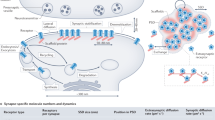
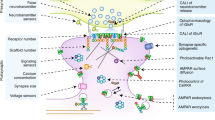
Abstract
The ability of the mammalian brain to undergo experience-based adaptations is among its most important and fascinating properties. Such plasticity is reflected in the capacity of neuronal activity to continuously modify the neural circuitry that underlies thought, feeling and behavior. The locus of this plasticity occurs at the level of synapses, the specialized junctions where one neuron receives chemical signals from another. Synaptic connections become stronger or weaker in response to specific patterns of activity. This activity drives regulated changes in the neurotransmitter released by presynaptic neurons and in the receptors localized on postsynaptic neurons. Detailed studies of these receptors have advanced our understanding of synaptic plasticity. However, many key questions remain unresolved, and over the past decade innovative chemical approaches have emerged to tackle them. Here we review these chemical tools and their application to unraveling the molecular basis of synaptic plasticity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kauer, J.A. & Malenka, R.C. Synaptic plasticity and addiction. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 8, 844–858 (2007).
Stephan, K.E., Baldeweg, T. & Friston, K.J. Synaptic plasticity and dysconnection in schizophrenia. Biol. Psychiatry 59, 929–939 (2006).
Kessels, H.W. & Malinow, R. Synaptic AMPA receptor plasticity and behavior. Neuron 61, 340–350 (2009).
Citri, A. & Malenka, R.C. Synaptic plasticity: multiple forms, functions, and mechanisms. Neuropsychopharmacology 33, 18–41 (2008).
Neves, G., Cooke, S.F. & Bliss, T.V. Synaptic plasticity, memory and the hippocampus: a neural network approach to causality. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 9, 65–75 (2008).
Spedding, M., Neau, I. & Harsing, L. Brain plasticity and pathology in psychiatric disease: sites of action for potential therapy. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 3, 33–40 (2003).
Hebb, D.O. The Organization of Behavior: a Neuropsychological Theory (Wiley, New York, 1949).
Bliss, T.V. & Lomo, T. Long-lasting potentiation of synaptic transmission in the dentate area of the anaesthetized rabbit following stimulation of the perforant path. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 232, 331–356 (1973).
Bliss, T.V. & Gardner-Medwin, A.R. Long-lasting potentiation of synaptic transmission in the dentate area of the unanaestetized rabbit following stimulation of the perforant path. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 232, 357–374 (1973).
Whitlock, J.R., Heynen, A.J., Shuler, M.G. & Bear, M.F. Learning induces long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Science 313, 1093–1097 (2006).
Pastalkova, E. et al. Storage of spatial information by the maintenance mechanism of LTP. Science 313, 1141–1144 (2006).
Derkach, V.A., Oh, M.C., Guire, E.S. & Soderling, T.R. Regulatory mechanisms of AMPA receptors in synaptic plasticity. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 8, 101–113 (2007).
Shepherd, J.D. & Huganir, R.L. The cell biology of synaptic plasticity: AMPA receptor trafficking. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 23, 613–643 (2007).
Kerchner, G.A. & Nicoll, R.A. Silent synapses and the emergence of a postsynaptic mechanism for LTP. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 9, 813–825 (2008).
Collingridge, G.L., Olsen, R.W., Peters, J. & Spedding, M. A nomenclature for ligand-gated ion channels. Neuropharmacology 56, 2–5 (2009).
Dingledine, R., Borges, K., Bowie, D. & Traynelis, S.F. The glutamate receptor ion channels. Pharmacol. Rev. 51, 7–61 (1999).
Palmer, C.L., Cotton, L. & Henley, J.M. The molecular pharmacology and cell biology of alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 57, 253–277 (2005).
Mayer, M.L. & Armstrong, N. Structure and function of glutamate receptor ion channels. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 66, 161–181 (2004).
