Abstract
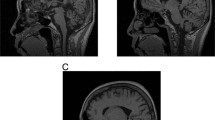
Hereditary dentatorubral–pallidoluysian atrophy (DRPLA) is an autosomal dominant neurologic disorder characterized by variable combinations of myoclonus, epilepsy, cerebellar ataxia, choreoathetosis and dementia. By specifically searching published brain cDNA sequences for the presence of CAG repeats we identified unstable expansion of a CAG in a gene on chromosome 12 in all the 22 DRPLA patients examined. A good correlation between the size of the CAG repeat expansion and the ages of disease onset is found in this group. Patients with earlier onset tended to have a phenotype of progressive myoclonus epilepsy and larger expansions. We propose that the wide variety of clinical manifestations of DRPLA can now be explained by the variable unstable expansion of the CAG repeat.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
McKusick V.A., Francomano, C.A. & Antonarakis, S.E. Mendelian Inheritance of Man. 10th edn 305–306 (The Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore, 1992).
Naito, H. & Oyanagi, S. Familial myoclonus epilepsy and choreoathetosis: Hereditary dentatorubral-pallidoluysian atrophy. Neurol. 32, 798–807 (1982).
Takahashi, H. et al. Hereditary dentatorubral-pallidoluysian atrophy: Clinical and pathologic variants in a family. Neurol. 38, 1065–1070 (1988).
Smith, J.K., Gonda, V.E. & Malamud, N. Unusual form of cerebellar ataxia: Combined dentato-rubral and pallido-Luysian degeneration. Neurol. 8, 205–209 (1958).
Naito, H. Progressive myoclonus epilepsy and DRPLA (in Japanese). Shinkei Kenkyu no Shinpo 34, 56–67 (1990).
Kondo, I. et al. Exclusion mapping of the hereditary dentatorubro pallidoluysian atrophy gene from the Huntington's disease locus. J. med. Genet. 27, 105–108 (1990).
Fu, Y.-H. et al. Variation of the CGG repeat at the fragile X site results in genetic instability: resolution of the Sherman paradox. Cell 67, 1047–1058 (1991).
Knight, S.J.L. et al. Trinucleotide repeat amplification and hypermethylation of a CpG island in FRAXE mental retardation. Cell 74, 127–134 (1993).
La Spada, A.R., Wilson, E.M., Lubahn, D.B., Harding, A.E. & Fishbeck, K.H. Androgen receptor gene mutations in X-linked spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy. Nature 352, 77–79 (1991).
Brook, J.D. et al. Molecular basis of myotonic dystrophy: expansion of a trinucleotide (CTG) repeat at the 3′ end of a transcript encoding a protein kinase family member. Cell 68, 799–808 (1992).
Buxton, J. et al. Detection of an unstable fragment of DNA specific to individuals with myotonic dystrophy. Nature 355, 547–548 (1992).
Fu, Y.-H. et al. An unstable triplet repeat in a gene related to myotonic muscular dystrophy. Science 255, 1256–1259 (1992).
Harley, H.G. et al. Expansion of an unstable DNA region and phenotypic variation in myotonic dystrophy. Nature 355, 545–546 (1992).
Mahadevan, M. et al. Myotonic dystrophy mutation: an unstable CTG repeat in the 3′ untranslated region of the gene. Science 255, 1253–1255 (1992).
The Huntington's Disease Collaborative Research Group. A novel gene containing a trinucleotide repeat that is expanded and unstable on Huntington's disease chromosomes. Cell 72, 971–983 (1993).
Orr, H.T. et al. Expansion of an unstable trinucleotide CAG repeat in spinocerebellar ataxia type 1. Nature Genet. 4, 221–226 (1993).
Gispert, S. et al. Chromosomal assignment of the second locus for autosomal dominant cerebellar ataxia (SCA2) to chromosome 12q23-24.1.. Nature Genet. 4, 295–299 (1993).
Nechiporuk, S.-M.P.A. & Starkman, S. Anticipation in spinocerebellar ataxia type 2. Nature Genet. 5, 8–10 (1993).
Takiyama, Y. et al. The gene for Machado-Joseph disease maps to human chromosome 14q. Nature Genet. 4, 300–304 (1993).
Riggins, G.J. et al. Human genes containing polymorphic trinucleotide repeats. Nature Genet. 2, 186–191 (1992).
Li, S.-H. et al. Novel triplet repeat containing genes in human brain: cloning, expression, and length polymorphisms. Genomics 16, 572–579 (1993).
