Abstract
Development of supercapacitors with high-energy density and high-power density is a tremendous challenge. Although the use of conductive carbon materials is promising, other methods are needed to reach high cyclability, which cannot be achieved by fully utilizing the surface-oxygen redox reactions of carbon. Here we introduce an effective strategy that utilizes Cu2+ reduction with carbon-oxygen surface groups of the binder-free electrode in a new redox-active electrolyte. We report a 10-fold increase in the voltammetric capacitance (4,700 F g−1) compared with conventional electrolyte. We measured galvanostatic capacitances of 1,335 F g−1 with a retention of 99.4% after 5,000 cycles at 60 A g−1 in a three-electrode cell and 1,010 F g−1 in a two-electrode cell. This improvement is attributed to the synergistic effects between surface-oxygen molecules and electrolyte ions as well as the low charge transfer resistance (0.04 Ω) of the binder-free porous electrode. Our strategy provides a versatile method for designing new energy storage devices and is promising for the development of high-performance supercapacitors for large-scale applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Electrochemical supercapacitors can deliver energy at higher rates than batteries and maintain their specific power for extended periods1,2, but their low-energy density limits their use in applications that require high-energy density, high-power density and ultralong cycle lives3. Carbon materials are commonly used in supercapacitors because of their low cost, good electrical conductivity and high surface area, which make them ideal for rapid storage and release of energy4. Their energy storage properties are generally attributed to electric double-layer capacitance and a pseudocapacitive contribution of quick faradaic reactions resulting from surface functionalities, mainly from oxygen and nitrogen5, at the electrode/electrolyte interface. Furthermore, polarization of these surface functional groups enhances the surface wettability of the porous carbon6,7,8 in aqueous electrolytes, decreases the resistance9,10 and thus reduces the high porosity demand for these materials11. However, the limited faradaic reactions of different surface functional groups and their instabilities that arise during cycling are the downside of carbon-based supercapacitors7,12,13.
Another high-efficiency strategy uses an alternative method to promote rapid faradaic reactions by utilizing redox-active electrolytes for activated carbon electrodes. Roldan et al.14 reported an increase in capacitance from 320 to 901 F g−1 by adding hydroquinone to H2SO4 electrolytes. Similarly, Senthilkumar et al.15 used hydroquinone addition into polyvinyl-alcohol H2SO4 gel electrolyte to increase the capacitance from 425 to 941 F g−1, and they reported potassium iodide addition into aqueous H2SO4 electrolyte16 to increase the capacitance from 472 to 912 F g−1. These increases in capacitances were attributed to rapid faradaic reactions at the electrode/electrolyte interface that occurred by introducing mediators (hydroquinone/quinine, iodide/iodine pairs) into electrolytes, which augmented the pseudocapacitive contribution to the system. Here capacitance enhancement from 900 to 940 F g−1 was observed. Surface functional groups were avoided to improve cycling stability, and a binder was used in the electrode preparation, which made synthesis more labour intensive.
In the present work, we design a redox-active electrolyte for surface functional groups of porous carbon-based supercapacitor, that is, cupric chloride (CuCl2) in an aqueous HNO3 solution. The reaction between carbon-oxygen surface groups and Cu2+ ions in acidic media has been reported previously17 and is concentration dependent. Its dependence on chloride can also be established because chloride in CuCl2 is very reactive with many carbon-based compounds. This compound is commonly used for the chlorination of carbonyls18 and aromatics19 and as a catalyst for carbonyl compound reactions with alkenes20. By fixing the position of the carbon–oxygen ( ) bond on the surface and reducing CuCl2 in the electrolyte21, we can easily generate an additional redox CuCl layer (Fig. 1). Moreover, chloride can stabilize the copper–oxygen interaction as proposed previously22. To increase the conductivity in the absence of a binder3,13, we develop a dip and dry technique to attach spherical, porous carbon material to the substrate.
) bond on the surface and reducing CuCl2 in the electrolyte21, we can easily generate an additional redox CuCl layer (Fig. 1). Moreover, chloride can stabilize the copper–oxygen interaction as proposed previously22. To increase the conductivity in the absence of a binder3,13, we develop a dip and dry technique to attach spherical, porous carbon material to the substrate.
