Abstract
It is well established that anthropogenic chlorine-containing chemicals contribute to ozone layer depletion. The successful implementation of the Montreal Protocol has led to reductions in the atmospheric concentration of many ozone-depleting gases, such as chlorofluorocarbons. As a consequence, stratospheric chlorine levels are declining and ozone is projected to return to levels observed pre-1980 later this century. However, recent observations show the atmospheric concentration of dichloromethane—an ozone-depleting gas not controlled by the Montreal Protocol—is increasing rapidly. Using atmospheric model simulations, we show that although currently modest, the impact of dichloromethane on ozone has increased markedly in recent years and if these increases continue into the future, the return of Antarctic ozone to pre-1980 levels could be substantially delayed. Sustained growth in dichloromethane would therefore offset some of the gains achieved by the Montreal Protocol, further delaying recovery of Earth’s ozone layer.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
In the 1970s, it was recognized that chlorine and bromine released from long-lived anthropogenic compounds, such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and halons, could destroy ozone in the stratosphere1,2. Industrial emissions of these halocarbons have led to widespread depletion of Earth’s ozone layer in recent decades, including the Antarctic ‘Ozone Hole’ phenomenon3,4,5. Peak ozone depletion was observed around the turn of the century, when globally the stratospheric ozone column was reduced by ∼5% relative to 1980 levels (a benchmark before which substantial ozone depletion had not been observed). While ozone depletion today remains a persistent environmental issue, there are signs that ozone recovery is underway6,7,8,9, owing to controls on the production of ozone-depleting compounds introduced by the 1987 Montreal Protocol and its amendments10,11. Given compliance with the Protocol, stratospheric levels of chlorine derived from controlled ozone-depleting compounds should continue to steadily decline in coming decades. As a result, stratospheric column ozone is projected to return to pre-1980 levels in the middle to latter half of this century, depending on location7,12.
Several human-produced chlorocarbons not controlled by the Montreal Protocol are present in Earth’s atmosphere. Among the most abundant of these compounds is dichloromethane (CH2Cl2)—an industrial solvent also used as a feedstock in the production of other chemicals, among other applications13,14. Unlike CFCs, which are virtually inert in the troposphere and have long atmospheric lifetimes (decades to centuries), CH2Cl2 is a so-called very short-lived substance (VSLS)15. Historically, VSLS have been thought to play a minor role in stratospheric ozone depletion due to their relatively short atmospheric lifetimes (typically <6 months) and therefore low atmospheric concentrations. However, substantial levels of both natural and anthropogenic VSLS have been detected in the lower stratosphere15,16,17,18 and numerical model simulations suggest a significant contribution of VSLS to ozone loss in this region19,20,21. Long-term measurements of CH2Cl2 reveal that its tropospheric abundance has increased rapidly in recent years15,21,22,23. For example, between 2000 and 2012, surface concentrations of CH2Cl2 increased at a global mean rate of almost 8% per year, with the largest growth observed in the Northern Hemisphere (NH)21. Given that natural emissions of CH2Cl2 are small, this recent growth likely reflects an increase in industrial emissions15. While the precise nature of the source remains poorly characterized, industrial CH2Cl2 emissions from Asia—in particular from the Indian subcontinent—appear to be growing in importance23. The impact of these observed changes and continued CH2Cl2 growth in coming decades on the timescale of stratospheric ozone recovery have not yet been considered.
Here, a state-of-the-art global chemical transport model (CTM) is used to examine the sensitivity of future stratospheric chlorine and ozone levels to sustained CH2Cl2 growth. CTMs are commonly used to investigate detailed chemical processes and here, because transport is specified in the model, we are able to isolate the ozone response solely to increasing levels of CH2Cl2 in the atmosphere. We find that continued growth in the atmospheric loading of CH2Cl2 could offset some of the future benefits of the Montreal Protocol and lead to a substantial delay (more than a decade) in the recovery of stratospheric ozone over Antarctica.
Results
Recent CH2Cl2 trends and future growth scenarios
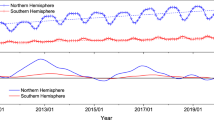
Figure 1 shows the measured surface abundance of CH2Cl2 from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) long-term surface monitoring network. Globally, CH2Cl2 concentrations approximately doubled between 2004 and 2014 (Fig. 1a), although growth rates varied considerably during this period (Fig. 1b). The abundance of CH2Cl2 at mid-latitudes in the NH is around a factor of 3 greater than in the Southern Hemisphere (SH), reflecting NH industrial sources. At present, it is unknown if a single industrial application of CH2Cl2, or several, is contributing to the observed upward trend. As a common solvent, CH2Cl2 has numerous applications, which include use in metal cleaning/degreasing, in paint remover, and use by the pharmaceutical industry for preparing drugs. It is also used as blowing agent in production of foam plastics. A specific use of CH2Cl2, which seems likely to have increased in recent years, is in the manufacture of hydrofluorocarbons—the non-ozone-depleting chemicals used as replacements for CFCs and hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs). Given these sources, it is probable that demand for CH2Cl2 from developing countries now, and in coming years, will be relatively high. This is supported by elevated levels of CH2Cl2 detected over Asia, where Indian emissions are estimated to have increased by two- to fourfold between 1998 and 2008 (ref. 23).
