Abstract
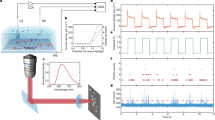
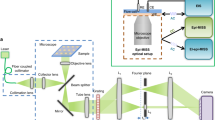
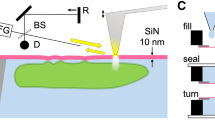
Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy is a crucial tool for the detection and study of various biological substances, from DNA and proteins to viruses and bacteria. It does not require any labelling species, and methods based on it have been developed to study cellular processes (such as cell spreading, adhesion, invasion, toxicology and mobility). However, data have so far lacked spatial information, which is essential for investigating heterogeneous processes and imaging high-throughput microarrays. Here, we report an electrochemical impedance microscope based on surface plasmon resonance that resolves local impedance with submicrometre spatial resolution. We have used an electrochemical impedance microscope to monitor the dynamics of cellular processes (apoptosis and electroporation of individual cells) with millisecond time resolution. The high spatial and temporal resolution makes it possible to study individual cells, but also resolve subcellular structures and processes without labels, and with excellent detection sensitivity (~2 pS). We also describe a model that simulates cellular and electrochemical impedance microscope images based on local dielectric constant and conductivity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Katz, E. & Willner, I. Probing biomolecular interactions at conductive and semiconductive surfaces by impedance spectroscopy: routes to impedimetric immunosensors, DNA-sensors, and enzyme biosensors. Electroanal. 15, 913–947 (2003).
Maalouf, R. et al. Label-free detection of bacteria by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy: comparison to surface plasmon resonance. Anal. Chem. 79, 4879–4886 (2007).
Giaever, I. & Keese, C. R. A morphological biosensor for mammalian cells. Nature 366, 591–592 (1993).
Giaever, I. & Keese, C. R. Monitoring fibroblast behavior in tissue-culture with an applied electric field. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 81, 3761–3764 (1984).
Slack, M. D., Martinez, E. D., Wu, L. F. & Altschuler, S. J. Characterizing heterogeneous cellular responses to perturbations. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 105, 19306–19311 (2008).
Schulte, A. & Schuhmann, W. Single-cell microelectrochemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 46, 8760–8777 (2007).
Rothermel, A. et al. Real-time measurement of PMA-induced cellular alterations by microelectrode array-based impedance spectroscopy. BioTechniques 41, 445–450 (2006).
Rahman, A. R. A., Register, J., Vuppala, G. & Bhansali, S. Cell culture monitoring by impedance mapping using a multielectrode scanning impedance spectroscopy system (CellMap). Physiol. Meas. 29, S227–S239 (2008).
Chai, K. T. C., Davies, J. H. & Cumming, D. R. S. Electrical impedance tomography for sensing with integrated microelectrodes on a CMOS microchip. Sens. Actuators B 127, 97–101 (2007).
Lin, Z., Ino, K., Shiku, H. & Matsue, T. Electrochemical topography of a cell monolayer with an addressable microelectrode array. Chem. Commun. 46, 559–561 (2010).
Alpuche-Aviles, M. A. & Wipf, D. O. Impedance feedback control for scanning electrochemical microscopy. Anal. Chem. 73, 4873–4881 (2001).
Katemann, B. B., Schulte, A., Calvo, E. J., Koudelka-Hep, M. & Schuhmann, W. Localised electrochemical impedance spectroscopy with high lateral resolution by means of alternating current scanning electrochemical microscopy. Electrochem. Commun. 4, 134–138 (2002).
Ervin, E. N., White, H. S. & Baker, L. A. Alternating current impedance imaging of membrane pores using scanning electrochemical microscopy. Anal. Chem. 77, 5564–5569 (2005).
Rothenhausler, B. & Knoll, W. Surface-plasmon microscopy. Nature 332, 615–617 (1988).
Andersson, O., Ulrich, C., Bjorefors, F. & Liedberg, B. Imaging SPR for detection of local electrochemical processes on patterned surfaces. Sens. Actuators B 134, 545–550 (2008).
Shan, X. N., Patel, U., Wang, S. P., Iglesias, R. & Tao, N. J. Imaging local electrochemical current via surface plasmon resonance. Science 327, 1363–1366 (2010).
Foley, K. J., Shan, X. & Tao, N. J. Surface impedance imaging technique. Anal. Chem. 80, 5146–5151 (2008).
Giaever, I. & Keese, C. R. Micromotion of mammalian cells measured electrically. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 88, 7896–7900 (1991).
Urdapilleta, E., Bellotti, M. & Bonetto, F. J. Impedance analysis of cultured cells: a mean-field electrical response model for electric cell-substrate impedance sensing technique. Phys. Rev. E 74, 041908 (2006).
Bremer, E., van Dam, G., Kroesen, B., de Leij, L. & Helfrich, W. Targeted induction of apoptosis for cancer therapy: current progress and prospects. Trends Mol. Med. 12, 382–393 (2006).
Hougardy, B. M. T. et al. Proteasome inhibitor MG132 sensitizes HPV-positive human cervical cancer cells to rhTRAIL-induced apoptosis. Int. J. Cancer 118, 1892–1900 (2006).
Aihara, H. & Miyazaki, J.-I. Gene transfer into muscle by electroporation in vivo. Nature Biotechnol. 16, 867–870 (1998).
Olofsson, J. et al. Single-cell electroporation. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 14, 29–34 (2003).
Keese, C. R., Wegener, J., Walker, S. R. & Giaever, I. Eletrical wound-healing assay for cells in vitro. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 101, 1554–1559 (2004).
Huang, B., Yu, F. & Zare, R. N. Surface plasmon resonance imaging using a high numerical aperture microscope objective. Anal. Chem. 79, 2979–2983 (2007).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the National Institutes of Health (NIH, R21RR026235) and National Science Foundation (NSF, CHE-0554786) for support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
K.F. performed initial impedance imaging of cells. W.W. carried out the measurement and data analysis presented here. X.S. contributed to numerical simulation and prepared gold chips. S.E., V.J.N. and P.W. helped with cell culture. K.F. and U.P. developed imaging processing software. W.W., K.F. and S.W. designed and set up the experiment. N.J.T. conceived the experiment and model simulation, and wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information (PDF 1904 kb)
Supplementary information
Supplementary movie S1 (MOV 199 kb)
Supplementary information
Supplementary movie S2 (MOV 328 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Foley, K., Shan, X. et al. Single cells and intracellular processes studied by a plasmonic-based electrochemical impedance microscopy. Nature Chem 3, 249–255 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nchem.961
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nchem.961
This article is cited by
-
Determining the depth of surface charging layer of single Prussian blue nanoparticles with pseudocapacitive behaviors
Nature Communications (2022)
-
High-resolution impedance mapping using electrically activated quantitative phase imaging
Light: Science & Applications (2021)
-
Plasmonic scattering imaging of single proteins and binding kinetics
Nature Methods (2020)
-
Bioanalysis in single cells: current advances and challenges
Science China Chemistry (2020)
-
In situ mapping of activity distribution and oxygen evolution reaction in vanadium flow batteries
Nature Communications (2019)