Results
Characterization of porous electrode
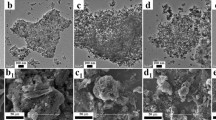
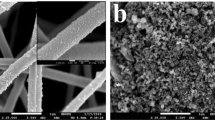
Porous carbon microspheres (PCMSs) were prepared by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis and attached with microwires composed of carbon fibre paper after the dip and dry method (Fig. 2a and Supplementary Figs S1 and S2). The loading of the PCMSs was confirmed by scanning electron microscopic images of the carbon fibre paper microwires before and after the dip and dry process (inset of Fig. 2b and Supplementary Fig. S3). These images show the pores on the spherical surface of amorphous PCMS and its attachment with conductive microwires. X-ray diffraction patterns of the PCMSs and the microwires are shown in Supplementary Fig. S4. A high-resolution transmission electron microscopic image shows diffracted fringes of the microwire’s cross-section (inset of Fig. 2c). The transmission electron microscopic images of the PCMS reflect void spaces (Fig. 2c and Supplementary Fig. S5), which were introduced after removal of the LiCl salt during synthesis23,24 (Supplementary Figs S1 and S2).
(a) A scanning electron microscopic image illustrating the spherical morphology of porous carbon micro sphere (PCMS) prepared by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis before and (b) after the dip and dry step. The inset shows a magnified image of a microwire composed of carbon fibre paper before the dip and dry step. (c) A transmission electron microscopic image of the attached PCMS. The inset shows the high-resolution transmission electron microscopic cross-section image of the microwires in the carbon fibre paper’s graphitic planes. (d) The nitrogen adsorption-desorption isotherms of the PCMSs. The inset shows the corresponding pore size distribution. (e) An X-ray photo spectroscopic (XPS) broad scan spectrum (0–1,100 eV) of the PCMSs showing the relative intensities of carbon C 1s and oxygen O 1s. (f) XPS O 1s spectra showing deconvolution, fitting with the CasaXPS software and the percentage of surface groups. The inset is the elemental analysis. Scale bar, 500 nm (a–c) and 5 nm (inset of c).
The specific surface area and pore size distribution of the PCMSs before the dip and dry step were tested by nitrogen adsorption-desorption measurements. The resulting isotherm (Fig. 2d) shows a hysteresis loop that is typical for mesoporous materials at high relative pressures25. Its specific surface area, calculated by the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller method26, was 910 m2 g−1. The pore size distribution, derived from the adsorption branch of the isotherm, is broad at ~20 nm (inset of Fig. 2d). Surface functional groups of the PCMSs were detected by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS), and the results are shown in Supplementary Figs S6 and S7b, respectively. They were also evaluated by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (Fig. 2e). Quantitative analysis shows (Fig. 2f) two types of surface functional groups,  carbonyl group at 532 eV with the dominant percentage of 78% and C-OH at 530.8 eV (24) with a percentage of 22%. The inset in Fig. 2f contains the results of the elemental analysis of PCMSs, which were found to have 10% oxygen in 0.1 g of the PCMSs.
carbonyl group at 532 eV with the dominant percentage of 78% and C-OH at 530.8 eV (24) with a percentage of 22%. The inset in Fig. 2f contains the results of the elemental analysis of PCMSs, which were found to have 10% oxygen in 0.1 g of the PCMSs.
Electrochemical properties
The PCMSs were selected as the active material. The prepared electrodes had carbon-oxygen surface groups within the pores of the PCMSs and were attached with microwires made of carbon fibre paper (COSG@PCMS/MCFP). The electrodes were checked using a three-electrode configuration. We calculated the voltammetric capacitance and average energy density as follows:


Cs (F g−1) represents the voltammetric specific capacitance. ∮IdV (A·V) is the voltammetric charge, that is, area under the curve of the cyclic voltammetry. V (V) is the potential window. S (V s−1) is the scan rate and m(g) represents the active mass (that is, mass of PCMSs).
The prepared electrode exhibited a cyclic voltammetric capacitance of 440 F g−1 using equation (1) based on an active mass (2.71±0.01 mg) of PCMSs and a scan rate of 5 mV s−1 in aqueous H2SO4 electrolyte (top inset of Fig. 3a). A quasi-rectangular capacitive curve with pseudocapacitive broad peaks27 at ~0.35 V was observed because of the presence of additional functional groups. This capacitance is ~2.5 times greater than the previously reported value of 185 F g−1 for the same material in which a binder was used to attach the PCMSs to a glassy carbon substrate24. The bottom inset in Fig. 3a shows a cyclic voltammetric capacitance of 420 F g−1 with the same electrode and scan rate when CuSO4 was added to the 1 M HNO3 electrolyte. Here a redox peak at 0.075 V was observed. A much weaker effect was also reported previously17,28 and was attributed to a redox reaction of Cu2+. When CuSO4 was replaced with CuCl2 in the solution, even at a lower concentration, very strong redox peaks were observed. This replacement enhanced the capacitance to 3,072 F g−1, and it reached a maximum of 4,700 F g−1 at higher concentrations (Fig. 3a). The details are provided in the Methods section. The potential window was selected to include complete redox peaks. This capacitance was ~10.5 times greater than the capacitance obtained in the absence of CuCl2 (that is, 440 F g−1). An average energy density Ea of 163 Wh kg−1 was calculated using equation (2).
