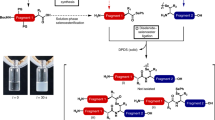
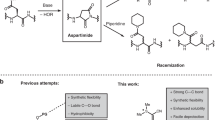
Abstract
Amide-forming ligation reactions allow the chemical synthesis of proteins by the union of unprotected peptide segments, and enable the preparation of protein derivatives not accessible by expression or bioengineering approaches. The native chemical ligation (NCL) of thioesters and N-terminal cysteines is unquestionably the most successful approach, but is not ideal for all synthetic targets. Here we describe the synthesis of an Fmoc-protected oxazetidine amino acid for use in the α-ketoacid–hydroxylamine (KAHA) amide ligation. When incorporated at the N-terminus of a peptide segment, this four-membered cyclic hydroxylamine can be used for rapid serine-forming ligations with peptide α-ketoacids. This ligation operates at low concentration (100 μM–5 mM) and mild temperatures (20–25 °C). The utility of the reaction was demonstrated by the synthesis of S100A4, a 12 kDa calcium-binding protein not easily accessible by NCL or other amide-forming reactions due to its primary sequence and properties.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kent, S. B. H. Bringing the science of proteins into the realm of organic chemistry: total chemical synthesis of SEP (synthetic erythropoiesis protein). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 52, 11988–11996 (2013).
Nilsson, B. L., Soellner, M. B. & Raines, R. T. Chemical synthesis of proteins. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 34, 91–118 (2005).
Hackenberger, C. P. R., Bode, J. W. & Schwarzer, D. in Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins in Organic Chemistry: Building Blocks, Catalysis and Coupling Chemistry Vol. 3 (ed Hughes, A. B.) 445–493 (Wiley-VCH, 2010).
Dawson, P., Muir, T., Clark-Lewis, I. & Kent, S. Synthesis of proteins by native chemical ligation. Science 266, 776–779 (1994).
Pattabiraman, V. R. & Bode, J. W. Rethinking amide bond synthesis. Nature 480, 471–479 (2011).
Bode, J. W., Fox, R. M. & Baucom, K. D. Chemoselective amide ligations by decarboxylative condensations of N-alkylhydroxylamines and α-ketoacids. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 45, 1248–1252 (2006).
Pattabiraman, V. R., Ogunkoya, A. O. & Bode, J. W. Chemical protein synthesis by chemoselective α-ketoacid-hydroxylamine (KAHA) ligations with 5-oxaproline. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 51, 5114–5118 (2012).
Wucherpfennig, T. G., Pattabiraman, V. R., Limberg, F. R. P., Ruiz-Rodríguez, J. & Bode, J. W. Traceless preparation of C-terminal α-ketoacids for chemical protein synthesis by α-ketoacid–hydroxylamine ligation: synthesis of SUMO2/3. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 53, 12248–12252 (2014).
Wucherpfennig, T. G., Rohrbacher, F., Pattabiraman, V. R. & Bode, J. W. Formation and rearrangement of homoserine depsipeptides and depsiproteins in the α-ketoacid–hydroxylamine ligation with 5-oxaproline. Angew. Chem Int. Ed. 53, 12244–12247 (2014).
Magers, D. H. & Davis, S. R. Ring strain in the oxazetidines. J. Mol. Struc. Theochem. 487, 205–210 (1999).
Florio, S., Capriati, V., & Luisi, R. in Comprehensive Heterocyclic Chemistry III Vol. 2 (eds Katritzky, A. R., Ramsden, C. A., Scriven, E. F. V. & Taylor, R. J. K.) Ch. 14, 689–711 (Elsevier, 2008).
Snider, B. B. & Duvall, J. R. Synthesis of the 4-methyl-1,2-oxazetidine-4-carboxylic acid moiety of the originally proposed halipeptin A and B structures. Tetrahedron Lett. 44, 3067–3070 (2003).
