Abstract
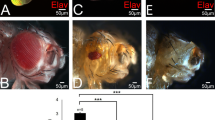
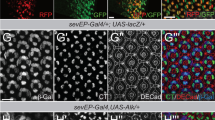
A prevailing paradigm posits that Polycomb Group (PcG) proteins maintain stem cell identity by repressing differentiation genes, and abundant evidence points to an oncogenic role for PcG proteins in human cancer1,2. Here we show using Drosophila melanogaster that a conventional PcG complex can also have a potent tumor suppressor activity. Mutations in any core PRC1 component cause pronounced hyperproliferation of eye imaginal tissue, accompanied by deregulation of epithelial architecture. The mitogenic JAK-STAT pathway is strongly and specifically activated in mutant tissue; activation is driven by transcriptional upregulation of Unpaired (Upd, also known as Outstretched, Os) family ligands. We show here that upd genes are direct targets of PcG-mediated repression in imaginal discs. Ectopic JAK-STAT activity is sufficient to induce overproliferation, whereas reduction of JAK-STAT activity suppresses the PRC1 mutant tumor phenotype. These findings show that PcG proteins can restrict growth directly by silencing mitogenic signaling pathways, shedding light on an epigenetic mechanism underlying tumor suppression.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sauvageau, M. & Sauvageau, G. Polycomb group genes: keeping stem cell activity in balance. PLoS Biol. 6, e113 (2008).
Valk-Lingbeek, M.E., Bruggeman, S.W. & van Lohuizen, M. Stem cells and cancer; the polycomb connection. Cell 118, 409–418 (2004).
Harvey, K.F., Pfleger, C.M. & Hariharan, I.K. The Drosophila Mst ortholog, hippo, restricts growth and cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis. Cell 114, 457–467 (2003).
Brumby, A.M. & Richardson, H.E. scribble mutants cooperate with oncogenic Ras or Notch to cause neoplastic overgrowth in Drosophila. EMBO J. 22, 5769–5779 (2003).
Hariharan, I.K. & Bilder, D. Regulation of imaginal disc growth by tumor-suppressor genes in Drosophila. Annu. Rev. Genet. 40, 335–361 (2006).
Newsome, T.P., Asling, B. & Dickson, B.J. Analysis of Drosophila photoreceptor axon guidance in eye-specific mosaics. Development 127, 851–860 (2000).
Brunk, B.P., Martin, E.C. & Adler, P.N. Drosophila genes Posterior Sex Combs and Suppressor two of zeste encode proteins with homology to the murine bmi-1 oncogene. Nature 353, 351–353 (1991).
Beuchle, D., Struhl, G. & Muller, J. Polycomb group proteins and heritable silencing of Drosophila Hox genes. Development 128, 993–1004 (2001).
Wu, C.T. & Howe, M. A genetic analysis of the Suppressor 2 of zeste complex of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 140, 139–181 (1995).
Lo, S.M., Ahuja, N.K. & Francis, N.J. Polycomb group protein suppressor 2 of zeste is a functional homolog of posterior sex combs. Mol. Cell Biol. 29, 515–525 (2008).
Schwartz, Y.B. & Pirrotta, V. Polycomb silencing mechanisms and the management of genomic programmes. Nat. Rev. Genet. 8, 9–22 (2007).
Schuettengruber, B., Chourrout, D., Vervoort, M., Leblanc, B. & Cavalli, G. Genome regulation by polycomb and trithorax proteins. Cell 128, 735–745 (2007).
Grimaud, C., Negre, N. & Cavalli, G. From genetics to epigenetics: the tale of Polycomb group and trithorax group genes. Chromosome Res. 14, 363–375 (2006).
Oktaba, K. et al. Dynamic regulation by polycomb group protein complexes controls pattern formation and the cell cycle in Drosophila. Dev. Cell 15, 877–889 (2008).
Ringrose, L. Polycomb comes of age: genome-wide profiling of target sites. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 19, 290–297 (2007).
Schwartz, Y.B. et al. Genome-wide analysis of Polycomb targets in Drosophila melanogaster. Nat. Genet. 38, 700–705 (2006).
Tolhuis, B. et al. Genome-wide profiling of PRC1 and PRC2 Polycomb chromatin binding in Drosophila melanogaster. Nat. Genet. 38, 694–699 (2006).
Janody, F. et al. A mosaic genetic screen reveals distinct roles for trithorax and polycomb group genes in Drosophila eye development. Genetics 166, 187–200 (2004).
Martinez, A.M. & Cavalli, G. The role of polycomb group proteins in cell cycle regulation during development. Cell Cycle 5, 1189–1197 (2006).