(a) Cyclic voltammogram at a scan rate of 5 mV s−1 in an acidic aqueous solution of the electrolyte CuCl2. The top inset is the magnified curve of the cyclic voltammogram in a 1-M H2SO4 solution, and the bottom inset shows the curve in 1 M HNO3 and 0.12 M CuSO4. (b) An EIS Nyquist plot in the frequency range of 10–50 MHz. The bottom inset shows data at high frequencies with a marked transition frequency and the top inset shows the equivalent circuit.
The reaction kinetics and charge transfer resistances were investigated by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) at three different potentials (Fig. 3b). The curve at 0.2 V exhibits a short tail that was more deviated from 90° than the other two curves at 0.01 and 0.32 V. The bottom inset of Fig. 3b shows a low equivalent series resistance RESR of 0.64 Ω (which is the intercept of the curve with the real part of the impedance in the high-frequency range). The inset also shows a very low charge transfer resistance RCT of 0.04 Ω (that is, the diameter of the depressed semicircle at 0.2 V), with electrolyte ion diffusion starting at the marked value of 362 Hz (1,29). The top inset of Fig. 3b shows the corresponding equivalent circuit.

C (F g−1) represents the galvanostatic charge-discharge (GCD)-specific capacitance. im= /m (A g−1) is the current density, where
/m (A g−1) is the current density, where  is the current and m is the active mass of the electrode. ∫Vdt is the integral current area, where V is the potential with initial and final values of Vi and Vf, respectively.
is the current and m is the active mass of the electrode. ∫Vdt is the integral current area, where V is the potential with initial and final values of Vi and Vf, respectively.
The galvanostatic capacitances were calculated with equation (3) using the integral current areas30,31 of the discharge curves in the inset of Fig. 4a. The mathematical details are provided in the Methods section. In an acidic electrolyte solution of 0.06 M CuCl2 at 20 A g−1, a galvanostatic capacitance of 946 F g−1 was observed with 98% capacitance retention. This capacitance decreased to 631 F g−1 at 60 A g−1. The stability of the carbon-oxygen surface groups inside the pores and the contact between the PCMSs and the microwires were confirmed by the cyclic GCD test.
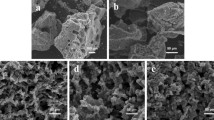
(a) The GCD cycling performance of the as-prepared electrode in 1 M HNO3 and 0.06 M CuCl2 aqueous electrolyte solution at 20 A g−1. The inset shows charge-discharge curves at different current densities. (b) A cyclic voltammogram of the as-prepared electrode and the microwires at a scan rate of 5 mV s−1 in 100 ml of 1 M HNO3 and 0.06 M CuCl2 aqueous electrolyte. The inset shows a magnified CV curve of the microwires made of carbon fibre paper. (c) The GCD cycling performance of the as-prepared electrode in 1 M HNO3 and 0.09 M CuCl2 aqueous electrolyte at a current density of 60 A g−1 with capacity retention of 99.4%. The inset shows the last five cycles. (d) A scanning electron microscopic image after 5,000 continuous charge-discharge cycles. Scale bar, 500 nm.
The microwires showed negligibly small contributions to the total capacitance (Supplementary Fig. S8a). Similar phenomenon was also observed in their cyclic voltammogram (Fig. 4b and its inset). The voltammetric charge of the microwires (7.5 × 10−5 V·A) was ~250 times smaller than the voltammetric charge of the as-prepared electrode (1.9 × 10−2 V·A).
Figure 4c shows the cycling performance of the supercapacitor in a more concentrated electrolyte, yielding a first-cycle galvanostatic capacitance of 1,335 F g−1. After 5,000 continuous cycles, the capacitance remained unchanged with 99.4% of the original value. A higher current density of 60 A g−1 was used to cause fast transport of the ions in the concentrated solution. Contact between the PCMS and the microfibre carbon paper after 5,000 cycles is clearly observable (Fig. 4d).
