Abstract
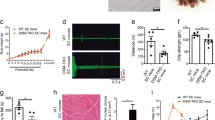
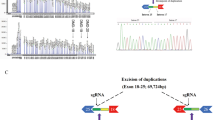
Myotonic dystrophy (DM) is one of a growing number of inherited human disorders associated with the expansion of triplet repeat DNA sequences1. Expanded alleles are highly unstable in both the germline and soma, accounting in large part for the unusual genetics of this disorder, its phenotypic variability and probably, the progressive nature of the symptoms2–7. However, the molecular mechanisms and the genetic factors modulating repeat stability in DM and the other human disorders associated with expanded repeats are not well understood. To provide a model system in which the turnover of triplet repeats could be studied throughout mammalian development, we have generated five transgenic mouse lines incorporating expanded CTG/CAG arrays derived from the human DM locus. Transgene analysis has revealed germline hypermutability, including expansions, deletions and parent-of-origin effects, somatic and early embryonic instability and segregation distortion. Mutational differences between lines and sexes demonstrate that stability, as in humans, is modulated by as yet unidentified cis and trans acting genetic elements.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Monckton, D.G. & Caskey, C.T. Unstable triplet repeat diseases. Circulation 91, 513–520 (1995).
Fu, Y.H. et al. An unstable triplet repeat in a gene related to myotonic muscular dystrophy. Science 255, 1256–1258 (1992).
Brook, J.D. et al. Molecular basis of myotonic dystrophy: expansion of a trinucleotide (CTG) repeat at the 3′ end of a transcript encoding a protein kinase family member. Cell 68, 799–808 (1992).
Mahadevan, M. et al. Myotonic dystrophy mutation: an unstable CTG repeat in the 3′ untranslated region of the gene. Science 255, 1253–1255 (1992).
Monckton, D.G., Wong, L.-J.C., Ashizawa, T. & Caskey, C.T. Somatic mosaicism, germline expansions, germline reversions and intergenerational reductions in myotonic dystrophy males: small pool PCR analyses. Hum. Mol. Genet. 4, 1–8 (1995).
Wong, L.-J.C., Ashizawa, T., Monckton, D.G., Caskey, C.T. & Richards, C.S. Somatic heterogeneity of the CTG repeat in myotonic dystrophy is age and size dependent. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 56, 114–122 (1995).
Jansen, G. et al. Gonosomal mosaicism in myotonic dystrophy patients: Involvement of mitotic events in (CTG)n variation and selection against extreme expansion in sperm. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 54, 575–585 (1994).
Igarashi, S. et al. Intergenerational instability of the GAG repeat of the gene for Machado-Joseph disease (MJD1) is affected by the genotype of the normal chromosome: implications for the molecular mechanisms of the instability of the CAG repeat. Hum. Mol. Genet. 5, 923–932 (1996).
Burright, E.N. et al. SCA1 transgenic mice: a model for neurodegeneration caused by an expanded CAG trinucleotide repeat. Cell 82, 937–948 (1995).
Bingham, P.M. et al. Stability of an expanded trinucleotide repeat in the androgen receptor gene in transgenic mice. Nature Genet. 9, 191–196 (1995).
Goldberg, Y.P. et al. Absence of disease phenotype and intergenerational stability of the CAG repeat in transgenic mice expressing the human Huntington disease transcript. Hum. Mol. Genet. 5, 177–185 (1996).
Kawaguchi, Y. et al. CAG expansions in a novel gene for Machado-Joseph disease at chromosome 14q32.1. Nature Genet. 8, 221–227 (1994).
Maruyama, H. et al. Molecular features of the CAG repeats and clinical manifestation of Machado-Joseph disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 4, 807–812 (1995).
Biancalana, V. et al. Moderate instability of the trinucleotide repeat in spino bulbar muscular atrophy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1, 255–258 (1992).
Orr, H.T. et al. Expansion of an unstable CAG repeat in spinocerebellar ataxia type 1. Nature Genet. 4, 221–226 (1993).
