Abstract
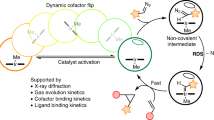
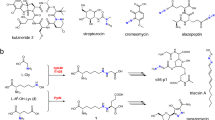
Berberine bridge enzyme catalyzes the conversion of (S)-reticuline to (S)-scoulerine by formation of a carbon-carbon bond between the N-methyl group and the phenolic ring. We elucidated the structure of berberine bridge enzyme from Eschscholzia californica and determined the kinetic rates for three active site protein variants. Here we propose a catalytic mechanism combining base-catalyzed proton abstraction with concerted carbon-carbon coupling accompanied by hydride transfer from the N-methyl group to the N5 atom of the FAD cofactor.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Steffens, P., Nagakura, N. & Zenk, M.H. Phytochem. 24, 2577–2583 (1985).
Kutchan, T.M. & Dittrich, H. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 24475–24481 (1995).
Edmondson, D.E., Binda, C. & Mattevi, A. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 464, 269–276 (2007).
Scrutton, N.S. Nat. Prod. Rep. 21, 722–730 (2004).
Fitzpatrick, P.F. Bioorg. Chem. 32, 125–139 (2004).
Winkler, A., Hartner, F., Kutchan, T.M., Glieder, A. & Macheroux, P. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 21276–21285 (2006).
Huang, C.-H. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 38831–38838 (2005).
Alexeev, I., Sultana, A., Mantsala, P., Niemi, J. & Schneider, G. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 6170–6175 (2007).
Heuts, D.P.H.M., Winter, R.T., Damsma, G.E., Janssen, D.B. & Fraaije, M.W. Biochem. J. 413, 175–183 (2008).
Rand, T., Qvist, K.B., Walter, C.P. & Poulsen, C.H. FEBS J. 273, 2693–2703 (2006).
Harayama, T., Tezuka, Y., Taga, T. & Yoneda, F. J. Chem. Soc. [Perkin 1] 75–83 (1987).
Iwata, M., Bruice, T.C., Carrell, H.L. & Glusker, J.P. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 102, 5036–5044 (1980).
Settembre, E.C. et al. Biochemistry 42, 2971–2981 (2003).
Malito, E., Coda, A., Bilyeu, K.D., Fraaije, M.W. & Mattevi, A. J. Mol. Biol. 341, 1237–1249 (2004).
Miller, J.R. & Edmondson, D.E. Biochemistry 38, 13670–13683 (1999).
Bjorklund, J.A. et al. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 117, 1533–1545 (1995).
Winkler, A., Kutchan, T.M. & Macheroux, P. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 24437–24443 (2007).
Sirikantaramas, S. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 39767–39774 (2004).
Taura, F. et al. FEBS Lett. 581, 2929–2934 (2007).
Acknowledgements
We appreciate the support of staff scientists at the synchrotron beamlines at DESY/EMBL-Hamburg during diffraction data collection and of Hansjörg Weber (Institute of Organic Chemistry, Graz University of Technology) for recording the NMR spectra. Financial support was provided by the Austrian Science Fund (Fonds zur Förderung der wissenschaftlichen Forschung) through the Doktoratskolleg “Molecular enzymology” W901-B05 (to K.G. and P.M.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.W., P.M. and K.G. designed experiments and analyzed results. A.W., P.M. and K.G. wrote the manuscript. A.W., A.L. and K.G. determined the crystal structures. A.W., S.R. and M.P. generated, expressed and purified mutant proteins. A.W. and M.P. performed enzyme kinetic experiments. T.M.K. prepared and provided special compounds and helped in editing the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–7, Supplementary Table 1, Supplementary Discussion and Supplementary Methods (PDF 749 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Winkler, A., Łyskowski, A., Riedl, S. et al. A concerted mechanism for berberine bridge enzyme. Nat Chem Biol 4, 739–741 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.123
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.123
This article is cited by
-
Elucidation of the (R)-enantiospecific benzylisoquinoline alkaloid biosynthetic pathways in sacred lotus (Nelumbo nucifera)
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Effects of codon optimization, N-terminal truncation and gene dose on the heterologous expression of berberine bridge enzyme
World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology (2022)
-
Engineering Saccharomyces cerevisiae to produce plant benzylisoquinoline alkaloids
aBIOTECH (2021)
-
Broadening the scope of biocatalytic C–C bond formation
Nature Reviews Chemistry (2020)
-
Benzylisoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis in opium poppy: an update
Phytochemistry Reviews (2019)