Abstract
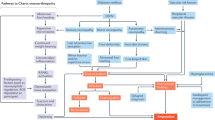
Diabetic neuropathies are a heterogeneous group of disorders that include a wide range of abnormalities. They can be focal or diffuse, proximal or distal, affecting both peripheral and autonomic nervous systems, causing morbidity with significant impact on the quality of life of the person with diabetes, and can result in early death. Distal symmetric polyneuropathy, the most common form of diabetic neuropathy, usually involves small and large nerve fibers. Small-nerve-fiber neuropathy often presents with pain but without objective signs or electrophysiologic evidence of nerve damage, and is recognized as a component of the impaired glucose tolerance and metabolic syndromes. The greatest risk resulting from small-fiber neuropathy is foot ulceration and subsequent gangrene and amputation. Large-nerve-fiber neuropathies produce numbness, ataxia and uncoordination, impairing activities of daily living and causing falls and fractures. A careful history and detailed physical examination are essential for the diagnosis. Symptomatic therapy has become available and newer and better treatment modalities, based on etiologic factors, are being explored with potential for significant impact on morbidity and mortality. Preventive strategies and patient education still remain key factors in reducing complication rates and mortality.
Key Points
-
Diabetic neuropathies are among the commonest, long-term complications of diabetes although often are not recognized by physicians
-
A thorough history and detailed physical examination, with the aid of simple tests that can be done in the clinic, are essential for the diagnosis
-
Management of the disease is complex and the key to success depends, in part, on discovering the underlying pathological processes in each particular clinical presentation
-
There has been increasing understanding of the pathogenesis of diabetic neuropathies over the last decades and new therapies are emerging that hold promise for the treatment of this disease
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Caputo GM et al. (1994) Assessment and management of foot disease in patients with diabetes. N Engl J Med 331: 854–860
Vinik E et al. (2005) The development and validation of the Norfolk QOL-DN, a new measure of patients' perception of the effects of diabetes and diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes Technol Ther 7: 497–508
Vinik AI (2004) Advances in diabetes for the millennium: new treatments for diabetic neuropathies. MedGenMed 6 (3 Suppl): 13
Boulton A et al. (2004) Diabetic somatic neuropathies. Diabetes Care 27: 1458–1486
Dyck PJ (2003) Severity and staging of diabetic polyneuropathy. In Textbook of Diabetic Neuropathy, 170–175 (Eds Gries FA et al.) Stuttgart: Thieme
Thomas PK (1997) Classification, differential diagnosis and staging of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Diabetes 46 (Suppl 2): S54–S57
Boulton AJ et al. (2005) Position statement: diabetic neuropathies. Diabetes Care 28: 956–962
Vinik A and Mehrabyan A (2004) Diabetic neuropathies. Med Clin North Am 88: 947–999
Oyibo SO et al. (2002) The relationship between blood glucose excursions and painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a pilot study. Diabet Med 19: 870–873
Tesfaye S et al. (1996) Arterio-venous shunting and proliferating new vessels in acute painful neuropathy of rapid glycemic control (insulin neuritis). Diabetologia 39: 329–335
Sinnreich M et al. (2005) Diabetic neuropathies. Classification, clinical features, and pathophysiological basis. Neurologist 11: 63–79
Harris M et al. (1993) Symptoms of sensory neuropathy in adults with NIDDM in the US population. Diabetes Care 16: 1446–1452
Singleton JR et al. (2001) Painful sensory polyneuropathy associated with impaired glucose tolerance. Muscle Nerve 24: 1225–1228
Singleton JR et al. (2001) Increased prevalence of impaired glucose tolerance in patients with painful sensory neuropathy. Diabetes Care 24: 1448–1453
Sumner C et al. (2003) The spectrum of neuropathy in diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance. Neurology 60: 108–111
Cavanagh PR et al. (1993) Ulceration, unsteadiness, and uncertainty: the biomechanical consequences of diabetes mellitus. J Biomech 26 (Suppl 1): 23–40
Katoulis EC et al. (1997) Gait abnormalities in diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes Care 20: 1904–1907
Dyck PJ et al. (1993) The prevalence by staged severity of various types of diabetic neuropathy, retinopathy, and nephropathy in a population-based cohort: the Rochester Diabetic Neuropathy Study. Neurology 43: 817–824
Dyck PJ (1988) Detection, characterization and staging of polyneuropathy: assessed in diabetics. Muscle Nerve 11: 21–32
Vinik AI et al. (1995) Quantitative measurement of cutaneous perception in diabetic neuropathy. Muscle Nerve 18: 574–584
Abbott CA et al. (2002) The North-West Diabetes Foot Care Study: incidence of, and risk factors for, new diabetic foot ulceration in a community-based patient cohort. Diabet Med 19: 377–384
Dyck PJ et al. (1997) Approaches to improve epidemiological studies of diabetic neuropathy: insights from the Rochester Diabetic Neuropathy Study. Diabetes 46 (Suppl 2): S5–S8