(a) CH2Cl2 surface mixing ratio in p.p.t. from 2004 to 2015 derived from NOAA measurements as the annual mean observed at 4 sites in the SH, and 5 sites in the NH between 30° and 60° N (ref. 36). The time series is an update of ref. 21, years 2014 and 2015 are new data. Error bars denote ±1 s.d. and the solid lines denote a linear fit to these data with the shaded regions representing ±1 s.d. uncertainty on the fit. (b) Corresponding CH2Cl2 growth rates (% per year). (c) Observed surface CH2Cl2 mixing ratio in the NH (green circles, as in a) and trend (black line), along with projections of surface CH2Cl2 between 30 and 60° N latitude under future scenarios (dashed lines); CH2Cl2 increases at the mean rate observed over the 2004–2014 period (Scenario 1, blue), CH2Cl2 increases at the mean rate observed over the 2012–2014 period (Scenario 2, red) and CH2Cl2 remains at 2016 levels (Scenario 3, no future growth, orange). (d) Modelled chlorine (p.p.t.) from CH2Cl2 entering the stratosphere in the recent past and projections. This is derived by multiplying the simulated CH2Cl2 mixing ratio at the tropical tropopause by 2, to account for the 2 Cl atoms in the molecule. Data between 2005 and 2013 are an update of ref. 22, while subsequent years and future projections are from this study. Annual means in decadal intervals (2020–2050) are shown (filled circles) with ±1 s.d. (error bars) for Scenarios 1 (blue) and 2 (red). Solid lines denote a linear fit to these data, dashed portions extrapolate this fit prior to 2020. The orange line (dashed throughout) represents Scenario 3 (no future growth). Inset; Enlarged model curve for 2004–2014 with observed estimates from NASA aircraft measurements (stars).
Based on the NOAA surface measurements presented in Fig. 1a, we estimate a global emission source of around 1 Tg CH2Cl2 per year to sustain the observed CH2Cl2 concentrations in recent years (Fig. 2). We note that this is a far larger source than that of individual CFCs and other long-lived ozone-depleting gases (for example, carbon tetrachloride) in the 1980s, when emissions of those gases peaked. For CH2Cl2, and other VSLS more generally, relatively large emissions do not have the same impact on atmospheric concentrations, compared to say CFCs, as CH2Cl2 is more rapidly oxidized in the troposphere and has a much shorter atmospheric lifetime.
Emissions derived from a simple 1-box model for CCl4 (dotted line), CFC-11 (dashed line) and CH2Cl2 (crosses) in units of Gigagrams (Gg) of source gas per year. Calculation for CH2Cl2 based on a parameterized global mean lifetime of 0.43 years. Also shown are recent independent estimates of CH2Cl2 emissions (orange points) from the AGAGE 12-box model15. Error bars denote uncertainty range.
Two future scenarios encompassing potential surface CH2Cl2 increases from 2015 to 2100 have been derived and are considered in our forward model simulations. Both are based on observed long-term surface trends (Fig. 1c), and are designed to test the sensitivity of ozone to potential future changes in chlorine derived from CH2Cl2 growth. Scenario 1 assumes that surface CH2Cl2 continues to increase at the mean rate observed during the 2004–2014 period: 2.85 parts per trillion (p.p.t.) per year at mid-latitudes in the NH. Scenario 2, a more extreme growth scenario to test the sensitivity of ozone to larger CH2Cl2 increases, assumes CH2Cl2 continues to increase at the mean rate observed in the 2012–2014 period only: 6.1 p.p.t. per year. This period saw comparatively large CH2Cl2 growth compared to other recent years (Fig. 1b). In addition to the two growth scenarios, we also consider a third scenario in which no further CH2Cl2 growth occurs post 2016 (Methods section). In this scenario (Scenario 3), surface CH2Cl2 concentrations are fixed at 2016 levels throughout the forward simulation.
Constrained by the growth scenarios, our model simulations show a monotonic increase in chlorine from CH2Cl2 entering the stratosphere (Fig. 1d) in coming decades, from ∼70 p.p.t. Cl in 2014, to ∼180 p.p.t. Cl or ∼360 p.p.t. Cl by 2050, under Scenarios 1 or 2, respectively. Critically, the model reproduces well observed levels of CH2Cl2 around the tropopause in the recent past (Fig. 1d, inset) and, therefore, the stratospheric chlorine perturbation in response to increasing surface CH2Cl2 concentrations is realistic in our simulations.
Impact of CH2Cl2 growth on stratospheric inorganic chlorine
The dissociation of ozone-depleting compounds in the stratosphere liberates chlorine radicals which catalyse ozone loss. Owing to its relatively short stratospheric partial lifetime (of the order of 1–2 years in our model outside of the poles), CH2Cl2 dissociates rapidly and thereby makes its largest relative contribution to the pool of inorganic chlorine (Cly) in the lowermost stratosphere, at low latitudes (Fig. 3a–c). At present, CH2Cl2 accounts for <10% of stratospheric Cly, although this contribution would increase significantly in coming decades if CH2Cl2 growth continues and as chlorine from long-lived gases decreases. By 2050 under Scenario 1, CH2Cl2 is projected to account for 20–30% of total Cly in the lower stratosphere. An examination of the stratospheric Cly trend in recent decades in our model reveals a peak in Cly around the turn of the century at mid-latitudes (Fig. 3d,e). In the absence of CH2Cl2, here lower stratospheric Cly is projected to return to pre-1980 levels by 2049, in line with ongoing decreases in levels of CFCs and other controlled long-lived Cly precursors7. When CH2Cl2 growth is considered, this Cly return date is delayed by around 15–17 years under Scenario 1. Under Scenario 2—an extreme scenario—the Cly return date occurs after 2080.