Sobolevsky, A.I., Rosconi, M.P. & Gouaux, E. X-ray structure, symmetry and mechanism of an AMPA-subtype glutamate receptor. Nature 462, 745–756 (2009).
Kato, A.S., Siuda, E.R., Nisenbaum, E.S. & Bredt, D.S. AMPA receptor subunit-specific regulation by a distinct family of type II TARPs. Neuron 59, 986–996 (2008).
Milstein, A.D., Zhou, W., Karimzadegan, S., Bredt, D.S. & Nicoll, R.A. TARP subtypes differentially and dose-dependently control synaptic AMPA receptor gating. Neuron 55, 905–918 (2007).
Schwenk, J. et al. Functional proteomics identify cornichon proteins as auxiliary subunits of AMPA receptors. Science 323, 1313–1319 (2009).
Cho, C.H., St.- Gelais, F., Zhang, W., Tomita, S. & Howe, J.R. Two families of TARP isoforms that have distinct effects on the kinetic properties of AMPA receptors and synaptic currents. Neuron 55, 890–904 (2007).
Soto, D., Coombs, I.D., Kelly, L., Farrant, M. & Cull-Candy, S.G. Stargazin attenuates intracellular polyamine block of calcium-permeable AMPA receptors. Nat. Neurosci. 10, 1260–1267 (2007).
Tomita, S. et al. Stargazin modulates AMPA receptor gating and trafficking by distinct domains. Nature 435, 1052–1058 (2005).
Vandenberghe, W., Nicoll, R.A. & Bredt, D.S. Stargazin is an AMPA receptor auxiliary subunit. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 485–490 (2005).
Bats, C., Groc, L. & Choquet, D. The interaction between Stargazin and PSD-95 regulates AMPA receptor surface trafficking. Neuron 53, 719–734 (2007).
Menuz, K., Kerchner, G.A., O'Brien, J.L. & Nicoll, R.A. Critical role for TARPs in early development despite broad functional redundancy. Neuropharmacology 56, 22–29 (2009).
Newpher, T.M. & Ehlers, M.D. Glutamate receptor dynamics in dendritic microdomains. Neuron 58, 472–497 (2008).
Triller, A. & Choquet, D. New concepts in synaptic biology derived from single-molecule imaging. Neuron 59, 359–374 (2008).
Kennedy, M.J. & Ehlers, M.D. Organelles and trafficking machinery for postsynaptic plasticity. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 29, 325–362 (2006).
Sutton, M.A. & Schuman, E.M. Dendritic protein synthesis, synaptic plasticity, and memory. Cell 127, 49–58 (2006).
Wenthold, R.J., Petralia, R.S., Blahos, J. II & Niedzielski, A.S. Evidence for multiple AMPA receptor complexes in hippocampal CA1/CA2 neurons. J. Neurosci. 16, 1982–1989 (1996).
Sans, N. et al. Aberrant formation of glutamate receptor complexes in hippocampal neurons of mice lacking the GluR2 AMPA receptor subunit. J. Neurosci. 23, 9367–9373 (2003).
Conrad, K.L. et al. Formation of accumbens GluR2-lacking AMPA receptors mediates incubation of cocaine craving. Nature 454, 118–121 (2008).
Argilli, E., Sibley, D.R., Malenka, R.C., England, P.M. & Bonci, A. Mechanism and time course of cocaine-induced long-term potentiation in the ventral tegmental area. J. Neurosci. 28, 9092–9100 (2008).
Liu, S.Q. & Cull-Candy, S.G. Synaptic activity at calcium-permeable AMPA receptors induces a switch in receptor subtype. Nature 405, 454–458 (2000).
Shi, S., Hayashi, Y., Esteban, J.A. & Malinow, R. Subunit-specific rules governing AMPA receptor trafficking to synapses in hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Cell 105, 331–343 (2001).
Malinow, R. AMPA receptor trafficking and long-term potentiation. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 358, 707–714 (2003).
Shi, S.H. et al. Rapid spine delivery and redistribution of AMPA receptors after synaptic NMDA receptor activation. Science 284, 1811–1816 (1999).
