Abstract
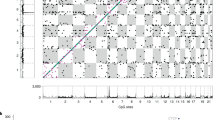
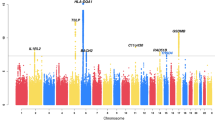
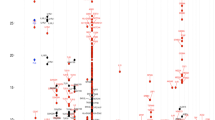
Eosinophils are pleiotropic multifunctional leukocytes involved in initiation and propagation of inflammatory responses and thus have important roles in the pathogenesis of inflammatory diseases. Here we describe a genome-wide association scan for sequence variants affecting eosinophil counts in blood of 9,392 Icelanders. The most significant SNPs were studied further in 12,118 Europeans and 5,212 East Asians. SNPs at 2q12 (rs1420101), 2q13 (rs12619285), 3q21 (rs4857855), 5q31 (rs4143832) and 12q24 (rs3184504) reached genome-wide significance (P = 5.3 × 10−14, 5.4 × 10−10, 8.6 × 10−17, 1.2 × 10−10 and 6.5 × 10−19, respectively). A SNP at IL1RL1 associated with asthma (P = 5.5 × 10−12) in a collection of ten different populations (7,996 cases and 44,890 controls). SNPs at WDR36, IL33 and MYB that showed suggestive association with eosinophil counts were also associated with atopic asthma (P = 4.2 × 10−6, 2.2 × 10−5 and 2.4 × 10−4, respectively). We also found that a nonsynonymous SNP at 12q24, in SH2B3, associated significantly (P = 8.6 × 10−8) with myocardial infarction in six different populations (6,650 cases and 40,621 controls).
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hogan, S.P. et al. Eosinophils: biological properties and role in health and disease. Clin. Exp. Allergy 38, 709–750 (2008).
Lee, J.J. et al. Defining a link with asthma in mice congenitally deficient in eosinophils. Science 305, 1773–1776 (2004).
International Hap Map Consortium. A haplotype map of the human genome. Nature 437, 1299–1320 (2005).
Schmitz, J. et al. IL-33, an interleukin-1-like cytokine that signals via the IL-1 receptor-related protein ST2 and induces T helper type 2-associated cytokines. Immunity 23, 479–490 (2005).
Carriere, V. et al. IL-33, the IL-1-like cytokine ligand for ST2 receptor, is a chromatin-associated nuclear factor in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 282–287 (2007).
Cherry, W.B., Yoon, J., Bartemes, K.R., Iijima, K. & Kita, H. A novel IL-1 family cytokine, IL-33, potently activates human eosinophils. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 121, 1484–1490 (2008).
Zhernakova, A. et al. Genetic analysis of innate immunity in Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis identifies two susceptibility loci harboring CARD9 and IL18RAP. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 82, 1202–1210 (2008).
Hunt, K.A. et al. Newly identified genetic risk variants for celiac disease related to the immune response. Nat. Genet. 40, 395–402 (2008).
Shimizu, M. et al. Functional SNPs in the distal promoter of the ST2 gene are associated with atopic dermatitis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 14, 2919–2927 (2005).
Zhu, G. et al. Interleukin 18 receptor 1 gene polymorphisms are associated with asthma. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 16, 1083–1090 (2008).
Reijmerink, N.E. et al. Association of IL1RL1, IL18R1, and IL18RAP gene cluster polymorphisms with asthma and atopy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 122, 651–654 (2008).
Mao, M. et al. T lymphocyte activation gene identification by coregulated expression on DNA microarrays. Genomics 83, 989–999 (2004).
Zhou, B. et al. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin as a key initiator of allergic airway inflammation in mice. Nat. Immunol. 6, 1047–1053 (2005).
Ying, S. et al. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin expression is increased in asthmatic airways and correlates with expression of Th2-attracting chemokines and disease severity. J. Immunol. 174, 8183–8190 (2005).
Thein, S.L. et al. Intergenic variants of HBS1L-MYB are responsible for a major quantitative trait locus on chromosome 6q23 influencing fetal hemoglobin levels in adults. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 11346–11351 (2007).
Menzel, S. et al. The HBS1L-MYB intergenic region on chromosome 6q23.3 influences erythrocyte, platelet, and monocyte counts in humans. Blood 110, 3624–3626 (2007).
Martinez-Moczygemba, M. & Huston, D.P. Biology of common β receptor-signaling cytokines: IL-3, IL-5, and GM-CSF. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 112, 653–665 (2003).
Thorgeirsson, T.E. et al. A variant associated with nicotine dependence, lung cancer and peripheral arterial disease. Nature 452, 638–642 (2008).
Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium. Genome-wide association study of 14,000 cases of seven common diseases and 3,000 shared controls. Nature 447, 661–678 (2007).
Todd, J.A. et al. Robust associations of four new chromosome regions from genome-wide analyses of type 1 diabetes. Nat. Genet. 39, 857–864 (2007).
Velazquez, L. et al. Cytokine signaling and hematopoietic homeostasis are disrupted in Lnk-deficient mice. J. Exp. Med. 195, 1599–1611 (2002).
Hirasawa, R. et al. Essential and instructive roles of GATA factors in eosinophil development. J. Exp. Med. 195, 1379–1386 (2002).
Iwasaki, H. et al. The order of expression of transcription factors directs hierarchical specification of hematopoietic lineages. Genes Dev. 20, 3010–3021 (2006).
Rebollo, A. & Schmitt, C. Ikaros, Aiolos and Helios: transcription regulators and lymphoid malignancies. Immunol. Cell Biol. 81, 171–175 (2003).
Gudbjartsson, D.F. et al. ASIP and TYR pigmentation variants associate with cutaneous melanoma and basal cell carcinoma. Nat. Genet. 40, 886–891 (2008).
Vitart, V. et al. SLC2A9 is a newly identified urate transporter influencing serum urate concentration, urate excretion and gout. Nat. Genet. 40, 437–442 (2008).
Devlin, B., Bacanu, S.A. & Roeder, K. Genomic Control to the extreme. Nat. Genet. 36, 1129–1130 (2004).
Gretarsdottir, S. et al. The gene encoding phosphodiesterase 4D confers risk of ischemic stroke. Nat. Genet. 35, 131–138 (2003).
Acknowledgements
The genotyping of some of the myocardial infarction sample sets was funded in part through a grant from the US National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (SR01HL089650-01). The New Zealand cohort study was supported by a programme grant from the Health Research Council of New Zealand. The Korean study was supported by a grant from the Korean Health 21 R&D project, Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (A010249).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
D.F.G., U.S.B., M.W., I.P.H., D.S.P., I.J., U.T. and K.S. wrote the first draft of the paper. U.S.B., E.H., A. Helgadottir, B.J., D. Gislason, B.R.L., D.L., G.I.E., D.A. and G. Thorgeirsson participated in the collection of the Icelandic data. C.W., J.H., J.B., N.M.W., A.J., L.J.P. and P.J.T. collected the Australian data. G.H.K., H.M.B. and D.S.P. collected the Dutch data. A. Heinzmann, M.K., J.A.,K.D. and M.W. collected the German data. A.W. and I.P.H. collected the UK data. H.D.S., S.-T.U., H.S.C. and C.-S.P. collected the Korean data. L.M.R., C.P., J.W.H., V.B. and T.W. collected the Danish data. C.J. and U.-B.J. collected the Swedish data. M.C.Y.N., J.C., W.Y.S. and R.M. collected the Hong Kong data. S.H.S., C.B.G, A.A.Q., A.I.L., V.V., M.P.R. and D.J.R. collected the US data. M.J.A.W., A.M.V.R. and G.T.J. collected the New Zealand data. E.T., G.M., P.F.P., A.B., L.P., D. Girelli, O.O. and N.M. collected the Italian data. E.H., A. Helgadottir, H.H., V.S. and U.T. carried out the genotyping. D.F.G., P.S., G.M.J., G. Thorleifsson, H.S. and A.K. analyzed the data. D.F.G., U.S.B., K.D., P.J.T., M.W., I.P.H., D.S.P., T.G., J.G., I.J., U.T. and K.S. planned and supervised the work. All authors contributed to the final version of the paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors from deCODE own stocks and stock options in the company.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Methods, Supplementary Tables 1–7 and Supplementary Figures 1–3 (PDF 2110 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gudbjartsson, D., Bjornsdottir, U., Halapi, E. et al. Sequence variants affecting eosinophil numbers associate with asthma and myocardial infarction. Nat Genet 41, 342–347 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.323
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.323
This article is cited by
-
Pathogenesis of allergic diseases and implications for therapeutic interventions
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2023)
-
Increased expression of IL1-RL1 is associated with type 2 and type 1 immune pathways in asthma
BMC Immunology (2022)
-
Clonal hematopoiesis in cardiovascular disease and therapeutic implications
Nature Cardiovascular Research (2022)
-
Interplay between inflammation and thrombosis in cardiovascular pathology
Nature Reviews Cardiology (2021)
-
Impacts of lipid-related metabolites, adiposity, and genetic background on blood eosinophil counts: the Nagahama study
Scientific Reports (2021)