Abstract
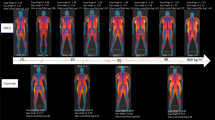
Obesity is strongly implicated in the pathophysiology of insulin resistance, diabetes mellitus and dyslipidemia1–3. The mechanisms, however, by which obesity causes these complications are not known. The study of single-gene disorders affecting adipose tissue may elucidate some of the mechanisms involved in these processes. Familial partial lipodystrophy, Dunnigan variety, (FPLD, OMIM 308980) is an autosomal-dominant condition characterized by marked loss of subcutaneous adipose tissue affecting the trunk and extremities but with excess fat deposition in the head and neck areas4–14. Affected individuals show an increased preponderance of insulin resistance, diabetes mellitus, dyslipidemia and acanthosis nigricans4–14. The genetic basis of FPLD is unknown. We carried out a genome-wide scan with a set of highly polymorphic short tandem-repeats (STR) in individuals from five well-characterized pedigrees and mapped the FPLD locus to chromosome 1q21–22. The maximum two-point lod score obtained with a highly polymorphic microsatellite at D1S2624 at θmax=0 was 5.84. Multipoint-linkage analysis yielded a peak lod score of 8.25 between D75305 and D1S1600. There was no evidence for genetic heterogeneity (α=1) in the pedigrees.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reaven, G.M. Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes 37, 1595–1607 (1988).
DeFronzo, R.A. Insulin resistance: a multifaceted syndrome responsible for NIDDM, obesity, hypertension, dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis. Neth. J. Med. 50, 191–197 (1997).
Landsberg, L. Obesity and the insulin resistance syndrome. Hypertens. Res. 19, S51–55 (1996).
Ozer, F.L., Lichtenstein, J.R., Kwiterovich, P.O. & McKusick, V.A. A new genetic variety of lipodystrophy. Clin. Res. 21, 533 (1973)
Dunnigan, M.G., Cochrane, M.A., Kelly, A. & Scott, J.W. Familial lipoatrophic diabetes with dominant transmission: a new syndrome. Q. J. Med. 49, 33–48 (1974).
Kobberling, J., Willms, B., Kattermann, R. & Creutzfeldt, W. Lipodystrophy of the extremities. A dominantly inherited syndrome associated with lipoatrophic diabetes. Humangenetik 29, 111–120 (1975).
Kobberling, J. & Dunnigan, M.G. Familial partial lipodystrophy: two types of an X linked dominant syndrome, lethal in the hemizygous state. J. Med. Genet 23, 120–127 (1986).
Davidson, M.B. & Young, R.T. Metabolic studies in familial partial lipodystrophy of the lower trunk and extremities. Diabetologia 11, 561–568 (1975).
Kobberling, J. et al. Partielle Lipodystrophie mit lipatrophischem Diabetes und Hyperlipoproteinamie. Verh. Dtsch. Ges. Inn. Med. 87, 958–961 (1981).
Burn, J. & Baraitser, M. Partial lipoatrophy with insulin resistant diabetes and hyperlipidaemia (Dunnigan syndrome). J. Med. Genet. 23, 128–130 (1986).
Robbins, D.C., Norton, E.S., Tulp, O. & Sims, E.A.H. Familial partial lipodystrophy: complications of obesity in the non-obese? Metabolism 31, 445–452 (1982).
Lillystone, D. & West, R.J. Lipodystrophy of limbs associated with insulin resistance. Arch. Dis. Child. 50, 737–739 (1975).
Hook, B., Freudlsperger, F., Adam, W. & Seif, F.J. Partielles lipodystrophie-syndrom (Typ Dunnigan). Hautarzt 35, 530–535 (1984).
Jackson, S.N., Howlett, T.A., McNally, P.G., O'Rahilly, S. & Trembath, R.C. Dunnigan-Kobberling syndrome: an autosomal dominant form of partial lipodystrophy. Q. J. Med. 90, 27–36 (1997).
Flagiello, D. et al. Assignment of the genes for cellular retinoic acid binding protein 1 (CRABP1) and 2 (CRABP2) to human chromosome band 15q24 and 1q21.3, respectively, by in situ hybridization. Cytogenet. Cell. Genet. 76, 17–18 (1997).
Johnson, B. et al. The Ah receptor nuclear translocator (ARNT) is located on q21 of human chromosome 1 and on mouse chromosome 3 near Cf-3. Genomics 17, 592–598(1993).
Wanner, R., Panteleyev, A., Henz, B.M. & Rosenbach, T. Retinoic acid affects the expression rate of the differentiation-related genes aryl hydrocarbon receptor, ARNT and keratin 4 in proliferative keratinocytes only. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1317, 105–111(1996).
Marenholz, I. et al. Genetic analysis of the epidermal differentiation complex (EDC) on human chromosome 1q21: chromosomal orientation, new markers, and a 6-Mb YAC contig. Genomics 37, 295–302 (1996).
Feder, J. et al. A systematic approach for detecting high-frequency restriction fragment polymorphisms using large genomic probes. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 37, 635–649 (1985).
Kruglyak, L., Daly, M.J., Reeve-Daly, M.P. & Lander, E.S. Parametric and nonparametric linkage analysis: a unified multipoint approach. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 58, 1347–1363 (1996).
Lander, E.S. & Green, P. Construction of multilocus genetic linkage maps in humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84, 2363–2367 (1987).
Lathrop, G.M., Lalouel, J.M., Julier, C. & Ott, J. Strategies for multilocus linkage analysis in humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 81, 3443–3446 (1984).
Schaffer, A.A., Gupta, S.K., Shriram, K. & Cottingham, R.W., Jr. Avoiding recomputation in linkage analysis. Hum. Hered. 44, 225–237 (1994).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peters, J., Barnes, R., Bennett, L. et al. Localization of the gene for familial partial lipodystrophy (Dunnigan variety) to chromosome 1q21–22. Nat Genet 18, 292–295 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0398-292
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0398-292
This article is cited by
-
Phospholipid biosynthetic pathways and lipodystrophies: a novel syndrome due to PLAAT3 deficiency
Nature Reviews Endocrinology (2024)
-
Characteristic and fate determination of adipose precursors during adipose tissue remodeling
Cell Regeneration (2023)
-
Phenotypic and Genetic Characteristics of Lipodystrophy: Pathophysiology, Metabolic Abnormalities, and Comorbidities
Current Diabetes Reports (2018)
-
Familial partial lipodystrophy, Dunnigan variety - challenges for patient care during pregnancy: a case report
BMC Research Notes (2015)
-
Exploring the pathophysiology behind the more common genetic and acquired lipodystrophies
Journal of Human Genetics (2014)