Ashby, M.C., Ibaraki, K. & Henley, J.M. It's green outside: tracking cell surface proteins with pH-sensitive GFP. Trends Neurosci. 27, 257–261 (2004).
Meng, Y., Zhang, Y. & Jia, Z. Synaptic transmission and plasticity in the absence of AMPA glutamate receptor GluR2 and GluR3. Neuron 39, 163–176 (2003).
Zamanillo, D. et al. Importance of AMPA receptors for hippocampal synaptic plasticity but not for spatial learning. Science 284, 1805–1811 (1999).
Jensen, V. et al. A juvenile form of postsynaptic hippocampal long-term potentiation in mice deficient for the AMPA receptor subunit GluR-A. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 553, 843–856 (2003).
Hoffman, D.A., Sprengel, R. & Sakmann, B. Molecular dissection of hippocampal theta-burst pairing potentiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 7740–7745 (2002).
Lu, W. et al. Subunit composition of synaptic AMPA receptors revealed by a single-cell genetic approach. Neuron 62, 254–268 (2009).
Andrasfalvy, B.K., Smith, M.A., Borchardt, T., Sprengel, R. & Magee, J.C. Impaired regulation of synaptic strength in hippocampal neurons from GluR1-deficient mice. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 552, 35–45 (2003).
Lester, H.A., Krouse, M.E., Nass, M.M., Wassermann, N.H. & Erlanger, B.F. A covalently bound photoisomerizable agonist: comparison with reversibly bound agonists at Electrophorus electroplaques. J. Gen. Physiol. 75, 207–232 (1980).
Szobota, S. et al. Remote control of neuronal activity with a light-gated glutamate receptor. Neuron 54, 535–545 (2007).
Fortin, D.L. et al. Photochemical control of endogenous ion channels and cellular excitability. Nat. Methods 5, 331–338 (2008).
Griffin, B.A., Adams, S.R. & Tsien, R.Y. Specific covalent labeling of recombinant protein molecules inside live cells. Science 281, 269–272 (1998).
Tour, O., Meijer, R.M., Zacharias, D.A., Adams, S.R. & Tsien, R.Y. Genetically targeted chromophore-assisted light inactivation. Nat. Biotechnol. 21, 1505–1508 (2003).
Poskanzer, K.E., Marek, K.W., Sweeney, S.T. & Davis, G.W. Synaptotagmin I is necessary for compensatory synaptic vesicle endocytosis in vivo. Nature 426, 559–563 (2003).
Marek, K.W. & Davis, G.W. Transgenically encoded protein photoinactivation (FlAsH-FALI): acute inactivation of synaptotagmin I. Neuron 36, 805–813 (2002).
Wang, F.S. & Jay, D.G. Chromophore-assisted laser inactivation (CALI): probing protein function in situ with a high degree of spatial and temporal resolution. Trends Cell Biol. 6, 442–445 (1996).
Stroffekova, K., Proenza, C. & Beam, K.G. The protein-labeling reagent FLASH-EDT2 binds not only to CCXXCC motifs but also non-specifically to endogenous cysteine-rich proteins. Pflugers Arch. 442, 859–866 (2001).
Griffin, B.A., Adams, S.R., Jones, J. & Tsien, R.Y. Fluorescent labeling of recombinant proteins in living cells with FlAsH. Methods Enzymol. 327, 565–578 (2000).
Marks, K.M., Braun, P.D. & Nolan, G.P. A general approach for chemical labeling and rapid, spatially controlled protein inactivation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 9982–9987 (2004).
Ju, W. et al. Activity-dependent regulation of dendritic synthesis and trafficking of AMPA receptors. Nat. Neurosci. 7, 244–253 (2004).
Groc, L. et al. Surface trafficking of neurotransmitter receptor: comparison between single-molecule/quantum dot strategies. J. Neurosci. 27, 12433–12437 (2007).
Giepmans, B.N., Adams, S.R., Ellisman, M.H. & Tsien, R.Y. The fluorescent toolbox for assessing protein location and function. Science 312, 217–224 (2006).