Discussion
The superior electrochemical performance (a 2.5-fold improvement in the capacitance compared with previous results24) of the as-prepared electrode in H2SO4 (top inset of Fig. 3a) can be explained by the following two characteristics: (1) the binder-free interfaces of the PCMSs and (2) the surface oxygen groups. The binder-free attachment of the PCMSs improved the electrical conductivity and allowed the electrolyte ions to diffuse easily through the open pore channels of the PCMS13. The polarized carbon-oxygen surface groups attract water molecules, increase the wettability of the PCMSs and fully utilize the surface of the PCMS32. These groups also provide active sites for reactions24 and contribute to pseudocapacitance33,34,35, which leads to the observed quasi-rectangular cyclic voltammetric curves27 (top inset of Fig. 3a).
When CuSO4 was added to the electrolyte, the capacitance was comparable to that obtained in the acidic electrolyte, but a redox peak was also observed (bottom inset of Fig. 3a). When CuSO4 was replaced with CuCl2, the pseudocapacitance contribution was substantially improved, which caused the capacitance to be 10.5-fold larger than the capacitance in the acidic electrolyte (Fig. 3a). This increase is attributable to the reaction of CuCl2 with carbonyl groups21 at the surface of the PCMSs (Fig. 2f):

Here CuCl2 is reduced and a reversible surface layer of CuCl is formed on  surface layer (equation (4)).
surface layer (equation (4)).


According to the Pourbaix diagram of CuCl2 (36), Cu2+ can follow two reduction steps in acidic solutions28,37,38 (equations (5) and (6)) where the redox potentials are Cu2+ concentration dependent17. As shown in Supplementary Fig. S9, no obvious deposition is observed after the first reaction (bottom inset), but it exists after the second reduction (top inset). Thus, a potential window was selected to avoid deposition and promote reversible adsorption of Cu+, which resulted in very high pseudocapacitive contribution.
Excellent reaction kinetics was also achieved, which is critical for a good supercapacitor electrode1,39. The as-prepared electrode possesses fast electron and ion transport, which lead to a low charge transfer resistance RCT of 0.04 Ω (Fig. 3b), compared with 1,361 Ω for the microwires (Supplementary Fig. S8b). This behaviour highlights the importance of loaded PCMSs on microwires. These PCMSs contain a large number of oxygen groups on the surface (Fig. 2e), whereas the microwires have a negligible amount of oxygen groups (Supplementary Fig. S8c). This difference indicates that the absence of oxygen groups on the surface allows the faradaic reactions to be avoided and hence increases the RCT (40). A similar effect was previously observed for nitrogen surface groups on carbon8. Thus, each oxygen surface group acts as an active site for the transport of electrons and electrolyte ions through conductive microwires1,39 and open pore channels of PCMSs40, respectively. According to the electrochemical impedance spectroscopic (EIS) test in HNO3 electrolyte, the RCT value increase to 1.7 Ω, which confirms the importance of CuCl2 (Supplementary Fig. S8d).
Another factor that makes the electron and ion transport more efficient is the very low RESR (0.65 Ω), which included all of the ohmic resistances of the supercapacitor39 and the PCMSs’ contacts. Furthermore, the EIS curve at 0.2 V (Fig. 3b) displays a short tail indicating fast diffusion of the electrolyte ions into the pores16. Moreover, at 0.2 V, the greater deviation from 90° than the other two curves at 0.01 and 0.32 V is attributed to the high diffusion rate41,42 and the strong scan-rate dependence43. These findings indicate that electrolyte ion diffusion starts at a high frequency of 362 Hz.
The high cyclability of the as-prepared electrode material with 99.4% capacitance retention after 5,000 charge-discharge cycles at a very high current density of 60 A g−1 can be ascribed to (1) stable copper-oxygen interaction in the presence of chloride22 and (2) stable attachment between PCMSs and the microwires with reduced superficial tension in the solution (Supplementary Movie 1). As further evidence of this high cyclability, the replacement of PCMSs with commercially available acetylene carbon black on microwires carbon paper electrode gave poor cyclability in the same experimental conditions (Supplementary Fig. S10).
