Abstract
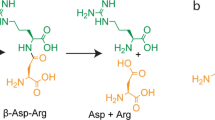
The availability of whole genome sequences boosts the identification of biochemical pathways conserved across species using tools of comparative genomics. A cross-organism protein association analysis allowed us to identify two enzymes, ureidoglycine aminohydrolase and ureidoglycolate amidohydrolase, that catalyze the final reactions of purine degradation in the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana. A similar pathway was found in Escherichia coli, while an alternative metabolic route via ureidoglycine transaminase can be predicted for other organisms.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Chou, H.C. et al. Infect. Immun. 72, 3783–3792 (2004).
Todd, C.D. et al. J. Exp. Bot. 57, 5–12 (2006).
Vogels, G.D. & Van der Drift, C. Bacteriol. Rev. 40, 403–468 (1976).
Werner, A.K., Sparkes, I.A., Romeis, T. & Witte, C.P. Plant Physiol. 146, 418–430 (2008).
Cusa, E., Obradors, N., Baldoma, L., Badia, J. & Aguilar, J. J. Bacteriol. 181, 7479–7484 (1999).
Schultz, A.C., Nygaard, P. & Saxild, H.H. J. Bacteriol. 183, 3293–3302 (2001).
van der Drift, C., de Windt, F.E. & Vogels, G.D. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 136, 273–279 (1970).
Gravenmade, E.J., Vogels, G.D. & van der Drift, C. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 198, 569–582 (1970).
Munoz, A., Piedras, P., Aguilar, M. & Pineda, M. Plant Physiol. 125, 828–834 (2001).
Winkler, R.G., Blevins, D.G. & Randall, D.D. Plant Physiol. 86, 1084–1088 (1988).
Höglund, A., Dönnes, P., Blum, T., Adolph, H.W. & Kohlbacher, O. Bioinformatics 22, 1158–1165 (2006).
Scheible, W.R. et al. Plant Physiol. 136, 2483–2499 (2004).
Schmid, M. et al. Nat. Genet. 37, 501–506 (2005).
von Mering, C. et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 35, D358–D362 (2007).
Agarwal, R., Burley, S.K. & Swaminathan, S. J. Mol. Biol. 368, 450–463 (2007).
van der Drift, C., Van Helvoord, P.E.M. & Vogels, G.D Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 145, 465–469 (1971).
Ramazzina, I., Folli, C., Secchi, A., Berni, R. & Percudani, R. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2, 144–148 (2006).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank F.-Q. Cao for technical support and A. Schäfer from the Institute for Chemistry of the Freie Universität Berlin for NMR measurements. This work was financially supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (WI 3411/1-1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.K.W., experimental design and biochemical experiments; T.R., supply of the laboratory environment; C.-P.W., project planning and design and bioinformatic analysis.
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–6 and Supplementary Methods (PDF 2917 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Werner, A., Romeis, T. & Witte, CP. Ureide catabolism in Arabidopsis thaliana and Escherichia coli. Nat Chem Biol 6, 19–21 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.265
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.265
This article is cited by
-
Allantoate Amidohydrolase OsAAH is Essential for Preharvest Sprouting Resistance in Rice
Rice (2024)
-
Enzymes and cellular interplay required for flux of fixed nitrogen to ureides in bean nodules
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Initiation of cytosolic plant purine nucleotide catabolism involves a monospecific xanthosine monophosphate phosphatase
Nature Communications (2021)
-
Ureide metabolism in Arabidopsis thaliana is modulated by C:N balance
Journal of Plant Research (2020)
-
Interactive effects of polyamines and arbuscular mycorrhiza in modulating plant biomass, N2 fixation, ureide, and trehalose metabolism in Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp. genotypes under nickel stress
Environmental Science and Pollution Research (2020)