Martinez, A.M., Colomb, S., Dejardin, J., Bantignies, F. & Cavalli, G. Polycomb group-dependent Cyclin A repression in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 20, 501–513 (2006).
Grewal, S.S., Li, L., Orian, A., Eisenman, R.N. & Edgar, B.A. Myc-dependent regulation of ribosomal RNA synthesis during Drosophila development. Nat. Cell Biol. 7, 295–302 (2005).
Tseng, A.S. et al. Capicua regulates cell proliferation downstream of the receptor tyrosine kinase/ras signaling pathway. Curr. Biol. 17, 728–733 (2007).
Tanimoto, H., Itoh, S., ten Dijke, P. & Tabata, T. Hedgehog creates a gradient of DPP activity in Drosophila wing imaginal discs. Mol. Cell 5, 59–71 (2000).
Nellesen, D.T., Lai, E.C. & Posakony, J.W. Discrete enhancer elements mediate selective responsiveness of enhancer of split complex genes to common transcriptional activators. Dev. Biol. 213, 33–53 (1999).
Willecke, M. et al. The fat cadherin acts through the hippo tumor-suppressor pathway to regulate tissue size. Curr. Biol. 16, 2090–2100 (2006).
Bach, E.A. et al. GFP reporters detect the activation of the Drosophila JAK/STAT pathway in vivo. Gene Expr. Patterns 7, 323–331 (2007).
Goodliffe, J.M., Wieschaus, E. & Cole, M.D. Polycomb mediates Myc autorepression and its transcriptional control of many loci in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 19, 2941–2946 (2005).
Sun, Y.H. et al. White as a reporter gene to detect transcriptional silencers specifying position-specific gene expression during Drosophila melanogaster eye development. Genetics 141, 1075–1086 (1995).
Bach, E.A., Vincent, S., Zeidler, M.P. & Perrimon, N. A sensitized genetic screen to identify novel regulators and components of the Drosophila janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription pathway. Genetics 165, 1149–1166 (2003).
Ekas, L.A., Baeg, G.H., Flaherty, M.S., Ayala-Camargo, A. & Bach, E.A. JAK/STAT signaling promotes regional specification by negatively regulating wingless expression in Drosophila. Development 133, 4721–4729 (2006).
Tsai, Y.C. & Sun, Y.H. Long-range effect of upd, a ligand for Jak/STAT pathway, on cell cycle in Drosophila eye development. Genesis 39, 141–153 (2004).
Sehnal, F. & Bryant, P.J. Delayed pupariation in Drosophila imaginal disc overgrowth mutants is associated with reduced ecdysteroid titer. J. Insect Physiol. 39, 1051–1059 (1993).
Menut, L. et al. A mosaic genetic screen for Drosophila neoplastic tumor suppressor genes based on defective pupation. Genetics 177, 1667–1677 (2007).
Brown, S., Hu, N. & Hombria, J.C. Identification of the first invertebrate interleukin JAK/STAT receptor, the Drosophila gene domeless. Curr. Biol. 11, 1700–1705 (2001).
Callus, B.A. & Mathey-Prevot, B. SOCS36E, a novel Drosophila SOCS protein, suppresses JAK/STAT and EGF-R signalling in the imaginal wing disc. Oncogene 21, 4812–4821 (2002).
Sparmann, A. & van Lohuizen, M. Polycomb silencers control cell fate, development and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 6, 846–856 (2006).
Pietersen, A.M. & van Lohuizen, M. Stem cell regulation by polycomb repressors: postponing commitment. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 20, 201–207 (2008).
Calás, C. et al. Inactivation of the polycomb group protein Ring1B unveils an antiproliferative role in hematopoietic cell expansion and cooperation with tumorigenesis associated with Ink4a deletion. Mol. Cell. Biol. 28, 1018–1028 (2008).
Kanno, M., Hasegawa, M., Ishida, A., Isono, K. & Taniguchi, M. mel-18, a Polycomb group-related mammalian gene, encodes a transcriptional negative regulator with tumor suppressive activity. EMBO J. 14, 5672–5678 (1995).
Majewski, I.J. et al. Polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) restricts hematopoietic stem cell activity. PLoS Biol. 6, e93 (2008).
McClure, K.D. & Schubiger, G. Transdetermination: Drosophila imaginal disc cells exhibit stem cell-like potency. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 39, 1105–1118 (2007).
Dreesen, O. & Brivanlou, A.H. Signaling pathways in cancer and embryonic stem cells. Stem Cell Rev. 3, 7–17 (2007).