Synchronous GCD experiments in symmetric two- and three-electrode system44,45 (Supplementary Fig. S11a) were conducted to compare the double-layer behaviour at the positive electrode with a potential window of 0.88 V. Pseudocapacitive behaviour was observed at the negative electrode with a potential window of 0.47 V. Following the principle of equal charge44, different potential windows give rise to the 432 and 1,010 F g−1 capacitances at the positive and negative electrode, respectively. The enhanced double-layer capacitance in the CuCl2 electrolyte (Supplementary Fig. S11b) can be attributed to reversible ion adsorption in porous carbon46. This phenomenon in the high voltage range and its explanation have been reported for other redox electrolytes27,44,47. The two-electrode cell capacitance, calculated from the galvanostatic discharge curve in total potential window of 1.35 V, was 294 F g−1, which is very close to the capacitance calculated by equation for two capacitors in series (1/C=1/C++1/C−)48. The cycling performance of the two-electrode cell was found to be 99.1% after 1,000 cycles (Supplementary Fig. S11c).


E is the energy density,  is the current and M is the total active mass of both electrodes. ∫Vdt is the galvanostatic discharge current area. P is the power density and t is the discharge time.
is the current and M is the total active mass of both electrodes. ∫Vdt is the galvanostatic discharge current area. P is the power density and t is the discharge time.
The energy density E and power density P of the cell using equations (7) and (8) are 73 W·h kg−1 (0.82 mW·h cm−3 volumetric energy density) and 7.5 kW kg−1 (85 mW cm−3 volumetric power density), respectively.
In summary, we define an electrolyte for surface-functionalized, porous and binder-free carbon-based electrode that was prepared by a facile dip and dry method. We demonstrate that this design exhibits ultrahigh voltammetric capacitance and energy density resulting from redox reactions between surface oxygen groups and CuCl2 in acidic media. The electrode has a long cycle life that is attributed to the stability of the oxygen surface groups and the binder-free contact between the active material and the microwires. The outstanding electrochemical performance demonstrates the effectiveness of this strategy to enhance the capacitance and cycle lifetime. This strategy has great potential for the development and large-scale applications of high-performance supercapacitors.
Methods
Synthesis of PCMSs
To prepare the porous electrode material for this supercapacitor, a precursor solution of lithium dichloroacetate was first prepared by mixing 1.5 molar mass of LiOH with 1.5 molar mass of Cl2CH-COOH in 100 ml of deionized water. This precursor was ultrasonically nebulized into microdroplets with the humidifier from an ultrasonic spray pyrolysis apparatus. These microdroplets were then suspended in a nitrogen gas flow and heated by passing them through a quartz tube in a furnace at 800 °C. Here thermally induced chemical reactions decomposed the lithium dichloroacetate droplets into a spherical carbon network, LiCl (which acted as a self-sacrificial template) and some carbon-oxygen surface groups. The black powder that was collected in a bubbler was washed three times with ethanol and deionized water. The washed powder was then centrifuged to dissolve the LiCl salt. After drying in an oven at 80 °C, the PCMSs were obtained.
Fabrication and electrochemical test of supercapacitor
A commercially available microfibre carbon paper with 2 × 3 cm2 dimensions was dipped for 30 s into 5 ml solution of ethanol containing 0.1 g PCMSs and dried at room temperature for 10 min, that is, dip and dry. This process was repeated three times to get good coating of PCMSs on microwires of carbon fibre paper. Finally, it was washed with deionized water to remove extra layers of PCMSs and dried again for 3 h at 80 °C. Total mass of PCMSs loaded on microwires carbon fibre paper was 2.71+0.01 mg by calculating the difference of the microwires carbon fibre paper weights before and after diping and drying process. Mass per unit area of the electrode was 0.00046, g cm−2. Three-electrode method used to test electrochemical properties, consist of working electrode, Pt wire as counter electrode and Ag/AgCl (saturated KCL) as a reference electrode. Two-electrode method is also used, which consists of two identical electrodes separated by plastic porous separator, and simultaneous two to three electrodes system is also used. In addition, before each electrochemical test, we put the electrode into the electrolyte for 4–5 h. Cyclic voltammetry and GCD measurements were performed in 100 ml solutions using an Autolab potentiostat galvanostat.
Structure characterization
To observe the morphology, scanning electron microscopy was performed by JEOL JSM-7100F at an acceleration voltage of 15 kV, transmission electron microscopic and high-resolution transmission electron microscopic images were recorded by a JEOL JEM-2010 FEF microscope at an acceleration voltage of 200 kV. EDS was performed by JEM 2100F STEM/EDS where X-ray energy resolution was 132 eV. X-ray diffraction patterns were recorded by a Rigaku D/MAX-III diffractometer (Rigaku) with monochromatized Cu Ka radiation (k=1.5406 Å). Fourier transform infrared spectra were recorded using 60-SXB infrared spectrometer. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic analysis was done on VG Multilab 2000. Elemental analysis was performed in Varioel = 3 \* ROMAN III CHNS. The Brunauer–Emmett–Teller surface area was measured using Gemini 2360 instrument by adsorption of nitrogen at −197 °C.