Alivisatos, A.P., Gu, W. & Larabell, C. Quantum dots as cellular probes. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 7, 55–76 (2005).
Lavis, L.D. & Raines, R.T. Bright ideas for chemical biology. ACS Chem. Biol. 3, 142–155 (2008).
Dahan, M. et al. Diffusion dynamics of glycine receptors revealed by single-quantum dot tracking. Science 302, 442–445 (2003).
Howarth, M., Takao, K., Hayashi, Y. & Ting, A.Y. Targeting quantum dots to surface proteins in living cells with biotin ligase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 7583–7588 (2005).
Chen, I., Choi, Y.A. & Ting, A.Y. Phage display evolution of a peptide substrate for yeast biotin ligase and application to two-color quantum dot labeling of cell surface proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 6619–6625 (2007).
Liu, W. et al. Compact biocompatible quantum dots functionalized for cellular imaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 1274–1284 (2008).
Adams, S.R. & Tsien, R.Y. Controlling cell chemistry with caged compounds. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 55, 755–784 (1993).
Thompson, S.M. et al. Flashy science: controlling neural function with light. J. Neurosci. 25, 10358–10365 (2005).
Ellis-Davies, G.C. Caged compounds: photorelease technology for control of cellular chemistry and physiology. Nat. Methods 4, 619–628 (2007).
DiGregorio, D.A., Rothman, J.S., Nielsen, T.A. & Silver, R.A. Desensitization properties of AMPA receptors at the cerebellar mossy fiber granule cell synapse. J. Neurosci. 27, 8344–8357 (2007).
Denk, W., Strickler, J.H. & Webb, W.W. Two-photon laser scanning fluorescence microscopy. Science 248, 73–76 (1990).
Kandler, K., Katz, L.C. & Kauer, J.A. Focal photolysis of caged glutamate produces long-term depression of hippocampal glutamate receptors. Nat. Neurosci. 1, 119–123 (1998).
Matsuzaki, M., Honkura, N., Ellis-Davies, G.C. & Kasai, H. Structural basis of long-term potentiation in single dendritic spines. Nature 429, 761–766 (2004).
Bagal, A.A., Kao, J.P., Tang, C.M. & Thompson, S.M. Long-term potentiation of exogenous glutamate responses at single dendritic spines. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 14434–14439 (2005).
Volgraf, M. et al. Reversibly caged glutamate: a photochromic agonist of ionotropic glutamate receptors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 260–261 (2007).
Chambers, J.J., Gouda, H., Young, D.M., Kuntz, I.D. & England, P.M. Photochemically knocking out glutamate receptors in vivo. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126, 13886–13887 (2004).
Adesnik, H., Nicoll, R.A. & England, P.M. Photoinactivation of native AMPA receptors reveals their real-time trafficking. Neuron 48, 977–985 (2005).
England, P.M. Rapid photoinactivation of native AMPA receptors on live cells using ANQX. Sci. STKE 2006, pl1 (2006).
Cruz, L.A. et al. 6-Azido-7-nitro-1,4-dihydroquinoxaline-2,3-dione (ANQX) forms an irreversible bond to the active site of the GluR2 AMPA receptor. J. Med. Chem. 51, 5856–5860 (2008).
Stromgaard, K., Jensen, L.S. & Vogensen, S.B. Polyamine toxins: development of selective ligands for ionotropic receptors. Toxicon 45, 249–254 (2005).
Nilsen, A. & England, P.M. A subtype-selective, use-dependent inhibitor of native AMPA receptors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 4902–4903 (2007).
Axelrod, D., Koppel, D.E., Schlessinger, J., Elson, E. & Webb, W.W. Mobility measurement by analysis of fluorescence photobleaching recovery kinetics. Biophys. J. 16, 1055–1069 (1976).
Jaskolski, F. & Henley, J.M. Synaptic receptor trafficking: the lateral point of view. Neuroscience 158, 19–24 (2009).
