Abstract
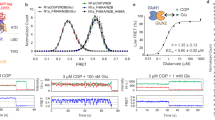
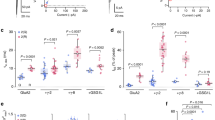
AMPA receptors mediate fast excitatory neurotransmission by converting chemical signals into electrical signals, and thus it is important to understand the relationship between their chemical biology and their function. We used single-molecule fluorescence resonance energy transfer to examine the conformations explored by the agonist-binding domain of the AMPA receptor for wild-type and T686S mutant proteins. Each form of the agonist binding domain showed a dynamic, multistate sequential equilibrium, which could be identified only using wavelet shrinkage, a signal processing technique that removes experimental shot noise. These results illustrate that the extent of activation depends not on a rigid closed cleft but instead on the probability that a given subunit will occupy a closed-cleft conformation, which in turn is determined not only by the lowest energy state but also by the range of states that the protein explores.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Keinänen, K. et al. A family of AMPA-selective glutamate receptors. Science 249, 556–560 (1990).
Nakanishi, S. & Masu, M. Molecular diversity and functions of glutamate receptors. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 23, 319–348 (1994).10.1146/annurev.bb.23.060194.001535
Dingledine, R., Borges, K., Bowie, D. & Traynelis, S.F. The glutamate receptor ion channels. Pharmacol. Rev. 51, 7–61 (1999).
Fleming, J.J. & England, P.M. AMPA receptors and synaptic plasticity: a chemist's perspective. Nat. Chem. Biol. 6, 89–97 (2010).
Rosenmund, C., Stern-Bach, Y. & Stevens, C.F. The tetrameric structure of a glutamate receptor channel. Science 280, 1596–1599 (1998).
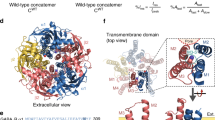
Sobolevsky, A.I., Rosconi, M.P. & Gouaux, E. X-ray structure, symmetry and mechanism of an AMPA-subtype glutamate receptor. Nature 462, 745–756 (2009).
Armstrong, N. & Gouaux, E. Mechanisms for activation and antagonism of an AMPA-sensitive glutamate receptor: crystal structures of the GluA2 agonist binding core. Neuron 28, 165–181 (2000).
Armstrong, N., Mayer, M. & Gouaux, E. Tuning activation of the AMPA-sensitive GluA2 ion channel by genetic adjustment of agonist-induced conformational changes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 5736–5741 (2003).
Gouaux, E. Structure and function of AMPA receptors. J. Physiol. 554, 249–253 (2004).
Armstrong, N., Sun, Y., Chen, G.-Q. & Gouaux, E. Structure of a glutamate-receptor agonist-binding core in complex with kainate. Nature 395, 913–917 (1998).
Birdsey-Benson, A., Gill, A., Henderson, L.P. & Madden, D.R. Enhanced efficacy without further cleft closure: reevaluating twist as a source of agonist efficacy in AMPA receptors. J. Neurosci. 30, 1463–1470 (2010).
Ahmed, A.H., Wang, Q., Sondermann, H. & Oswald, R.E. Structure of the S1S2 glutamate binding domain of GluR3. Proteins 75, 628–637 (2009).
Maltsev, A.S., Ahmed, A.H., Fenwick, M.K., Jane, D.E. & Oswald, R.E. Mechanism of partial agonism at the GluA2 AMPA receptor: measurements of lobe orientation in solution. Biochemistry 47, 10600–10610 (2008).
Ramanoudjame, G., Du, M., Mankiewicz, K.A. & Jayaraman, V. Allosteric mechanism in AMPA receptors: a FRET-based investigation of conformational changes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 10473–10478 (2006).
Robert, A., Armstrong, N., Gouaux, J.E. & Howe, J.R. AMPA receptor binding cleft mutations that alter affinity, efficacy, and recovery from desensitization. J. Neurosci. 25, 3752–3762 (2005).