(a–c) Percentage (%) of total stratospheric inorganic chlorine (Cly) derived from CH2Cl2 in 2015, 2030 and 2050 under model run Scenario 1 (assuming CH2Cl2 continues to increase at the mean rate observed over the 2004–2014 period). (d,e) Modelled annual mean mid-latitude Cly change in northern (35–60° N) and southern (35–60° S) hemisphere. The Cly change is expressed in parts per billion (p.p.b.) relative to 1980 baseline at 50 hPa (lower stratosphere). Cly changes are shown for model simulations without CH2Cl2 (black) and with CH2Cl2 under growth Scenarios 1 (blue, see above) and 2 (red, assuming CH2Cl2 increases at the mean rate observed over the 2012–2014 period), and for the no additional growth Scenario 3 (orange). The projected dates when Cly returns to 1980 levels in the NH are 2050 (no CH2Cl2), 2067 (Scenario 1) and 2054 (Scenario 3). In the SH: 2049 (no CH2Cl2), 2064 (Scenario 1) and 2053 (Scenario 3). The horizontal purple lines show best estimated range of 1980 return dates from previous CCMs6 which did not include CH2Cl2.
The delay in the Cly return date discussed above under Scenario 1 is significant and is additional to, and of a similar magnitude, to other factors which have previously been considered when assessing the uncertainty in return dates, for example, coupled chemistry-transport differences between climate models or different future greenhouse gas scenarios. The effect on the Cly return date is also much larger than the influence of potentially eliminating remaining small levels of production or emission of CFCs and HCFCs24. In the upper stratosphere, Cly return dates occur later than in the lower stratosphere and are less sensitive to future CH2Cl2 growth (Supplementary Fig. 1). Here, the contribution of CH2Cl2 to total Cly remains at <10% in 2050 (Fig. 3c).
Impact of past and potential future CH2Cl2 growth on ozone
We consider next the impact of CH2Cl2 on ozone. Ozone is most sensitive to CH2Cl2 in polar regions; by the time air reaches high latitudes all chlorine that entered the stratosphere as CH2Cl2 has been converted to Cly. The largest ozone decreases attributable to CH2Cl2 are simulated in the SH, where the Antarctic Ozone Hole—the most drastic manifestation of the effect of halogen-driven ozone loss—forms each spring. Although modest, the impact of CH2Cl2 is non-negligible in the present day with springtime column ozone up to ∼3%, or 6 dobson units (DU), lower in simulations in which CH2Cl2 is considered relative to an atmosphere without CH2Cl2 in 2016 (Supplementary Fig. 2). The equivalent relative ozone decrease in the spring of 2010 was ∼1.5% (3 DU), which allows quantification of CH2Cl2 increases on polar ozone depletion during spring, over this period, and highlights that this impact has already doubled in the past 6 years alone.
Figure 4 shows simulated ozone changes due to CH2Cl2 in the recent past and future period. Ozone loss due to further CH2Cl2 growth is projected to increase significantly in coming decades. By 2050, expressed as an annual mean, ozone is ∼6% lower in the Antarctic lower stratosphere under growth Scenario 1 (Fig. 4a), and annual mean column ozone is decreased by up to 8 DU, relative to the no CH2Cl2 simulation (Fig. 4c), against a background of recovering ozone. At mid-latitudes, column ozone decreases are smaller (up to several DU) and despite CH2Cl2 making a relatively large contribution to Cly in the tropics, ozone decreases here remain small (<1%). Recall, our simulations in the future period reflect the ozone response to changes in projected stratospheric composition only, comparing scenarios with CH2Cl2 growth to one with no CH2Cl2. Future ozone is also expected to be influenced by other factors, including climate-driven changes to stratospheric temperature and circulation7,12,25 and possibly due to changes in natural halocarbon emissions26. By isolating the ozone response due to CH2Cl2, we highlight its increasing influence on ozone evolution in coming decades. Such findings could also be relevant from a climate perspective21 as ozone absorbs both ultraviolet and infrared radiation, and as ozone perturbations in the lower stratosphere cause a relatively large radiative effect27.
(a) Difference in zonal mean annual mean ozone (%) between run Scenario 1, assuming surface CH2Cl2 continues to increase at the mean rate observed over the 2004–2014 period, and run no_CH2Cl2 in 2050. (b) As a for Scenario 2, assuming CH2Cl2 continues to increase at the mean rate observed over the 2012–2014 period. (c) Difference in zonal mean annual mean column ozone (DU) between run Scenario 1 and run no_CH2Cl2 as a function of year. (d) As c for Scenario 2.
