Abstract
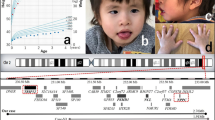
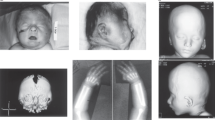
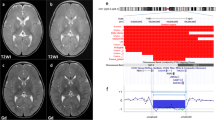
The chromosome 17q21.31 deletion syndrome is a genomic disorder characterized by highly distinctive facial features, moderate-to-severe intellectual disability, hypotonia and friendly behavior. Here, we show that de novo loss-of-function mutations in KANSL1 (also called KIAA1267) cause a full del(17q21.31) phenotype in two unrelated individuals that lack deletion at 17q21.31. These findings indicate that 17q21.31 deletion syndrome is a monogenic disorder caused by haploinsufficiency of KANSL1.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Koolen, D.A. et al. Nat. Genet. 38, 999–1001 (2006).
Sharp, A.J. et al. Nat. Genet. 38, 1038–1042 (2006).
Shaw-Smith, C. et al. Nat. Genet. 38, 1032–1037 (2006).
Koolen, D.A. et al. J. Med. Genet. 45, 710–720 (2008).
Tan, T.Y. et al. J. Med. Genet. 46, 480–489 (2009).
Sharkey, F.H. et al. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 127, 61–66 (2009).
Dubourg, C. et al. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 54, 144–151 (2011).
Cooper, G.M. et al. Nat. Genet. 43, 838–846 (2011).
Wang, K., Li, M. & Hakonarson, H. Nucleic Acids Res. 38, e164 (2010).
Smith, E.R. et al. Mol. Cell Biol. 25, 9175–9188 (2005).
Mendjan, S. et al. Mol. Cell 21, 811–823 (2006).
Cai, Y. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 4268–4272 (2010).
Li, X., Wu, L., Corsa, C.A., Kunkel, S. & Dou, Y. Mol. Cell 36, 290–301 (2009).
Slager, R.E., Newton, T.L., Vlangos, C.N., Finucane, B. & Elsea, S.H. Nat. Genet. 33, 466–468 (2003).
Wilson, H.L. et al. J. Med. Genet. 40, 575–584 (2003).
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the collaboration of the study participants and their families. This work was supported by a MIUR-University Grant 2011 (to M.Z.). We obtained written informed consent from parents and approval from the Ethics Committee of our institution for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.Z. designed the study and drafted the manuscript. D.O. and S.L. performed a-CGH. M.M. performed FISH analysis. E.M., C.S. and D.B. referred patients. P.C. conducted the bioinformatic analysis. G.N. critically reviewed the manuscript. G.M. performed sequencing analysis and validation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Table 1, Supplementary Methods, Supplementary Note and Supplementary Figures 1–5 (PDF 562 kb)
Supplementary Table 2
Gene Ontology (XLS 224 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zollino, M., Orteschi, D., Murdolo, M. et al. Mutations in KANSL1 cause the 17q21.31 microdeletion syndrome phenotype. Nat Genet 44, 636–638 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2257
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2257
This article is cited by
-
A new blood DNA methylation signature for Koolen-de Vries syndrome: Classification of missense KANSL1 variants and comparison to fibroblast cells
European Journal of Human Genetics (2024)
-
COX17 acetylation via MOF–KANSL complex promotes mitochondrial integrity and function
Nature Metabolism (2023)
-
Integrated analysis of copy number variation-associated lncRNAs identifies candidates contributing to the etiologies of congenital kidney anomalies
Communications Biology (2023)
-
Expanding the speech and language phenotype in Koolen-de Vries syndrome: late onset and periodic stuttering a novel feature
European Journal of Human Genetics (2023)
-
PhenoScore quantifies phenotypic variation for rare genetic diseases by combining facial analysis with other clinical features using a machine-learning framework
Nature Genetics (2023)