Abstract
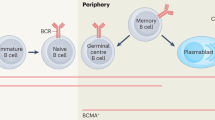
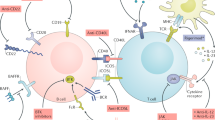
Rituximab, a monoclonal antibody directed against the CD20 molecule found on pre-B cells and mature B cells (but not on plasma cells), was introduced in the late 1990s for the treatment of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Recently, this antibody has been used to treat autoimmune diseases, especially those associated with a prominent humoral component and with potentially pathogenic autoantibodies. Small cohort studies have indicated that rituximab could have an important role in the management of these disorders. Rituximab has also been utilized in the transplant setting, to diminish levels of alloreactive antibodies in highly sensitized patients, to manage ABO-incompatible transplants, and to treat rejection associated with B cells and antibodies. The exact mechanism by which rituximab exerts its effects in autoimmunity and transplantation remains unclear, as specific autoantibody or alloantibody levels often seem not to diminish in parallel with clinical improvement. A role for rituximab in depleting B cells and compromising their antigen-presenting function seems likely; rituximab might also inhibit T-cell activation. A synergistic effect has been noted in vitro following administration of corticosteroids to B-cell lines, with accentuation of B-cell cytotoxicity; this observation might be relevant to certain studies, as some regimens have utilized both agents simultaneously. This article reviews the current use of rituximab in renal disease and transplantation, and includes discussion of the drug's potential role in novel therapeutic protocols.
Key Points
-
Immune responses mediated by B cells (which produce antibodies and cytokines and present antigen to T cells) are important in autoimmune renal disease and transplantation
-
B-cell depletion can alter the course of autoimmune and alloimmune responses
-
Monoclonal antibodies to B-cell antigens can effectively deplete circulating B cells, diminishing their effector functions
-
Rituximab, a monoclonal antibody directed against CD20, has been successfully used in hematological B-cell disorders
-
Rituximab has been used in a number of autoimmune conditions and in transplantation with some success
-
Randomized trials are required to compare the short-term and long-term efficacy of B-cell deletional strategies with conventional immuno-suppressants in the treatment of renal disease
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anolik JH et al. (2003) The relationship of FcγRIIIa genotype to degree of B cell depletion by rituximab in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 48: 455–459
Teeling JL et al. (2004) Characterization of new human CD20 monoclonal antibodies with potent cytolytic activity against non-Hodgkin lymphomas. Blood 104: 1793–1800
McLaughlin P et al. (1998) Rituximab chimeric anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody therapy for relapsed indolent lymphoma: half of patients respond to a four-dose treatment program. J Clin Oncol 16: 2825–2833
Mohrbacher A (2005) B cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: rituximab safety experience. Arthritis Res Ther 7 (Suppl 3): S19–S25
Edwards JC et al. (2004) Efficacy of B-cell-targeted therapy with rituximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 350: 2572–2581
Vieira CA et al. (2004) Rituximab for reduction of anti-HLA antibodies in patients awaiting renal transplantation: 1. Safety, pharmacodynamics, and pharmacokinetics. Transplantation 77: 542–548
Looney RJ et al. (2004) B cell depletion as a novel treatment for systemic lupus erythematosus: a phase I/II dose-escalation trial of rituximab. Arthritis Rheum 50: 2580–2589
Cohen CD et al. (2005) CD20-positive infiltrates in human membranous glomerulonephritis. J Nephrol 18: 328–333
Remuzzi G et al. (2002) Rituximab for idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Lancet 360: 923–924
Ruggenenti P et al. (2003) Rituximab in idiopathic membranous nephropathy: a one-year prospective study. J Am Soc Nephrol 14: 1851–1857
Rossi P et al. (2005) Anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody for the treatment of refractory autoimmune haemolytic anaemia associated with idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Rheumatology (Oxford) 44: 403–405
Benz K et al. (2004) Change of the course of steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome after rituximab therapy. Pediatr Nephrol 19: 794–797