Yarnitsky D and Sprecher E (1994) Thermal testing: normative data and repeatability for various test algorithms. J Neurol Sci 125: 39–45
Anonymous (1988) Consensus Statement. Report and recommendations of the San Antonio conference on diabetic neuropathy. American Diabetes Association American Academy of Neurology. Diabetes Care 11: 592–597
Anonymous (1995) Peripheral Nerve Society. Diabetic polyneuropathy in controlled clinical trials: consensus report of the Peripheral Nerve Society. Ann Neurol 38: 478–482
Partanen J et al. (1995) Natural history of peripheral neuropathy in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 333: 89–94
DCCT Research Group (1995) The effect of intensive diabetes therapy on the development and progression of neuropathy. Ann Intern Med 122: 561–568
Vinik A et al. (2004) Focal entrapment neuropathies in diabetes. Diabetes Care 27: 1783–1788
Kennedy WR et al. (1996) Quantitation of epidermal nerves in diabetic neuropathy. Neurology 47: 1042–1048
Polydefkis M et al. (2001) Skin biopsy as a tool to assess distal small fiber innervation in diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes Technol Ther 3: 23–28
Pittenger G et al. (2004) Intraepidermal nerve fibers are indicators of small fiber neuropathy in both diabetic and non-diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 27: 1974–1979
Vileikyte L et al. (2003) The development and validation of a neuropathy- and foot ulcer-specific quality of life instrument. Diabetes Care 26: 2549–2555
Maser RE et al. (2003) The association between cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy and mortality in individuals with diabetes: a meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 26: 1895–1901
Ziegler D et al. (1992) The epidemiology of diabetic neuropathy. Diabetic Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathy Multicenter Study Group. J Diabetes Complications 6: 49–57
Vinik AI et al. (2003) Diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Diabetes Care 26: 1553–1579
Ziegler D and Gries FA (1997) α-Lipoic acid in the treatment of diabetic peripheral and cardiac autonomic neuropathy. Diabetes 46 (Suppl 2): S62–S66
Athyros VG et al. (1998) Long-term effect of converting enzyme inhibition on circadian sympathetic and parasympathetic modulation in patients with diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Acta Cardiol 53: 201–209
Gaede P et al. (1999) Intensified multifactorial intervention in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and microalbuminuria: the Steno type 2 randomized study. Lancet 353: 617–622
Wilbourn AJ (1999) Diabetic entrapment and compression neuropathies. In Diabetic Neuropathy, 481–508 (Eds Dyck PJ and Thomas PK) Philadelphia: Saunders
Watanabe K et al. (1990) Characteristics of cranial nerve palsies in diabetic patients. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 10: 19–27
Perkins B et al. (2002) Carpal tunnel syndrome in patients with diabetic polyneuropathy. Diabetes Care 25: 565–569
Dyck PJ and Windebank AJ (2002) Diabetic and nondiabetic lumbosacral radiculoplexus neuropathy: new insights into pathophysiology and treatment. Muscle Nerve 25: 477–491
Sharma K et al. (2002) Demyelinating neuropathy in diabetes mellitus. Arch Neurol 59: 758–765
Krendel DA et al. (1997) Autoimmune diabetic neuropathy. Neurol Clin 15: 959–971
Ayyar DR and Sharma KR (2004) Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy in diabetes mellitus. Curr Diab Rep 4: 409–412
DCCT Research Group (1993) The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 329: 977–986
UK Prospective Diabetes Study Group (1998) Tight blood pressure control and risk of macrovascular and microvascular complications in type 2 diabetes: UKPDS 38. BMJ 317: 703–713
UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group (1998) Effect of intensive blood-glucose control with metformin on complications in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 34). Lancet 352: 854–865
Gaede P et al. (2003) Multifactorial intervention and cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 348: 383–393
Tesfaye S et al. (2005) Vascular risk factors and diabetic neuropathy. N Engl J Med 352: 341–350
Ziegler D et al. (2004) Oxidative stress and antioxidant defense in relation to the severity of diabetic polyneuropathy and cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy. Diabetes Care 27: 2178–2183
Vincent AM et al. (2004) Oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of diabetic neuropathy. Endocr Rev 25: 612–628
Bril V and Buchanan RA (2004) Aldose reductase inhibition by AS-3201 in sural nerve from patients with diabetic sensorimotor polyneuropathy. Diabetes Care 27: 2369–2375
Keen H et al. (1993) Treatment of diabetic neuropathy with γ-linolenic acid. The γ-Linolenic Acid Multicenter Trial Group. Diabetes Care 16: 8–15
Ziegler D et al. (2004) Treatment of symptomatic diabetic polyneuropathy with the antioxidant α-lipoic acid: a meta-analysis. Diabet Med 21: 114–121
Vinik A et al. (2005) Sural sensory nerve action potential identifies diabetic peripheral neuropathy responders to therapy. Muscle Nerve 32: 619–625