Calculation of voltammetric capacitance
On the basis of equation (1), and the voltammatric charge (that is, area under the curve) of 0.03185 (A·V), the mass of the active material of 0.00271, g, the potential window of 0.5 V and the scan rate of 0.005 V s−1), we obtain a voltammetric capacitance of 4,700 F g−1.
Calculation of the GCD capacitance
For symmetric (or linear) GCD behaviour, the charge/voltage ratio remains constant over the entire range of applied voltages, and the energy density E can be calculated by equation (9) (dashed line in Supplementary Fig. S12a).

However, the quasi-reversible faradic reactions in the cell make the GCD curve non-symmetric30. Thus, the faradic reaction charge/voltage ratio no longer remains constant and varies with time, which leads to equation (10) (solid line in Supplementary Fig. S12a)49.

E is integral current area under the curve of Supplementary Fig. S12a. Using the differential form of capacitance50 (equation (11)), we can obtain the integral form.

Now, if we rearrange equation (11) and multiply by V/V, this expression can be integrated to give equation (12).

At a constant current, we obtain

The numerator of equation (13) is the same integral current area as in equation (10). By integrating the denominator of equation (13) and dividing by the mass m, we can obtain equation (14).


Here the current integral area is 6.15 A·V·s, the current density is 20 A g−1 and the voltage window square (taking absolute value) is 0.25 V·V. Substituting them into equation (15) gives a capacitance of 946 F g−1.
According to Supplementary Fig. S12b, Vf=0, Vi=sΔV and the integral current area ∫V dt=ΔV × Δt/2, substituting these values into equation (15) gives



Equation (18) was used to calculate the average capacitance, which is applicable for symmetric behaviour.
Additional information
How to cite this article: Mai, L.-Q. et al. Synergistic interaction between redox-active electrolyte and binder-free functionalized carbon for ultrahigh supercapacitor performance. Nat. Commun. 4:2923 doi: 10.1038/ncomms3923 (2013).
References
Zhu, Y. et al. Carbon-based supercapacitors produced by activation of graphene. Science 332, 1537–1541 (2011).
Miller, J. R. & Simon, P. Electrochemical capacitors for energy management. Science 321, 651–652 (2008).
Simon, P. & Gogotsi, Y. Materials for electrochemical capacitors. Nat. Mater. 7, 845–854 (2008).
Huang, J., Sumpter, B. G. & Meunier, V. Theoretical model for nanoporous carbon supercapacitor. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 47, 520–524 (2008).
Qu, D. studies of the activated carbons used in double-layer supercapacitors. J. Power Sources 109, 403–411 (2002).
Li, W. et al. A Self-template strategy for the synthesis of mesoporous carbon nanofibers as advanced supercapacitor electrodes. Adv. Energy Mater. 1, 382–386 (2011).
Hsieh, C. T. & Teng, H. Influence of oxygen treatment on electric double-layer capacitance of activated carbon fabrics. Carbon 40, 667–674 (2002).
Li, W. et al. Nitrogen-containing carbon spheres with very large uniform mesopores: The superior electrode materials for EDLC in organic electrolyte. Carbon 45, 1757–1763 (2007).
Wong, C. H. A., Ambrosi, A. & Pumera, M. Thermally reduced graphenes exhibiting a close relationship to amorphous carbon. Nanoscale 4, 4972–4977 (2012).
Chen, P. & McCreery, R. L. Control of electron transfer kinetics at glassy carbon electrodes by specific surface modification. Anal. Chem. 68, 3958–3965 (1996).
Pinero, E. R., Leroux, F. & Beguin, F. A high-performance carbon for supercapacitors obtained by carbonization of a seaweed biopolymer. Adv. Mater. 18, 1877–1882 (2006).
Cheng, P. Z. & Teng, H. Electrochemical responses from surface oxide present on HNO3-treated carbon. Carbon 41, 2057–2063 (2003).
Hu, C. C. & Wang, C. C. Effects of electrolytes and electrochemical pretreatments on the capacitive characteristics of activated carbon fabrics for supercapacitors. J. Power Sources 125, 299–308 (2004).