Lau, A.Y. & Roux, B. The free energy landscapes governing conformational changes in a glutamate receptor agonist-binding domain. Structure 15, 1203–1214 (2007).
Li, C.-B., Yang, H. & Komatsuzaki, T. Multiscale complex network of protein conformational fluctuations in single-molecule time series. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 536–541 (2008).
Schuler, B., Lipman, E.A. & Eaton, W.A. Probing the free-energy surface for protein folding with single-molecule fluorescence spectroscopy. Nature 419, 743–747 (2002).
Schuler, B. & Eaton, W.A. Protein folding studied by single-molecule FRET. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 18, 16–26 (2008).
Flynn, E.M., Hanson, J.A., Alber, T. & Yang, H. Dynamic active-site protection by the M. tuberculosis protein tyrosine phosphatase PtpB lid domain. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132, 4772–4780 (2010).
Chung, H.S., Louis John, M. & Eaton William, A. Distinguishing between protein dynamics and dye photophysics in single-molecule FRET experiments. Biophys. J. 98, 696–706 (2010).
McKinney, S.A., Joo, C. & Ha, T. Analysis of single-molecule FRET trajectories using hidden Markov modeling. Biophys. J. 91, 1941–1951 (2006).
Talaga, D.S. Markov processes in single molecule fluorescence. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 12, 285–296 (2007).
Li, C.-B., Yang, H. & Komatsuzaki, T. New quantification of local transition heterogeneity of multiscale complex networks constructed from single-molecule time series. J. Phys. Chem. B 113, 14732–14741 (2009).
Taylor, J.N., Makarov, D.E. & Landes, C.F. Denoising single-molecule FRET trajectories with wavelets and Bayesian inference. Biophys. J. 98, 164–173 (2010).
Taylor, J.N. & Landes, C.F. Improved resolution of complex single-molecule FRET systems via wavelet shrinkage. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, published online, doi:10.1021/jp1050707 (10 January 2011).
Darugar, Q., Kim, H., Gorelick, R.J. & Landes, C.F. Human T-Cell lympotropic virus type 1 nucleocapsid protein-induced structural changes in transactivation response DNA measured by single molecule fluorescence resonance energy transfer. J. Virol. 82, 12164–12171 (2008).
Taylor, J.N., Darugar, Q., Kourentzi, K., Willson, R.C. & Landes, C.F. Dynamics of an anti-VEGF aptamer: A single molecule study. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 373, 213–218 (2008).
Mamonova, T., Yonkunas, M.J. & Kurnikova, M.G. Energetics of the cleft closing transition and the role of electrostatic interactions in conformational rearrangements of the glutamate receptor agonist binding domain. Biochemistry 47, 11077–11085 (2008).
Benítez, J.J. et al. Probing transient copper chaperone-wilson disease protein interactions at the single-molecule level with nanovesicle trapping. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 2446–2447 10.1021/ja7107867 (2008).
Cheng, Q., Du, M., Ramanoudjame, G. & Jayaraman, V. Evolution of glutamate interactions during binding to a glutamate receptor. Nat. Chem. Biol. 1, 329–332 (2005).
Ahmed, A.H., Loh, A.P., Jane, D.E. & Oswald, R.E. Dynamics of the S1S2 glutamate binding domain of GluA2 measured using 19F NMR spectroscopy. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 12773–12784 (2007).
Fenwick, M.K. & Oswald, R.E. On the mechanisms of α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid (AMPA) receptor binding to glutamate and kainate. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 12334–12343 (2010).
McFeeters, R.L. & Oswald, R.E. Structural mobility of the extracellular agonist-binding core of an ionotropic glutamate receptor. Analysis of NMR relaxation dynamics. Biochemistry 41, 10472–10481 (2002).
Robert, A. & Howe, J.R. How AMPA receptor desensitization depends on receptor occupancy. J. Neurosci. 23, 847–858 (2003).