A novel gene containing a trinucleotide repeat that is expanded and unstable on Huntington's disease chromosomes. Cell 72, 971–983 (1993).
Koide, R. et al. Unstable expansion of CAG repeat in hereditary dentatorubral-pallidoluysian atrophy (DRPLA). Nature Genet. 6, 9–13 (1994).
Nagafuchi, S. et al. Dentatorubral and pallidoluysian atrophy expansion of an unstable CAG trinucleotide on chromosome 12. Nature Genet. 6, 14–18 (1994).
Mahon, K.A., Overbeek, P.A. & Westphal, H. Prenatal lethality in a transgenic mouse line is the result of a chromosomal translocation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85, 1165–1168 (1988).
Yu, Y.E., Nemeth, M., Pathak, S., Meistrich, M.L. & Wong, P.K. Preliminary characterization of transgenic males harboring an unbalanced product of the reciprocal translocation T (3;10). Mouse Genome(in the press).
Chakraborty, R. et al. Segregation Distortion of the CTG repeats at the myotonic dystrophy locus. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 59, 109–118 (1996).
Ikeuchi, T. et al. Non-Mendelian transmission in dentatorubral-pallidoluysian atrophy and Machado-Joseph disease: the mutant allele is preferentially transmitted in male meiosis. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 58, 730–733 (1996).
Kelly, R.G., Gibbs, M., Collick, A. & Jeffreys, A.J. Spontaneous mutation at the hypervariable mouse minisatellite locus Ms6-hm: flanking DNA sequence and analysis of germline and early somatic mutation events. Proc. R. Soc. Lon. B 245, 235–245 (1991).
Gibbs, M., Collick, A., Kelly, R.G. & Jeffreys, A.J. A tetranucleotide repeat mouse minisatellite displaying substantial somatic instability during early preimplantation development. Genomics 17, 121–128 (1993).
Collick, A. et al. Variable germline and embryonic instability of the human minisatellite MS32 (D1S8) in transgenic mice. EMBO J. 13, 5745–5753 (1994).
Collick, A. et al. Instability of long inverted repeats within mouse transgenes. EMBO J. 15, 1163–1171 (1996).
Wörhle, D., Hennig, I., Vogel, W. & Steinbach, P. Mitotic stability of fragile X mutations in differentiated Cells indicates early post-conceptional trinucleotide repeat expansion. Nature Genet. 4, 140–142 (1993).
Jeffreys, A.J., Neumann, R. & Wilson, V. Repeat unit sequence variation in minisatellites: a novel source of polymorphism for studying allelic variation and mutation by single molecule analysis. Cell 60, 473–485 (1990).
Pinkert, C.A. Transgenic Animal Technology: A Laboratory Handbook. (San Diego, Academic Press, 1994).
Henrion, A.A., Martinez, A., Mattei, M.-G., Kahn, A. & Raymondjean, M., Structure, sequence and chromosomal location of the gene for USF2 transcription factor in mouse. Genomics 25, 36–43 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Monckton, D., Coolbaugh, M., Ashizawa, K. et al. Hypermutable myotonic dystrophy CTG repeats in transgenic mice. Nat Genet 15, 193–196 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0297-193
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0297-193
This article is cited by
-
Pathogenic expansions of the SCA6 locus are associated with a common CACNA1A haplotype across the globe: founder effect or predisposing chromosome?
European Journal of Human Genetics (2008)
-
Features of trinucleotide repeat instability in vivo
Cell Research (2008)
-
The GAA triplet-repeat is unstable in the context of the human FXN locus and displays age-dependent expansions in cerebellum and DRG in a transgenic mouse model
Human Genetics (2006)
-
Repeat instability: mechanisms of dynamic mutations
Nature Reviews Genetics (2005)
-
Evidence of cis-acting factors in replication-mediated trinucleotide repeat instability in primate cells
Nature Genetics (2002)