Lamprecht P et al. (2003) Rituximab induces remission in refractory HCV associated cryoglobulinaemic vasculitis. Ann Rheum Dis 62: 1230–1233
Roccatello D et al. (2004) Long-term effects of anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody treatment of cryoglobulinaemic glomerulonephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 19: 3054–3061
Zaja F et al. (2003) Efficacy and safety of rituximab in type II mixed cryoglobulinemia. Blood 101: 3827–3834
Ghijsels E et al. (2004) Anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody (rituximab) treatment for hepatitis C-negative therapy-resistant essential mixed cryoglobulinemia with renal and cardiac failure. Am J Kidney Dis 43: e34–e38
Ghobrial IM et al. (2004) Initial increase in the cryoglobulin level after rituximab therapy for type II cryoglobulinemia secondary to Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia does not indicate failure of response. Am J Hematol 77: 329–330
Sfikakis PP et al. (2005) Remission of proliferative lupus nephritis following B cell depletion therapy is preceded by down-regulation of the T cell costimulatory molecule CD40 ligand: an open-label trial. Arthritis Rheum 52: 501–513
Leandro MJ et al. (2002) An open study of B lymphocyte depletion in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 46: 2673–2677
van Vollenhoven RF et al. (2004) Biopsy-verified response of severe lupus nephritis to treatment with rituximab (anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody) plus cyclophosphamide after biopsy-documented failure to respond to cyclophosphamide alone. Scand J Rheumatol 33: 423–427
Smith KGC et al. (2004) A prospective trial of B-cell depletion with Rituximab in refractory SLE [abstract #113]. JASN 15
Gottenberg J et al. (2004) Tolerance and short-term efficacy of rituximab in 43 patients with systemic autoimmune diseases. Ann Rheum Dis 64: 913–920
Marks SD et al. (2005) B lymphocyte depletion therapy in children with refractory systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 52: 3168–3174
Edelbauer M et al. (2005) Rituximab in childhood systemic lupus erythematosus refractory to conventional immunosuppression: case report. Pediatr Nephrol 20: 811–813
Specks U et al. (2001) Response of Wegener's granulomatosis to anti-CD20 chimeric monoclonal antibody therapy. Arthritis Rheum 44: 2836–2840
Keogh KA et al. (2005) Induction of remission by B lymphocyte depletion in eleven patients with refractory antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. Arthritis Rheum 52: 262–268
Smith KGC et al. (2004) Effective treatment of refractory vasculitis by B cell depletion with rituximab [abstract #170]. Kidney Blood Press Res 28
Kallenbach M et al. (2005) Rituximab induced remission in a patient with Wegener's granulomatosis. Nephron Clin Pract 99: c92–c96
Ferraro AJ et al. (2005) Effective therapeutic use of rituximab in refractory Wegener's granulomatosis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 20: 622–625
Eriksson P (2005) Nine patients with anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-positive vasculitis successfully treated with rituximab. J Intern Med 257: 540–548
Keogh KA et al. (2006) Rituximab for refractory Wegener's granulomatosis: report of a prospective, open-label pilot trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 173: 180–187
Aries PM et al. (2005) Lack of efficacy of Rituximab in Wegener's granulomatosis with refractory granulomatous manifestations. Ann Rheum Dis [doi: 10.1136/ard.2005.044420]
Omdal R et al. (2005) Anti-CD20 therapy of treatment-resistant Wegener's granulomatosis: favourable but temporary response. Scand J Rheumatol 34: 229–232
Mandreoli M et al. (2004) Successful resumption of epoetin alfa after rituximab treatment in a patient with pure red cell aplasia. Am J Kidney Dis 44: 757–761
Yassa SK et al. (2005) Anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody (Rituximab) for life-threatening hemolytic-uremic syndrome. Clin Transplant 19: 423–426
Chemnitz J et al. (2002) Successful treatment of severe thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura with the monoclonal antibody rituximab. Am J Hematol 71: 105–108
Stein GY et al. (2004) Treatment of resistant thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura with rituximab and cyclophosphamide. Int J Hematol 80: 94–96
Yomtovian R et al. (2004) Rituximab for chronic recurring thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: a case report and review of the literature. Br J Haematol 124: 787–795
Reddy PS et al. (2005) Rituximab in the treatment of relapsed thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Ann Hematol 84: 232–235