Tomoda, A., Ikezawa, M., Ohtani, Y., Miike, T. & Kumamoto, T. Progressive myoclonus epilepsy: Dentato-rubro-pallido-luysian atrophy (DRPLA) in childhood. Brain Dev. 13, 266–269 (1991).
Naito, H., Izawa, K., Kurosaki, T., Kaji, S. & Sawa, M. Two families of progressive myoclonus epilepsy with Mendelian dominant heredity (in Japanese). Psychiatr. Neurol. Jpn 74, 871–897 (1972).
Naito, H. et al. A family of dentatorubro-pallidoluysian atrophy (DRPLA) including two cases with schizophrenic symptoms (in Japanese). Psychiatr. Neurol. Jpn 89, 144–158 (1987).
Miyashita, K. et al. Hereditary dentatorubro-pallidoluysian atrophy. — Clinical variants in a family and degeneration of cerebral white matter in a proband — (in Japanese). Brain Nerve 44, 279–284 (1992).
Morioka, E. et al. An autopsy case of dentatorubro-pallidoluysian atrophy showing marked atrophy of the brain stem (in Japanese). Brain Nerve 39, 769–773 (1987).
Nakano, T. et al. An autopsy case of dentatorubro-pallidoluysian atrophy (DRPLA) clinically diagnosed as Huntington's chorea (In Japanese). Brain Nerve 37, 767–774 (1985).
Akashi, T., Ando, J., Inose, T., Uemura, H. & Mizushima, S. Dentato-rubro-pallido-luysian atrophy: A clinico-neuropathological study (in Japanese). Rinsho Seishin Igaku 16, 1163–1172 (1987).
Iwabuchi, K. et al. A clinicopathological study on autosomal dominant hereditary dentatorubro-pallidoluysian atrophy (Naito-Oyanagi's disease) (in Japanese). Shinkei Kenkyu no Shinpo 37, 678–691 (1993).
Iizuka,R. & Hirayama, K. Dentato-rubro-pallido-luysian atrophy. In Handoook of Clinical Neurology Vol 49 (eds Vinken, P. J., Bruyn, G. W. & Klawans, H. L. ) 437–143 (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1986).
Iizuka, R., Hirayama, K. & Maehara, K. Dentato-rubro-pallido-luysian atrophy: a clinico-pathological study. J. neurol. neurosurg. Psychiat. 47, 1288–1298 (1984).
Smith, J.K. dentatorubro-pallidoluysian atrophy. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology, Vol 21 (eds Vinken, P. J. & Bruyn, G. W. ) 519–534 (North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1975).
Duyao, M. et al. Trinucleotide repeat length instability and age of onset in Huntington's disease. Nature Genet. 4, 387–392 (1993).
Snell, R.G. et al. Relationship between trinucleotide repeat expansion and phenotypic variation in Huntington's disease. Nature Genet. 4, 393–397 (1993).
Andrew, S.E. et al. The relationship between trinucleotide (CAG) repeat length and clinical features of Huntington's disease. Nature Genet. 4, 398–403 (1993).
Maniatis, T., Fritsch, E.F. & Sambrook, J. Molecular Coning: A Laboratory Manual. 2nd edn (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, 1989).
Marchuk, D., Drumm, M., Saulino, A. & Collins, F.S. Construction of T-vectors, a rapid and general system for direct cloning of unmodified PCR products. Nuci. Acids Res. 19,1154 (1991).
Sanger, F., Nicklen, S. & Coulson, A.R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 74, 5463–5467 (1977).
Chen, E.Y. & Seeburg, P.M. Supercoil sequencing: A first and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA 4, 165–170 (1985).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koide, R., Ikeuchi, T., Onodera, O. et al. Unstable expansion of CAG repeat in hereditary dentatorubral–pallidoluysian atrophy (DRPLA). Nat Genet 6, 9–13 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0194-9
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0194-9
This article is cited by
-
Pallidal degenerations and related disorders: an update
Journal of Neural Transmission (2022)
-
A Case of Irreversible Corneal Edema Associated with Dentatorubropallidoluysian Atrophy Following Corneal Endothelial Transplantation
SN Comprehensive Clinical Medicine (2021)
-
DRPLA: understanding the natural history and developing biomarkers to accelerate therapeutic trials in a globally rare repeat expansion disorder
Journal of Neurology (2021)
-
Spinocerebellar ataxia
Nature Reviews Disease Primers (2019)
-
PSP-Phenotype in SCA8: Case Report and Systemic Review
The Cerebellum (2019)