Roldan, S. et al. Towards a further generation of high-energy carbon-based capacitors by using redox-active electrolytes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 50, 1699–1701 (2011).
Senthilkumar, S. T., Selvan, R. K., Ponpandian, N. & Melo, J. S. Redox additive aqueous gel electrolyte for an electric double layer capacitor. RSC Adv. 2, 8937–8940 (2012).
Senthilkumar, S. T. et al. Electric double layer capacitor and its improved specific capacitance using redox additive electrolyte. Mater. Chem. A 1, 1086–1095 (2013).
Popa, D. E. et al. Carbon paste electrode modified with organofunctionalized mesoporous silica for electrochemical detection and determination of copper(II) using cyclic voltammetry and anodic stripping voltammetry. Rev. Roum. Chim. 55, 123–130 (2010).
Castro, C. E., Gaughan, E. J. & Owsley, D. C. Cupric halide halogenations. J. Org. Chem. 30, 587–592 (1965).
Kodomari, M., Satoh, H. & Yoshitomi, S. Selective nuclear halogenation of polymethylbenzenes with alumina-supported copper(II) halides. Bull Chem. Soc. Jpn 61, 4149–4150 (1988).
Attanasi, O., Bonifazi, P., Foresti, E. & Pradella, G. Effect of metal ions in organic synthesis. part 10. synthesis and X-ray crystal structure of some 1-(Arylamino)pyrrole derivatives by reaction of (Arylazo)alkenes and P-dicarbonyl compounds in the presence of copper(II) chloride. J. Org. Chem. 47, 684–687 (1982).
Kochi, J. K. The reduction of cupric chloride by carbonyl compound. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 77, 5274–5278 (1955).
Suleiman, I. A. et al. Interaction of chlorine and oxygen with the Cu(100) surface. J. Phys. Chem. C 114, 19048–19054 (2010).
Skrabalak, S. E. & Suslick, K. S. Porous carbon powders prepared by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128, 12642–12643 (2006).
Kim, H. et al. Carbon microspheres as supercapacitors. J. Phys. Chem. C. 115, 20481–20486 (2011).
Pin, E. R., Cadek, M. & Beguin, F. Tuning carbon materials for supercapacitors by direct pyrolysis of seaweeds. Adv. Funct. Mater. 19, 1032–1039 (2009).
Brunauer, S., Emmett, P. H. & Teller, E. Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 60, 309–319 (1938).
Senthilkumar, S. T., Selvan, R. K., Lee, Y. S. & Melo, J. S. Electric double layer capacitor and its improved specific capacitance using redox additive electrolyte. J. Mater. Chem. A 1, 1086–1095 (2013).
Li, Q. et al. An investigation of Cu2+ and Fe2+ ions as active materials for electrochemical redox supercapacitors. J. Electroanal. Chem. 611, 43–50 (2007).
Taberna, P. L., Simon, P. & Fauvarque, J. F. Electrochemical characteristics and impedance spectroscopy studies of carbon-carbon supercapacitors. J. Electrochem. Soc. 150, A292–A300 (2003).
Chen, G. Z. Understanding supercapacitors based on nano-hybrid materials with interfacial conjugation. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mat. Int. 23, 245–255 (2013).
Kim, J. Y. & Chung, I. J. An All-solid-state electrochemical supercapacitor based on Poly3-(4-fluorophenylthiophene) composite electrodes. Electrochem. Soc. 149, A1376–A1380 (2002).
Conway, B. E. Electrochemical Supercapacitors: Scientific Fundamentals and Technological Applications Plenum Press (1999).
Kinoshita, K. Carbon: Electrochemical and Physicochemical Properties Wiley (1988).
Frackowiak, E. & Beguin, F. Carbon materials for the electrochemical storage of energy in capacitors. Carbon 39, 937–950 (2001).
Kim, Y. T. et al. Drastic change of electric double layer capacitance by surface functionalization of carbon nanotubes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 234106-1–234106-3 (2005).
Kear, G., Barker, B. D. & Walsh, F. C. Electrochemical corrosion of unalloyed copper in chloride media––a critical review. Corros. Sci. 46, 109–135 (2004).
Pirogov, B. Y. & Zelinsky, A. G. Numeric simulation of electrode process in Cu/CuSO4 + H2SO4 system. Electrochim. Acta. 49, 3283–3292 (2004).
Tantavichet, N. & Pritzker, M. D. Low and high frequency pulse current plating of copper onto a rotating disk electrode. J. Electrochem. Soc. 149, C289–C299 (2002).