Zhang, W., Cho, Y., Lolis, E. & Howe, J.R. Structural and single-channel results indicate that the rates of agonist binding domain closing and opening directly impact AMPA receptor gating. J. Neurosci. 28, 932–943 (2008).
Makarov, D.E. & Metiu, H. A model for the kinetics of protein folding: kinetic Monte Carlo simulations and analytical results. J. Chem. Phys. 116, 5205–5216 (2002).
Fichthorn, K.A. & Weinberg, W.H. Theoretical foundations of dynamical Monte Carlo simulations. J. Chem. Phys. 95, 1090–1096 (1991).
Metiu, H., Lu, Y.-T. & Zhang, Z. Epitaxial growth and the art of computer simulations. Science 255, 1088–1092 (1992).
Voter, A.F. Classically exact overlayer dynamics: diffusion of rhodium clusters on Rh(100). Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter 34, 6819–6929 (1986).
Madden, D.R., Armstrong, N., Svergun, D., Perez, J. & Vachette, P. Solution X-ray scattering evidence for agonist- and antagonist-induced modulation of cleft closure in a glutamate receptor agonist-binding domain. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 23637–23642 (2005).
Ha, T. et al. Single-molecule fluorescence spectroscopy of enzyme conformational dynamics and cleavage mechanism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 893–898 (1999).
Landes, C.F., Zeng, Y., Liu, H.W., Musier-Forsyth, K. & Barbara, P.F. Single-molecule study of the inhibition of HIV-1 transactivation response region DNA/DNA annealing by argininamide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 10181–10188 (2007).
Cosa, G. et al. Secondary structure and secondary structure dynamics of DNA hairpins complexed with HIV-1 NC protein. Biophys. J. 87, 2759–2767 (2004).
Hanson, J.A. et al. Illuminating the mechanistic roles of enzyme conformational dynamics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 18055–18060 (2007).
Zeng, Y. et al. Probing nucleation, reverse annealing, and chaperone function along the reaction path of HIV-1 single-strand transfer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 12651–12656 10.1073/pnas.0700350104 (2007).
Cordes, T., Vogelsang, J. & Tinnefeld, P. On the mechanism of Trolox as antiblinking and antibleaching reagent. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 5018–5019 (2009).
Rasnik, I., McKinney, S.A. & Ha, T. Nonblinking and long-lasting single-molecule fluorescence imaging. Nat. Methods 3, 891–893 (2006).
Acknowledgements
C.F.L. thanks the Norman Hackerman Welch Young Investigator Program at Rice University. We acknowledge the Donors of the American Chemical Society Petroleum Research Fund for partial support of this research (to C.F.L.). This work was supported by US National Institutes of Health Grant R01GM073102 (to V.J.) and American Heart Association Grant 0855081F (V.J.).We also thank H. Yang and R. Goldsmith for suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C.F.L. and V.J. directed the research and wrote the manuscript. A.R. prepared and purified the protein samples and performed single-molecule experiments. J.N.T. analyzed the single-molecule data and prepared figures. F.S. performed single-molecule experiments and analyzed data.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Methods, Supplementary Figures 1–13 and Supplementary Tables 1–4 (PDF 1307 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Landes, C., Rambhadran, A., Taylor, J. et al. Structural landscape of isolated agonist-binding domains from single AMPA receptors. Nat Chem Biol 7, 168–173 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.523
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.523
This article is cited by
-
Allosteric coupling of sub-millisecond clamshell motions in ionotropic glutamate receptor ligand-binding domains
Communications Biology (2021)
-
The structural arrangement at intersubunit interfaces in homomeric kainate receptors
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
The structure–energy landscape of NMDA receptor gating
Nature Chemical Biology (2017)
-
Mechanism of partial agonism in AMPA-type glutamate receptors
Nature Communications (2017)
-
Role of the Ion Channel Extracellular Collar in AMPA Receptor Gating
Scientific Reports (2017)