Vinik A et al. (2005) Treatment of symptomatic diabetic peripheral neuropathy with protein kinase CB inhibitor ruboxistaurin mesylate during a 1-year, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial. Clin Ther 27: 1164–1180
Pittenger G and Vinik A (2003) Nerve growth factor and diabetic neuropathy Exp Diabesity Res 4: 271–285
Vinik AI (1999) Treatment of diabetic polyneuropathy (DPN) with recombinant human nerve growth factor (rhNGF). In National Diabetes Association, 59th Scientific Sessions: 1999, June 19–22; San Diego, CA, 48: 0232:A54
Rivard A et al. (1999) Rescue of diabetes-related impairment of angiogenesis by intramuscular gene therapy with adeno-VEGF. Am J Pathol 154: 355–363
Milicevic Z et al. (1997) Anti-ganglioside GM1 antibody and distal symmetric “diabetic polyneuropathy” with dominant motor features. Diabetologia 40: 1364–1365
Vinik AI et al. (2005) Antibodies to neuronal structures: innocent bystanders or neurotoxins? Diabetes Care 28: 2067–2072
Granberg V et al. (2005) Autoantibodies to autonomic nerves associated with cardiac and peripheral autonomic neuropathy. Diabetes Care 28: 1959–1964
Krendel DA et al. (1995) Successful treatment of neuropathies in patients with diabetes mellitus. Arch Neurol 52: 1053–1061
Rains C and Bryson HM (1995) Topical capsaicin. A review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic potential in post-herpetic neuralgia, diabetic neuropathy and osteoarthritis. Drugs Aging 7: 317–328
Goldstein DJ et al. (2005) Duloxetine vs. placebo in patients with painful diabetic neuropathy. Pain 116: 109–118
Rosenstock J et al. (2004) Pregabalin for the treatment of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Pain 110: 628–638
Said G et al. (1998) Uncommon early-onset neuropathy in diabetic patients. J Neurol 245: 61–68
Harati Y et al. (1998) Double-blind randomized trial of tramadol for the treatment of the pain of diabetic neuropathy. Neurology 50: 1842–1846
Dworkin RH et al. (2003) Advances in neuropathic pain: diagnosis, mechanisms, and treatment recommendations. Arch Neurol 60: 1524–1534
Sindrup S et al. (1990) The selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor paroxetine is effective in treatment of diabetic neuropathy symptoms. Pain 42: 135–144
Goldstein DJ et al. (2005) Duloxetine vs. placebo in patients with painful diabetic neuropathy. Pain 116: 109–118
Backonja M et al. (1998) Gabapentin for the symptomatic treatment of painful neuropathy in patients with diabetes mellitus: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 280: 1831–1836
DeToledo JC et al. (1997) Changes in body weight with chronic, high-dose gabapentin therapy. Ther Drug Monit 19: 394–396
Raskin P et al. (2004) Topiramate vs placebo in painful diabetic neuropathy: analgesic and metabolic effects. Neurology 63: 865–873
Vinik A (2005) Use of antiepileptic drugs in the treatment of chronic painful diabetic neuropathy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 90: 4936–4945
Cavanagh PR et al. (1992) Problems with gait and posture in neuropathic patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabet Med 9: 469–474
Liu-Ambrose T et al. (2004) Resistance and agility training reduce fall risk in women aged 75 to 85 with low bone mass: a 6-month randomized, controlled trial. J Am Geriatr Soc 52: 657–665
Jude EB et al. (2001) Biphosphonates in the treatment of Charcot neuroarthropathy: a double-blind randomized controlled trial. Diabetologia 44: 2032–2037
Acknowledgements
Our work is supported by the American Diabetes Association, NIH, the Department of Housing and Urban Development, the Diabetes Institutes Foundation, the Commonwealth Health Research Board and various industrial companies (Astra Zeneca, Takeda, Pliva, Dainippon, Eli Lilly & Company).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vinik, A., Ullal, J., Parson, H. et al. Diabetic neuropathies: clinical manifestations and current treatment options. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2, 269–281 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncpendmet0142
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncpendmet0142
This article is cited by
-
Plasma 1,5-anhydro-d-glucitol is associated with peripheral nerve function and diabetic peripheral neuropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes and mild-to-moderate hyperglycemia
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome (2022)
-
Is diabetes the risk factor for poor neurological recovery after cervical spine surgery? A review of the literature
European Journal of Medical Research (2022)
-
Study Protocol titled as “Effectiveness of neural mobilization in improving the ankle ROM and plantar pressure distribution in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy: A single group, pre post, quasi experimental study protocol”
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders (2022)
-
Corneal nerve fiber loss relates to cognitive impairment in patients with Parkinson’s disease
npj Parkinson's Disease (2021)
-
Non-glucose risk factors in the pathogenesis of diabetic peripheral neuropathy
Endocrine (2020)