Although the severity of ozone loss over Antarctica is most strongly affected by the abundance of reactive halogens, inter-annual variability in temperature and dynamical influences that determine strength of the polar vortex provide additional influence. For example, relatively large levels of springtime (September–November) ozone have been observed (that is, less loss) following stratospheric warming events, such as in 2002 (ref. 28), during which the occurrence of polar stratospheric clouds was relatively low29. The sensitivity of the SH column ozone decrease due to CH2Cl2 to a range of assumed stratospheric meteorology in the future period (see Methods) is shown in Fig. 5. In all cases, the impact of CH2Cl2 is substantial, with the greatest ozone decreases towards the end of the century predicted under the assumed 2012 (base meteorology) and 2006 (relatively cold Antarctic winter) conditions. However, note, these CTM simulations did not explicitly consider climate-driven cooling of the upper stratosphere or changes in stratospheric dynamics (see below).
(a–d) Spring-time mean column ozone decrease (DU) in SLIMCAT in 2020, 2040, 2060 and 2080 calculated as run no_CH2Cl2 minus run Scenario 1 (assuming surface CH2Cl2 continues to increase at the mean rate observed over the 2004–2014 period). Shown are results for simulations assuming either 2012 (base meteorology), or 2002 (relatively warm) or 2006 (relatively cold) meteorological conditions in the future. (e–h) Corresponding monthly mean column ozone decreases south of −60° latitude.
Discussion
The Montreal Protocol has been extremely successful in alleviating polar ozone loss. For example, it has been estimated the Antarctic Ozone Hole would have been 40% larger by 2013 had the Protocol not come into effect30. Based on current understanding, the Ozone Hole is expected to recover in this century. The 17 chemistry-climate models (CCMs) that took part in the Stratospheric Processes and their Role in Climate (SPARC) CCMVal project predict that the Antarctic Ozone Hole—defined by the October average column ozone abundance—will return to pre-1980 levels between 2046 and 2057 (ref. 7), in line with the anticipated decline in controlled ozone-depleting substances. More recent model simulations have suggested a later ozone return date that approaches the end of the century31,32, though none of these previous estimates have considered CH2Cl2, or indeed CH2Cl2 growth.
Figure 6 shows our model estimate of Antarctic Cly and column ozone evolution with and without CH2Cl2. Antarctic column ozone returns to pre-1980 levels in 2065 when CH2Cl2 is not considered. The inclusion of CH2Cl2 delays the ozone return by 30 years under growth Scenario 1 (note, under Scenario 2 ozone does not return to pre-1980 levels this century). This is the difference that would be expected between an atmosphere without any CH2Cl2, for example, if its production was completely phased out, to an atmosphere in which sustained future growth of CH2Cl2 continues. Recall, Scenario 1 simply assumes CH2Cl2 continues to increase in the atmosphere following the average upward trend observed over the last decade. We estimate that even if the stratospheric input of CH2Cl2 remains at 2016 levels (that is, Scenario 3, a no future growth scenario), the return of ozone in the Antarctic Ozone Hole region is still delayed by ∼5 years, relative to the no CH2Cl2 simulation.
(a) Modelled October mean change in inorganic chlorine (Cly) in the lower stratosphere (50 hPa) over Antarctica (60–90° S). Cly is expressed in parts per billion (p.p.b.) relative to a 1980 baseline. (b) Corresponding modelled October mean change in Antarctic stratospheric column ozone (DU) relative to 1980. Cly and ozone changes shown for SLIMCAT model simulations without CH2Cl2 (black) and for CH2Cl2 Scenario 1 (blue, surface CH2Cl2 continues to increase at the mean rate observed over the 2004–2014 period), Scenario 2 (red, surface CH2Cl2 continues to increase at the mean rate observed over the 2012–2014 period) and Scenario 3 (orange, no future growth). Note, 1980 baseline is calculated from a model simulation performed with 2012 meteorology, in a similar manner to the forward simulations, to isolate the impact of CH2Cl2 growth from inter-annual variability due to meteorology. For Cly, the calculated return dates with respect to this baseline are 2056 (no CH2Cl2), 2069 (Scenario 1) and 2060 (Scenario 3). Similarly for ozone, 2065 (no CH2Cl2), 2095 (Scenario 1) and 2071 (Scenario 3).
The above return dates are calculated from a 1980 ozone baseline in an atmosphere that is assumed to contain no CH2Cl2. Emissions of CH2Cl2 in 1980 are highly uncertain, owing to a paucity of atmospheric measurements at that time. However, a global emission source of ∼800 Gg CH2Cl2 per year in the early 1980s has been derived from bottom–up methods33. Using this estimate and adjusting the ozone baseline to account for the presence of CH2Cl2 would change the 1980 return dates to 2063 (no CH2Cl2 simulation) and 2090 (growth Scenario 1). Clearly, additional increases in atmospheric CH2Cl2 could lead to an underestimate of the timescale for stratospheric ozone recovery in coming decades. Furthermore, as CH2Cl2 already has a non-negligible impact on polar ozone, which has increased in the recent past (Supplementary Fig. 2), in the nearer term CH2Cl2 growth could confound the search for ozone recovery attributable to the phase-out of controlled ozone-depleting compounds. We note that as the Antarctic column ozone changes scale to a good approximation linearly with the Cly load under each CH2Cl2 scenario (Supplementary Fig. 3), our results can be used to estimate the impact of different future trajectories of CH2Cl2, or indeed other chlorinated VSLS, on ozone.
