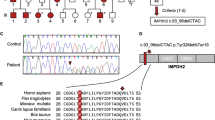
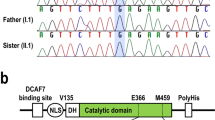
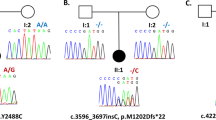
Abstract
We report the discovery of a mutation in the THAP1 gene in three Amish-Mennonite families with mixed-onset primary torsion dystonia (also known as DYT6 dystonia). Another mutation in a German family with primary torsion dystonia suggests that THAP1 mutations also cause dystonia in other ancestry groups. We demonstrate that the missense mutation impairs DNA binding, suggesting that transcriptional dysregulation may contribute to the phenotype of DYT6 dystonia.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fahn, S. Adv Neurol. 50, 1–8 (1988).
de Carvalho Aguiar, P.M. & Ozelius, L.J. Lancet Neurol. 1, 316–325 (2002).
Ozelius, L.J. et al. Nat. Genet. 17, 40–48 (1997).
Almasy, L. et al. Ann. Neurol. 42, 670–673 (1997).
Saunders-Pullman, R. et al. Am. J. Med. Genet. A. 143A, 2098–2105 (2007).
Kramer, P.L. et al. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 55, 468–475 (1994).
Clouaire, T. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 6907–6912 (2005).
Roussigne, M., Cayrol, C., Clouaire, T., Amalric, F. & Girard, J.P. Oncogene 22, 2432–2442 (2003).
Roussigne, M. et al. Trends Biochem. Sci. 28, 66–69 (2003).
Cayrol, C. et al. Blood 109, 584–594 (2007).
Duan, W., Zhang, Z., Gash, D.M. & Mattson, M.P. Ann. Neurol. 46, 587–597 (1999).
Bessiere, D. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 4352–4363 (2008).
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank all participants in this study. We thank P. de Carvalho Aguiar, G. Senthil and S. Singh for technical help; B. Ford, A. Hunt, P. Greene, N. Huang, A. Leder, P. Raj Kapoor, R. Tabamo, K. Blatt, E. Chai, S. Chouinard, A. Deligtish, P. Kavanagh, M. Brin, N. Lubarr and M. San Luciano for help with examination of the families; J. Soto-Valencia, K. Habermann, E. Ohmann, G. Heiman, D. de Leon and C. Moskowitz for organizing and coordinating family visits; and J. Haines for sharing control Amish-Mennonite samples. This work was supported by research grants from the Dystonia Medical Research Foundation (L.J.O., S.B.B., R.S.-P.), the Bachmann-Strauss Dystonia and Parkinson Foundation (S.B.B., L.J.O.), the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NS26636, L.J.O. and S.B.B.; K23NS047256, R.S.-P.), the National Institute of Aging (AG19085, J. Haines) and the Aaron Aronov Family Foundation (S.B.B.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
T.F. performed all of the molecular genetic studies and wrote the paper; D.R. collected samples and provided clinical information of the subjects; R.S.-P. and S.B.B. examined subjects and assigned clinical status; S.G. cloned the expression constructs and performed all experiments needed for the gel shift assays; M.E.E. designed and supervised the EMSA experiments; L.J.O. and S.B.B. designed and supervised the genetic studies; D.R., R.S.-P., S.G., M.E.E., S.B.B. and L.J.O. edited the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Methods and Supplementary Figures 1–3 (PDF 233 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fuchs, T., Gavarini, S., Saunders-Pullman, R. et al. Mutations in the THAP1 gene are responsible for DYT6 primary torsion dystonia. Nat Genet 41, 286–288 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.304
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.304
This article is cited by
-
Structural brain heterogeneity underlying symptomatic and asymptomatic genetic dystonia: a multimodal MRI study
Journal of Neurology (2024)
-
A case of novel DYT6 dystonia variant with serious complications after deep brain stimulation therapy: a case report
BMC Neurology (2022)
-
Dystonia updates: definition, nomenclature, clinical classification, and etiology
Journal of Neural Transmission (2021)
-
Emerging and converging molecular mechanisms in dystonia
Journal of Neural Transmission (2021)
-
Oromandibular and Laryngeal Dystonia Secondary to Dystonia 6 Due to THAP1 Variant in a Child
Indian Journal of Pediatrics (2021)