Rakhi, R. B., Chen, W., Cha, D. & Alshareef, H. N. Substrate dependent self-organization of mesoporous cobalt oxide nanowires with remarkable pseudocapacitance. Nano Lett. 12, 2559–2567 (2012).
Ates, M. Review study of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy and equivalent electrical circuits of conducting polymers on carbon surfaces. Prog. Org. Coat. 71, 1–10 (2011).
Zimmerman, A. H. & Effa, P. K. Discharge kinetics of nickel electrode. J. Electrochem. Soc. 131, 709–713 (1984).
Armstrong, R. D. & Wang, H. Behaviour of nickel hydroxide electrodes after prolonged potential float. Electrochim. Acta. 36, 759–762 (1991).
Susanti, D., Tsai, D. S., Huang, Y. S. & Korotcov, A. Structures and electrochemical capacitive properties of RuO2 vertical nanorods encased in Hydrous RuO2 . J. Phys. Chem. C 111, 9530–9537 (2007).
Roldan, S., Granda, M., Menendez, R., Santamaria, R. & Blanco, C. Mechanism of energy storage in carbon-based supercapacitors modified with a quinoid redox-active electrolyte. J. Phys. Chem. C 115, 17606–17611 (2011).
Roldan, S. et al. Redox-active electrolyte for carbon nanotube-based electric double layer capacitors. Electrochemica. Acta. 56, 3401–3405 (2011).
Merlet, C. et al. On the molecular origin of supercapacitance in nanoporous carbon electrodes. Nat. Mater. 11, 306–310 (2012).
Roldan, S., Blanco, R., Granda, C., Menendez, M. & Santamaria, R. Toward a further generation of high energy carbon-based capacitors by using redox-active electrolyes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 50, 1699–1701 (2011).
Khomenko, V., Raymundo-Pinero, E. & Benguin, F. A new type of high energy asymmetric capacitor with nanoporous carbon electrodes in aqueous electrolyte. J. Power Sources 195, 4234–4241 (2010).
Kim, J. Y. & Chung, I. J. An All-solid-state electrochemical supercapacitor based on Poly3-(4-fluorophenylthiophene) composite electrodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 149, A1376–A1380 (2002).
Ng, K. C., Zhang, S., Peng, C. & Chen, G. Z. Individual and bipolarly stacked asymmetric aqueous supercapacitors of CNTs/SnO2 and CNTs/MnO2 Nanocomposites. J. Electrochem. Soc. 156, A846–A853 (2009).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (2013CB934103, 2012CB933003), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51072153, 51272197), the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (NCET-10-0661) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2012-II-001, 2013-YB-01). We thank Professor C.M. Lieber of Harvard University, Professor Dongyuan Zhao of Fudan University, Professor Yuliang Cao of Wuhan University and Dr Jun Liu of Pacific Northwest National Laboratory for strong support and stimulating discussions. We are grateful to Professor J.L. Xie and Dr X.Q. Liu of the Center for Materials Research and Analysis of Wuhan University of Technology for materials characterization.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
L.-Q.M. and A.M.-K. designed the research. A.M.-K. performed the experiments. A.M.-K., X.T. and X.X. designed the apparatus. L.-Q.M., A.M.-K., K.M.H. and Y.-L.Z. discussed the interpretation of results and co-wrote the paper. All authors commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Figures S1-S12 (PDF 792 kb)
Supplementary Movie
Surface effect. Movie was recorded during SEM after the 5000 cycles, when electron beam evaporated the solution between PCMS and microwire of carbon fiber paper contact. (MOV 1252 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mai, LQ., Minhas-Khan, A., Tian, X. et al. Synergistic interaction between redox-active electrolyte and binder-free functionalized carbon for ultrahigh supercapacitor performance. Nat Commun 4, 2923 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms3923
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms3923
This article is cited by
-
Machine-learning-assisted material discovery of oxygen-rich highly porous carbon active materials for aqueous supercapacitors
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Performance evaluation of Bi2O3@GO and Bi2O3@rGO composites electrode for supercapacitor application
Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics (2023)
-
Fabrication of S,N co-doped graphene powders for symmetrical supercapacitors in different aqueous electrolytes
Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics (2023)
-
A review on electrolytes for supercapacitor device
Discover Materials (2023)
-
Brush-electroplated rGO@MnO2 composite supported on carbon cloth for flexible high-performance supercapacitor electrodes
Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics (2022)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.