While the future trajectory of CH2Cl2 is uncertain, in the absence of policy controls on its production, it is likely that future trends in this gas will fall within the range of the three scenarios presented here. From Fig. 5, the absolute impact of CH2Cl2 on SH polar ozone will exhibit some year-to-year variability, depending on stratospheric meteorology (Fig. 5), though the 1980 Antarctic ozone return date delay due to CH2Cl2 exhibited a weak sensitivity to the choice of future meteorology in our SLIMCAT simulations. However, we note these runs did not consider inter-annual dynamical variability in the future or the effects of climate change, such as an acceleration of the Brewer-Dobson circulation or prolonged stratospheric cooling, as predicted by most CCMs. Although ozone trends in the Antarctic lower stratosphere are most strongly affected by trends in ozone-depleting gases (that is, the time evolution of the stratospheric halogen content) and relative to the Arctic, are less sensitive to anticipated greenhouse gas changes in the future7, climate change is expected to accelerate ozone recovery in this region12. Furthermore, given the current spread of return dates predicted by CCMs, the delay in the ozone return due to CH2Cl2 is likely to vary between models, even when considering the same CH2Cl2 growth scenarios. For a given 1980 ozone baseline, models with an inherent slower rate of ozone return will see a greater impact of CH2Cl2 on the ozone return date. This is due to the divergence of stratospheric Cly concentrations in time between an atmosphere without CH2Cl2 in the future, and one in which sustained CH2Cl2 growth occurs.
To explore the above, we performed simulations with the UMSLIMCAT CCM, forced by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) RCP (Representative Concentration Pathway) 6.0 scenario, and with evolving meteorology in the future. UMSLIMCAT was evaluated in the SPARC CCMVal project12 and is participating in the ongoing Chemistry-Climate Model Initiative34 (CCMI – Methods section). Our CCM results show marked differences between a run with CH2Cl2 growth (Scenario 1) and a reference run without CH2Cl2 (Fig. 7a). The largest ozone decreases occur over Antarctica, where (i) the difference in October mean ozone between the with and without CH2Cl2 runs is statistically significant at the 95% confidence interval, and (ii) the influence of CH2Cl2 on ozone increases in coming decades—corroborating our main CTM findings. In both models, inclusion of CH2Cl2 growth delays the return of Antarctic lower stratospheric Cly to 1980 levels by 13 years. In UMSLIMCAT, column ozone return is delayed by 17 years (Fig. 7b). This is a substantial delay, albeit it is smaller than that predicted by the CTM, which assumed fixed dynamics in the future, and which predicts more severe springtime polar ozone loss (that is, for a given amount of chlorine from CH2Cl2, the ozone impact is smaller in the CCM). Ozone increases as a result of upper stratospheric cooling, a consequence of climate change7, may provide additional influence on the magnitude of the ozone delay from CH2Cl2 in CCM experiments. However, our CCM shows that ozone closely tracks the trajectory of Cly, highlighting the dominant influence of the halogen loading on Antarctic ozone trends7,12. As previously noted, the delay from CH2Cl2 growth will vary across models and crucially these results highlight that CH2Cl2 growth should be considered within the framework of multi-model ozone assessments in the future. As the Antarctic Ozone Hole is known to affect surface climate of the SH in several ways, such as by modifying the Southern Annular Mode35, a delayed recovery caused by CH2Cl2 may also be relevant for refining future climate predictions.
(a) Springtime mean column ozone decrease (DU) due to CH2Cl2 in the SH. (b) October mean Antarctic stratospheric ozone column (DU) relative to 1980. Results are shown for UMSLIMCAT run with CH2Cl2 growth Scenario 1 (blue, surface CH2Cl2 continues to increase at the mean rate observed over the 2004–2014 period) and without CH2Cl2 (black). While inter-annual variability is large, the two ozone time series are statistically different at the 95% significance level according to a Student’s t-test (P value=0.02). Ozone returns to the 1980 baseline in the year 2064 (without CH2Cl2) and in 2081 (Scenario 1).
In summary, although currently modest, the impact of CH2Cl2 on stratospheric ozone is increasing and if CH2Cl2 concentrations continue to increase they could significantly offset a portion of the decline in anthropogenic chlorine provided by the Montreal Protocol. This adds uncertainty into future assessments of ozone evolution and could lead to a significant delay in recovery of the ozone layer, particularly over Antarctica. Finally, we note that while this study has focused on CH2Cl2, for which long-term surface monitoring data exists, several other anthropogenic VSLS (for example, 1,2-Dichloroethane, C2H4Cl2) have been detected in Earth’s atmosphere22, though atmospheric measurements of these compounds are sparse. A broader consideration of the atmospheric trends of these non-Montreal Protocol compounds and other VSLS would be beneficial to improve future ozone predictions.
Methods
Surface CH2Cl2 measurements
Surface measurements of CH2Cl2 from NOAA’s long-term monitoring network36 were analysed. Results from paired flask samples collected at 13 sites were used to derive surface CH2Cl2 mixing ratios over the 2004–2014 period. The observed data were averaged in 5 latitude bins (60–90° N, 30–60° N, 0–30° N, 0–30° S and 30–90° S) and trends over the above period were derived in each bin (selected bin results are shown in Fig. 1a). These data form the basis of our current emission estimates and future CH2Cl2 growth scenarios.
Aircraft CH2Cl2 measurements
Aircraft measurements of CH2Cl2 around the tropopause (Fig. 1d, inset) were obtained onboard the Global Hawk unmanned aircraft deployed during the 2011 and 2013 legs of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Airborne Tropical Tropopause Experiment (ATTREX) mission18. CH2Cl2 mixing ratios were derived by the University of Miami from whole air samples analysed using gas chromatography/mass spectrometry.