Nirmal, M. et al. Fluorescence intermittency in single cadmium selenide nanocrystals. Nature 383, 802–804 (1996).
Triller, A. & Choquet, D. Surface trafficking of receptors between synaptic and extrasynaptic membranes: and yet they do move! Trends Neurosci. 28, 133–139 (2005).
Borgdorff, A.J. & Choquet, D. Regulation of AMPA receptor lateral movements. Nature 417, 649–653 (2002).
Bear, M.F., Connors, B.W. & Paradiso, M.A. Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain (Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, 2007).
Jane, D.E., Lodge, D. & Collingridge, G.L. Kainate receptors: pharmacology, function and therapeutic potential. Neuropharmacology 56, 90–113 (2009).
Pinheiro, P.S. & Mulle, C. Presynaptic glutamate receptors: physiological functions and mechanisms of action. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 9, 423–436 (2008).
Palmer, M.J., Isaac, J.T. & Collingridge, G.L. Multiple, developmentally regulated expression mechanisms of long-term potentiation at CA1 synapses. J. Neurosci. 24, 4903–4911 (2004).
Mansour, M., Nagarajan, N., Nehring, R.B., Clements, J.D. & Rosenmund, C. Heteromeric AMPA receptors assemble with a preferred subunit stoichiometry and spatial arrangement. Neuron 32, 841–853 (2001).
Isaac, J.T., Ashby, M. & McBain, C.J. The role of the GluR2 subunit in AMPA receptor function and synaptic plasticity. Neuron 54, 859–871 (2007).
Greger, I.H., Ziff, E.B. & Penn, A.C. Molecular determinants of AMPA receptor subunit assembly. Trends Neurosci. 30, 407–416 (2007).
Greger, I.H., Khatri, L., Kong, X. & Ziff, E.B. AMPA receptor tetramerization is mediated by Q/R editing. Neuron 40, 763–774 (2003).
Washburn, M.S., Numberger, M., Zhang, S. & Dingledine, R. Differential dependence on GluR2 expression of three characteristic features of AMPA receptors. J. Neurosci. 17, 9393–9406 (1997).
Jonas, P. & Burnashev, N. Molecular mechanisms controlling calcium entry through AMPA-type glutamate receptor channels. Neuron 15, 987–990 (1995).
Hume, R.I., Dingledine, R. & Heinemann, S.F. Identification of a site in glutamate receptor subunits that controls calcium permeability. Science 253, 1028–1031 (1991).
Blaschke, M. et al. A single amino acid determines the subunit-specific spider toxin block of alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionate/kainate receptor channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90, 6528–6532 (1993).
Washburn, M.S. & Dingledine, R. Block of alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) receptors by polyamines and polyamine toxins. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 278, 669–678 (1996).
Acknowledgements
We thank B. Shoichet and K. Shokat for their critical review of the manuscript. We apologize to those whose work we could not cite because of space limitations. J.J.F. is supported by grants from the Wheeler Center and the Sandler Foundation. Work in the lab of P.M.E. is supported by the US National Institutes of Health, the McKnight Foundation and the Sandler Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fleming, J., England, P. AMPA receptors and synaptic plasticity: a chemist's perspective. Nat Chem Biol 6, 89–97 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.298
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.298
This article is cited by
-
Ligand-directed two-step labeling to quantify neuronal glutamate receptor trafficking
Nature Communications (2021)
-
UPF2 leads to degradation of dendritically targeted mRNAs to regulate synaptic plasticity and cognitive function
Molecular Psychiatry (2020)
-
Molecular insights into the role of AMPA receptors in the synaptic plasticity, pathogenesis and treatment of epilepsy: therapeutic potentials of perampanel and antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) technology
Acta Neurologica Belgica (2020)
-
Chemical labelling for visualizing native AMPA receptors in live neurons
Nature Communications (2017)
-
Allosteric activation of membrane-bound glutamate receptors using coordination chemistry within living cells
Nature Chemistry (2016)