Abstract
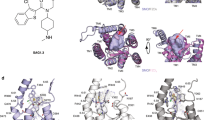
Dishevelled proteins are key regulators of Wnt signaling pathways that have been implicated in the progression of human cancers. We found that the binding cleft of the Dishevelled PDZ domain is more flexible than those of canonical PDZ domains and enables recognition of both C-terminal and internal peptides. These peptide ligands inhibit Wnt/β-catenin signaling in cells, showing that Dishevelled PDZ domains are potential targets for small-molecule cancer therapeutics.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Axelrod, J.D., Miller, J.R., Shulman, J.M., Moon, R.T. & Perrimon, N. Genes Dev. 12, 2610–2622 (1998).
Rothbacher, U. et al. EMBO J. 19, 1010–1022 (2000).
Polakis, P. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 17, 45–51 (2007).
Weitzel, H.E. et al. Development 131, 2947–2956 (2004).
Uematsu, K. et al. Oncogene 22, 7218–7221 (2003).
Uematsu, K. et al. Cancer Res. 63, 4547–4551 (2003).
Li, L. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 129–134 (1999).
Wong, H.C. et al. Mol. Cell 12, 1251–1260 (2003).
Wharton, K.A.J. Dev. Biol. 253, 1–17 (2003).
Wang, J. et al. Development 133, 1767–1778 (2006).
Shan, J., Shi, D.L., Wang, J. & Zheng, J. Biochemistry 44, 15495–15503 (2005).
Fujii, N. et al. Cancer Res. 67, 573–579 (2007).
Mahindroo, N., Punchihewa, C., Bail, A.M. & Fujii, N. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 18, 946–949 (2008).
Tonikian, R. et al. PLoS Biol. 6, e239 (2008).
Appleton, B.A. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 22312–22320 (2006).
Skelton, N.J. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 7645–7654 (2003).
Veeman, M.T., Slusarski, D.C., Kaykas, A., Louie, S.H. & Moon, R.T. Curr. Biol. 13, 680–685 (2003).
Derossi, D., Chassaing, G. & Prochiantz, A. Trends Cell Biol. 8, 84–87 (1998).
Abramoff, M.D., Magelhaes, P.J. & Ram, S.J. Biophotonics Int. 11, 36–42 (2004).
Acknowledgements
We thank the oligonucleotide synthesis and DNA sequencing groups at Genentech, Inc., C. Quan (Genentech, Inc.) for peptide synthesis and J. Gunzner (Genentech, Inc.) for synthesis of FJ9. We also thank L. Lasky for advice and discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y.Z., B.A.A., C.W., R.N.H. and S.S.S. designed the experiments and analyzed the results. Y.Z., B.A.A. and R.N.H. performed experiments. T.L. and M.C. designed, performed and analyzed the TOPbrite experiments. Y.Z., B.A.A., R.N.H. and S.S.S. wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–7, Supplementary Tables 1–3 and Supplementary Methods (PDF 11026 kb)
Supplementary Movie 1
Cellular internalization of fluorescently-labelled pen-N3 (MOV 498 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Appleton, B., Wiesmann, C. et al. Inhibition of Wnt signaling by Dishevelled PDZ peptides. Nat Chem Biol 5, 217–219 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.152
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.152
This article is cited by
-
Targeting PDZ domains as potential treatment for viral infections, neurodegeneration and cancer
Biology Direct (2021)
-
Comparative phosphorylation map of Dishevelled 3 links phospho-signatures to biological outputs
Cell Communication and Signaling (2019)
-
A selective peptide inhibitor of Frizzled 7 receptors disrupts intestinal stem cells
Nature Chemical Biology (2018)
-
Pharmacological targets of breast cancer stem cells: a review
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology (2018)
-
A potent and selective small molecule inhibitor of sirtuin 1 promotes differentiation of pluripotent P19 cells into functional neurons
Scientific Reports (2016)