Future CH2Cl2 growth scenarios
Two scenarios describing the future evolution of surface CH2Cl2 were derived by extrapolating observed surface CH2Cl2 trends in 5 latitude bins (see above). The forward scenarios cover the period 2015–2100. Scenario 1 assumes that surface CH2Cl2 increases linearly over this period, with a growth rate equal to the mean growth rate observed over the 2004–2014 period. In NH mid-latitudes, surface CH2Cl2 increases at a rate of 2.85 p.p.t. per year under Scenario 1 (Fig. 1c). Scenario 2 is a larger growth scenario and assumes that CH2Cl2 increases linearly with a rate equal to that observed over the 2012–2014 period only. In these years, CH2Cl2 growth was large compared to the decadal average used for Scenario 1, resulting in a surface trend of 6.1 p.p.t. per year in NH mid-latitudes. A third scenario, Scenario 3, was also considered in which it is assumed that no further growth of CH2Cl2 occurs beyond 2016 (that is, the surface concentration of CH2Cl2 is fixed throughout the forward simulation at 2016 levels, Fig. 1).
Global emission estimates of CH2Cl2
A simple 1-box model, previously used to study CH4 and CH3CCl3 emissions, was used to derive global CH2Cl2 emissions required to sustain the observed surface concentrations. The model treated emissions of CH2Cl2 with a parameterized global mean lifetime of 0.43 years, based on this work. In the present day, global CH2Cl2 emissions estimates (Fig. 2) agree well with similar independent estimates15. The box model was also used to estimate that an emission source of ∼2.8 Tg CH2Cl2 per year is required to sustain the modelled 2050 atmospheric CH2Cl2 concentration under Scenario 1.
Chemical transport model and experiment design
The TOMCAT/SLIMCAT global three-dimensional CTM37 was used to calculate the sensitivity of stratospheric chlorine and ozone to future growth in atmospheric CH2Cl2. The model has been widely evaluated and used in previous studies of tropospheric and stratospheric chemistry. The model is forced with meteorological fields from the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) ERA-Interim reanalysis data set. We first derived the time-dependent stratospheric injection of CH2Cl2 over the 2004–2100 period using a detailed tropospheric configuration of TOMCAT. The model contains a comprehensive description of tropospheric chemistry, including VSLS oxidation, and reproduces the tropospheric abundance of chlorine-containing VSLS well in the present day22. A transient simulation between 2004 and 2014 was performed in which surface CH2Cl2 was constrained in the model using the time-dependent surface measurements from NOAA, in the 5 latitude bins discussed above. Between 2015 and 2100, the model was integrated twice using the projected surface CH2Cl2 loadings from Scenario 1 and Scenario 2. We assumed present day meteorology and emissions of precursor gases that control tropospheric chemistry in the future period. The stratospheric chlorine injection from CH2Cl2 over these periods is given in Fig. 1d.
We next performed three simulations using a detailed stratospheric model configuration of TOMCAT/SLIMCAT, containing a comprehensive stratospheric chemistry scheme that includes a full description of processes relevant to polar ozone depletion. This version of the model reproduces observed stratospheric ozone trends well21,30. Experiments were performed over the 1980–2100 period at a horizontal resolution of 2.8° × 2.8° and with 32 vertical levels from the surface to ∼60 km. The stratospheric CH2Cl2 loading was prescribed in experiments Scenario 1 and Scenario 2 using the time-dependent loadings derived above. Annual averages of these data are given in Supplementary Tables 1 and 2. CH2Cl2 was only considered from 2004 onwards and the two growth scenarios diverge from 2015. A reference simulation in which CH2Cl2 was not considered (experiment No_CH2Cl2) was also performed. Time-dependent surface mixing ratios of all other long-lived ozone-depleting compounds (for example, CFCs, HCFCs, halons and others), CH4 and N2O, were taken from the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) A1 Scenario7,15. Our approach is to examine the sensitivity of future Cly and ozone to increasing CH2Cl2. Therefore, in the future period annually repeating meteorology was assumed for the arbitrarily chosen year 2012 (referred to here as ‘base meteorology’). We also examined the sensitivity of ozone changes due to CH2Cl2 growth to different and more remarkable assumed years of meteorology in the future period: 2002 (a year of relatively warm polar stratospheric temperatures) and 2006 (a year of very cold temperatures).
Chemistry-climate model experiments
UMSLIMCAT is a global CCM that has been evaluated extensively within the recent CCMVal and CCMI multi-model inter-comparison initiatives12,34. It is based on the troposphere–stratosphere–mesosphere version of the Met Office Unified Model (UM v4.5). The model has 64 vertical levels extending from the surface to 0.01 hPa (∼80 km), and was here run at a horizontal resolution of 3.75° × 2.5° (ref. 38). The stratospheric chemistry scheme is similar to that of the SLIMCAT CTM (see above). We performed a transient control simulation without CH2Cl2 over the 1970 to 2100 period. The loading of long-lived ozone-depleting compounds and greenhouse gases was prescribed according to the IPCC RCP 6.0 scenario. A similar run but including time-varying CH2Cl2 according to growth Scenario 1 was also performed.