Arbouzova, N.I. & Zeidler, M.P. JAK/STAT signalling in Drosophila: insights into conserved regulatory and cellular functions. Development 133, 2605–2616 (2006).
Chang, S. & Aune, T.M. Dynamic changes in histone-methylation 'marks' across the locus encoding interferon-gamma during the differentiation of T helper type 2 cells. Nat. Immunol. 8, 723–731 (2007).
Koyanagi, M. et al. EZH2 and histone 3 trimethyl lysine 27 associated with Il4 and Il13 gene silencing in Th1 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 31470–31477 (2005).
Mukherjee, T., Hombria, J.C. & Zeidler, M.P. Opposing roles for Drosophila JAK/STAT signalling during cellular proliferation. Oncogene 24, 2503–2511 (2005).
Coelho, C.M. et al. Growth and cell survival are unevenly impaired in pixie mutant wing discs. Development 132, 5411–5424 (2005).
Klebes, A. et al. Regulation of cellular plasticity in Drosophila imaginal disc cells by the Polycomb group, trithorax group and lama genes. Development 132, 3753–3765 (2005).
Lee, N., Maurange, C., Ringrose, L. & Paro, R. Suppression of Polycomb group proteins by JNK signalling induces transdetermination in Drosophila imaginal discs. Nature 438, 234–237 (2005).
McClure, K.D. & Schubiger, G. A screen for genes that function in leg disc regeneration in Drosophila melanogaster. Mech. Dev. 125, 67–80 (2008).
Parrish, J.Z., Emoto, K., Jan, L.Y. & Jan, Y.N. Polycomb genes interact with the tumor suppressor genes hippo and warts in the maintenance of Drosophila sensory neuron dendrites. Genes Dev. 21, 956–972 (2007).
Tapon, N., Ito, N., Dickson, B.J., Treisman, J.E. & Hariharan, I.K. The Drosophila tuberous sclerosis complex gene homologs restrict cell growth and cell proliferation. Cell 105, 345–355 (2001).
Peng, J.C. & Karpen, G.H. H3K9 methylation and RNA interference regulate nucleolar organization and repeated DNA stability. Nat. Cell Biol. 9, 25–35 (2007).
Strutt, H., Cavalli, G. & Paro, R. Co-localization of Polycomb protein and GAGA factor on regulatory elements responsible for the maintenance of homeotic gene expression. EMBO J. 16, 3621–3632 (1997).
Acknowledgements
We thank P. Lueras for assistance with genetic screening, C. Marconett for help with genetic mapping, members of the Vance and Barton laboratories for assistance with quantitative PCR, and G. Cavalli and A.-M. Martinez for communication before publication. We further thank the Bloomington Stock Center and the Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank, as well as J. Treisman, R. Emmons, I. Hariharan, J. Simon, J. Mueller, E. Bach, J. Parrish, R. Mann, G. Halder, N. Perrimon, D. Harrison and B. Mathey-Prevot, for kindly providing flies and reagents. The authors are grateful to members of the Bilder, Hariharan, Karpen, Speed and Biggin labs for their invaluable input and help. This work was supported by grants from the US National Institutes of Health (R01 GM068675) and The Burroughs Welcome Trust to D.B. A.K.C was supported by a fellowship from Jane Coffin Childs Memorial Foundation. K.F.H. holds Career Development Awards from the International Human Frontier Science Program Organization and the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia. T.V. was supported by a fellowship from the American Heart Association.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.K.C. and D.B. conceived the study and wrote the paper. A.K.C. carried out the experiments and analyzed the data. B.D.B. carried out the molecular and T.V. the genetic mapping of the P3C allele, which was isolated and initially characterized by K.F.H.
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–7 and Supplementary Tables 1 and 2 (PDF 1343 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Classen, AK., Bunker, B., Harvey, K. et al. A tumor suppressor activity of Drosophila Polycomb genes mediated by JAK-STAT signaling. Nat Genet 41, 1150–1155 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.445
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.445
This article is cited by
-
Mechanisms of Polycomb group protein function in cancer
Cell Research (2022)
-
DamID profiling of dynamic Polycomb-binding sites in Drosophila imaginal disc development and tumorigenesis
Epigenetics & Chromatin (2018)
-
An intrinsic tumour eviction mechanism in Drosophila mediated by steroid hormone signalling
Nature Communications (2018)
-
The mystery of puberty initiation: genetics and epigenetics of idiopathic central precocious puberty (ICPP)
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation (2017)
-
Coordinate redeployment of PRC1 proteins suppresses tumor formation during Drosophila development
Nature Genetics (2016)