Zheng X et al. (2003) Remission of chronic thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura after treatment with cyclophosphamide and rituximab. Ann Intern Med 138: 105–108
Fakhouri F et al. (2005) Efficiency of curative and prophylactic treatment with rituximab in ADAMTS13-deficient thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: a study of 11 cases. Blood 106: 1932–1937
Ganne V et al. (2003) Humanized anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody (Rituximab) treatment for post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder. Clin Transplant 17: 417–422
Al-Akash SI et al. (2005) Rapid response to rituximab in a pediatric liver transplant recipient with post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease and maintenance with sirolimus monotherapy. Pediatr Transplant 9: 249–253
Book BK et al. (2005) New crossmatch technique eliminates interference by humanized and chimeric monoclonal antibodies. Transplant Proc 37: 640–642
Sarwal M et al. (2003) Molecular heterogeneity in acute renal allograft rejection identified by DNA microarray profiling. N Engl J Med 349: 125–138
Alausa M et al. (2005) Refractory acute kidney transplant rejection with CD20 graft infiltrates and successful therapy with rituximab. Clin Transplant 19: 137–140
Becker YT et al. (2004) Rituximab as treatment for refractory kidney transplant rejection. Am J Transplant 4: 996–1001
Samaniego M et al. (2002) Early allograft outcomes in patients with antibody mediated rejection treated with rituximab: a single center experience [abstract #259]. Am J Transplant 2 (Suppl 3)
Tyden G et al. (2005) ABO incompatible kidney transplantations without splenectomy, using antigen-specific immunoadsorption and rituximab. Am J Transplant 5: 145–148
Sonnenday CJ et al. (2004) Plasmapheresis, CMV hyperimmune globulin, and anti-CD20 allow ABO-incompatible renal transplantation without splenectomy. Am J Transplant 4: 1315–1322
Sawada T et al. (2002) Successful A1-to-O ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation after a preconditioning regimen consisting of anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody infusions, splenectomy, and double-filtration plasmapheresis. Transplantation 74: 1207–1210
Sawada T et al. (2004) Preconditioning regimen consisting of anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody infusions, splenectomy and DFPP-enabled non-responders to undergo ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation. Clin Transplant 18: 254–260
Gloor JM et al. (2005) A comparison of splenectomy versus intensive posttransplant antidonor blood group antibody monitoring without splenectomy in ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation. Transplantation 80: 1572–1577
Sidner RA et al. (2004) In vivo human B-cell subset recovery after in vivo depletion with rituximab, anti-human CD20 monoclonal antibody. Hum Antibodies 13: 55–62
Gloor JM et al. (2003) Overcoming a positive crossmatch in living-donor kidney transplantation. Am J Transplant 3: 1017–1023
Choquet S et al. (2005) Efficacy and safety of rituximab in B-cell post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders: results of a prospective multicentre phase II study. Blood [doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-01-0377]
Oertel SH et al. (2005) Effect of anti-CD20 antibody rituximab in patients with post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder (PTLD). Am J Transplant 5: 2901–2906
Jain AB et al. (2005) Rituximab (chimeric anti-CD20 antibody) for posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder after solid organ transplantation in adults: long-term experience from a single center. Transplantation 80: 1692–1698
Gong Q et al. (2005) Importance of cellular microenvironment and circulatory dynamics in B cell immunotherapy. J Immunol 174: 817–826
Pijpe J et al. (2005) Rituximab treatment in patients with primary Sjogren's syndrome: an open-label phase II study. Arthritis Rheum 52: 2740–2750
Kimby E (2005) Tolerability and safety of rituximab (MabThera). Cancer Treat Rev 31: 456–473
Garrett HE Jr et al. (2005) Treatment of vascular rejection with rituximab in cardiac transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant 24: 1337–1342
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salama, A., Pusey, C. Drug Insight: rituximab in renal disease and transplantation. Nat Rev Nephrol 2, 221–230 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncpneph0133
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncpneph0133