Estimates of stratospheric chlorine and ozone return dates
Estimates of stratospheric Cly and ozone return dates relative to a 1980 baseline are presented. For the CTM experiments, this baseline was calculated from a 1980 model simulation run with 2012 meteorology (consistent with our forward simulations), to isolate the effect of changing composition on the return dates. Estimated Cly return date ranges are also shown (purple lines in Fig. 3) from previous CCM simulations7,12 that did not consider CH2Cl2. The model time series shown in Fig. 3 and all subsequent figures were smoothed by applying a 1:2:1 filter iteratively 30 times, consistent with previous studies12.
Code availability
The TOMCAT/SLIMCAT model is supported by the Natural Environment Research Council (NERC) and the National Centre for Atmospheric Science (NCAS) and is available to UK academic institutions working with these organizations. Enquiries about the model code should be directed to M.P.C. Post processing of model output was performed using Interactive Data Language (IDL) and the code is available on request from the corresponding author (R.H.). Output from all model simulations is available on request from the corresponding author (R.H.).
Data availability
The NOAA surface CH2Cl2 data are available to download at the following web address: http://www.esrl.noaa.gov/gmd/dv/ftpdata.html. Use of the data in a presentation, publication or report requires that users contact the principal investigator (S.A.M.) first to discuss your interests. The NASA CH2Cl2 data from the ATTREX missions are publically available at the following web address: https://espoarchive.nasa.gov/.
Additional information
How to cite this article: Hossaini, R. et al. The increasing threat to stratospheric ozone from dichloromethane. Nat. Commun. 8, 15962 doi: 10.1038/ncomms15962 (2017).
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
Molina, M. J. & Roland, F. S. Stratospheric sink for chlorofluoromethanes: chlorine atom-catalysed destruction of ozone. Nature 249, 810–812 (1974).
Wofsy, S. C., McElroy, M. B. & Yung, Y. L. The chemistry of atmospheric bromine. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2, 215–218 (1975).
Farman, J. C., Gardiner, B. G. & Shanklin, J. D. Large losses of total ozone in Antarctica reveal seasonal ClOx/NOx interaction. Nature 315, 207–210 (1985).
McElroy, M. B., Salawitch, R. J., Wofsy, S. C. & Logan, J. A. Reductions of Antarctic ozone due to synergistic interactions of chlorine and bromine. Nature 321, 759–762 (1986).
Solomon, S. Stratospheric ozone depletion: a review of concepts and history. Rev. Geophys. 37, 275–316 (1999).
Yang, E.-S. et al. First stage of Antarctic ozone recovery. J. Geophys. Res. 113, D20308 (2008).
Bekki, S. et al. in Scientific Assessment of Ozone Depletion 2010, Global Ozone Research and Monitoring Project - Report No. 52 Chapter 3, 2.78–3.60 (World Meteorological Organization, Geneva, Switzerland, 2011).
Kuttippurath, J. et al. Antarctic ozone loss in 1979–2010: first sign of ozone recovery. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 13, 1625–1635 (2013).
Solomon, S. et al. Emergence of healing in the Antarctic ozone layer. Science 353, 269–274 (2016).
Cunnold, D. M. et al. GAGE/AGAGE measurements indicating reductions in global emissions of CCl3F and CCl2F2 in 1992–1994. J. Geophys. Res. 102, 1259–1269 (1997).
Montzka, S. A., Butler, J. H., Hall, B. D., Mondeel, D. J. & Elkins, J. W. A decline in tropospheric organic bromine. Geophys. Res. Lett. 30, 1826 (2003).
Eyring, V. et al. Multi-model assessment of stratospheric ozone return dates and ozone recovery in CCMVal-2 models. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 10, 9451–9472 (2010).
Simmonds, P. G. et al. Global trends, seasonal cycles, and European emissions of dichloromethane, trichloroethene, and tetrachloroethene from the AGAGE observations at Mace Head, Ireland, and Cape Grim, Tasmania. J. Geophys. Res. 111, D18304 (2006).
Campbell, N. et al. in Safeguarding the Ozone Layer and the Global Climate System: Issues Related to Hydrofluorocarbons and Perfluorocarbons (eds Metz B.et al. Chapter 11, 403–436Cambridge Univ. Press (2005).
Carpenter, L. J. et al. in Scientific Assessment of Ozone Depletion 2014, Global Ozone Research and Monitoring Project - Report No. 55 Chapter 1, 1.1–1.101 (World Meteorological Organization, Geneva, Switzerland, 2014).
Laube, J. C. et al. Contribution of very short-lived organic substances to stratospheric chlorine and bromine in the tropics—a case study. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 8, 7325–7334 (2008).
Sala, S. et al. Deriving an atmospheric budget of total organic bromine using airborne in situ measurements from the western Pacific area during SHIVA. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 14, 6903–6923 (2014).
Navarro, M. A. et al. Airborne measurements of organic bromine compounds in the Pacific tropical tropopause layer. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 112, 13789–13793 (2015).
Salawitch, R. J. et al. Sensitivity of ozone to bromine in the lower stratosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 32, L05811 (2005).
Sinnhuber, B.-M. & Meul, S. Simulating the impact of emissions of brominated very short-lived substances on past stratospheric ozone trends. Geophys. Res. Lett. 42, 2449–2456 (2015).
Hossaini, R. et al. Efficiency of short-lived halogen at influencing climate through depletion of stratospheric ozone. Nat. Geosci. 8, 186–190 (2015).
