supplementary Table 2
Expression on control food correlated to survival time. (PDF 14 kb)
Supplementary Table 3
Primers. (PDF 9 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Passador-Gurgel, G., Hsieh, WP., Hunt, P. et al. Quantitative trait transcripts for nicotine resistance in Drosophila melanogaster. Nat Genet 39, 264–268 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1944
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1944
This article is cited by
-
Identification of microRNAs associated with allergic airway disease using a genetically diverse mouse population
BMC Genomics (2015)
-
Mapping genetic determinants of coronary microvascular remodeling in the spontaneously hypertensive rat
Basic Research in Cardiology (2013)
-
Co-regulated transcriptional networks contribute to natural genetic variation in Drosophila sleep
Nature Genetics (2009)
-
Systems genetics of complex traits in Drosophila melanogaster
Nature Genetics (2009)
-
The genetics of quantitative traits: challenges and prospects
Nature Reviews Genetics (2009)