Hossaini, R. et al. Growth in stratospheric chlorine from short-lived chemicals not controlled by the Montreal Protocol. Geophys. Res. Lett. 42, 4573–4580 (2015).
Leedham Elvidge, E. C. et al. Increasing concentrations of dichloromethane, CH2Cl2, inferred from CARIBIC air samples collected 1998–2012. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 15, 1939–1958 (2015).
Harris, N. R. P. et al. in Scientific Assessment of Ozone Depletion 2014, Global Ozone Research and Monitoring Project - Report No. 55 Chapter 5, 5.1–5.58 (World Meteorological Organization, Geneva, Switzerland, 2014).
Revell, L. E., Bodeker, G. E., Huck, P. E., Williamson, B. E. & Rozanov, E. The sensitivity of stratospheric ozone changes through the 21st century to N2O and CH4 . Atmos. Chem. Phys. 12, 11309–11317 (2012).
Yang, X. et al. How sensitive is the recovery of stratospheric ozone to changes in concentrations of very short-lived bromocarbons? Atmos. Chem. Phys. 14, 10431–10438 (2014).
Riese, M. et al. Impact of uncertainties in atmospheric mixing of simulated UTLS composition and related radiative effects. J. Geophys. Res. 117, D16305 (2012).
Sinnhuber, B.-M., Weber, M., Amankwah, A. & Burrows, J. P. Total ozone during the unusual Antarctic winter of 2002. Geophys. Res. Lett. 30, 1580 (2003).
Sonkaew, T. et al. Chemical ozone losses in Arctic and Antarctic polar winter/spring season derived from SCIAMACHY limb measurements 2002–2009. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 13, 1809–1835 (2013).
Chipperfield, M. P. et al. Quantifying the ozone and ultraviolet benefits already achieved by the Montreal Protocol. Nat. Commun. 6, 7233 (2015).
Dameris, M. et al. in Scientific Assessment of Ozone Depletion 2014, Global Ozone Research and Monitoring Project - Report No. 55 Chapter 3, 3.1–3.63 (World Meteorological Organization, Geneva, Switzerland, 2014).
Oman, L. D. et al. The effect of representing bromine from VSLS on the simulation and evolution of Antarctic ozone. Geophys. Res. Lett. 43, 9869–9876 (2016).
Trudinger, C. M. et al. Atmospheric histories of halocarbons from analysis of Antarctic firn air: Methyl bromide, methyl chloride, chloroform, and dichloromethane. J. Geophys. Res. 109, D22310 (2004).
Morgenstern, O. et al. Review of the global models used within phase 1 of the Chemistry–Climate Model Initiative (CCMI). Geosci. Model Dev. 10, 639–671 (2017).
Arblaster, J. M. et al. in Scientific Assessment of Ozone Depletion 2014, Global Ozone Research and Monitoring Project - Report No. 55 Chapter 4, 4.1–4.57 (World Meteorological Organization, Geneva, Switzerland, 2014).
Montzka, S. A. et al. Small interannual variability of global atmospheric hydroxyl. Science 331, 67–69 (2011).
Chipperfield, M. P. New version of the TOMCAT/SLIMCAT off-line chemical transport model: intercomparison of stratospheric tracer experiments. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 132, 1179–1203 (2006).
Tian, W. & Chipperfield, M. P. A new coupled chemistry-climate model for the stratosphere: the importance of coupling for future O3-climate predictions. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 131, 281–303 (2005).
Acknowledgements
R.H. thanks the Natural Environment Research Council (NERC) for funding a research fellowship (NE/N014375/1). We thank the European Research Council (ERC) for support under the ACCI project (Project number 267760). M.P.C. thanks the Royal Society for a Wolfson Research Merit Award. We thank Wuhu Feng (NCAS) for help with SLIMCAT. This work was performed using the Archer and ARC2 high performance computing facilities. NOAA measurements were supported in part by the NOAA Climate Program Office’s AC4 programme. We thank the two anonymous reviewers and Dr Robyn Schofield whose constructive comments strengthened the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
R.H., M.P.C. and S.S.D. conceived the idea and initiated the study in collaboration with J.A.P. and S.A.M.; R.H., M.P.C. and A.A.L. performed and analysed the SLIMCAT model runs. S.S.D. performed the UMSLIMCAT runs. The CH2Cl2 data and growth scenarios are based on ground-based measurements obtained by S.A.M.; R.H. and A.A.L. prepared the figures. All authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Hossaini, R., Chipperfield, M., Montzka, S. et al. The increasing threat to stratospheric ozone from dichloromethane. Nat Commun 8, 15962 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms15962
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms15962
This article is cited by
-
Extreme environmental adaptation mechanisms of Antarctic bryophytes are mainly the activation of antioxidants, secondary metabolites and photosynthetic pathways
BMC Plant Biology (2023)
-
Natural halogen-containing compounds cool the climate
Nature (2023)
-
Very short-lived halogens amplify ozone depletion trends in the tropical lower stratosphere
Nature Climate Change (2023)
-
Natural short-lived halogens exert an indirect cooling effect on climate
Nature (2023)
-
Proteogenomics of the novel Dehalobacterium formicoaceticum strain EZ94 highlights a key role of methyltransferases during anaerobic dichloromethane degradation
Environmental Science and Pollution Research (2023)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.