Denicola, A., Einhorn, C., Einhorn, J. & Luche, J. L. Intramolecular alkylation of carboxylic-acids—application to the synthesis of Boc-protected cyclic amino-acids. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 879–880 (1994).
Casadei, M. A., Galli, C. & Mandolini, L. Ring-closure reactions. 22. Kinetics of cyclization of diethyl (ω-bromoalkyl)malonates in the range of 4- to 21-membered rings. Role of ring strain. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 106, 1051–1056 (1984).
Baldwin, J. E. Rules for ring closure. Chem. Commun. 734–736 (1976).
Alabugin, I. V. & Gilmore, K. Finding the right path: Baldwin ‘rules for ring closure’ and stereoelectronic control of cyclizations. Chem. Commun. 49, 1124–11250 (2013).
Tanino, K. et al. Total synthesis of Solanoeclepin A. Nature Chem. 3, 484–488 (2011).
Medjahdi, M., Gonzalez-Gomez, J. C., Foubelo, F. & Yus, M. Stereoselective synthesis of azetidines and pyrrolidines from N-tert-butylsulfonyl(2-aminoalkyl)oxiranes. J. Org. Chem. 74, 7859–7865 (2009).
Davies, S. G., Jones, S., Sanz, M. A., Teixeira, F. C. & Fox, J. F. A novel [2,3] intramolecular rearrangement of N-benzyl-O-allylhydroxylamines. Chem. Commun. 2235–2236 (1998).
Wuts, P. G. M. & Greene, T. W. in Greene's Protective Groups in Organic Synthesis (Wiley, 2006).
Vallely, K. M. et al. Solution structure of human Mts1 (S100A4) as determined by NMR spectroscopy. Biochemistry 41, 12670–12680 (2002).
Kiss, B. et al. Crystal structure of the S100A4-nonmuscle myosin IIA tail fragment complex reveals an asymmetric target binding mechanism. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 109, 6048–6053 (2012).
Schäfer, B. W. & Heizmann, C. W. The S100 family of EF-hand calcium-binding proteins: functions and pathology. Trends Biochem. Sci. 21, 134–140 (1996).
Sohma, Y., Sasaki, M., Hayashi, Y., Kimura, T. & Kiso, Y. Novel and efficient synthesis of difficult sequence-containing peptides through O–N intramolecular acyl migration reaction of O-acyl E isopeptides. Chem. Commun. 124–125 (2004).
Avital-Shmilovici, M. et al. Fully convergent chemical synthesis of ester insulin: determination of the high resolution X-ray structure by racemic protein crystallography. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135, 3173–3185 (2013).
Kalia, J. & Raines, R. T. Advances in bioconjugation. Curr. Org. Chem. 14, 138–147 (2010).
Li, X., Lam, H. Y., Zhang, Y. & Chan, C. K. Salicylaldehyde ester-induced chemoselective peptide ligations: enabling generation of natural peptidic linkages at the serine/threonine sites. Org. Lett. 12, 1724–1727 (2010).
Zhang, Y., Xu, C., Lam, H. Y., Lee, C. L., & Li, X. Protein chemical synthesis by serine and threonine ligation. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 110, 6657–6662 (2012).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Swiss National Science Foundation (200020_150073) and ETH Zürich. F. Thuaud, S. Baldauf and M. Dao are thanked for contributions to the synthesis of compound 1, V. Pattabiraman for discussions, F. Saito for advice on kinetics and C. Wolfrum for biological evaluation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.W.B. and I.P. contributed equally to the design of the study. J.B., with contributions from I.P., wrote the paper. I.P performed the experiments and wrote the Supplementary Information.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information (PDF 5836 kb)
Supplementary information
Crystallographic data for compound 9. (CIF 16 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pusterla, I., Bode, J. An oxazetidine amino acid for chemical protein synthesis by rapid, serine-forming ligations. Nature Chem 7, 668–672 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nchem.2282
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nchem.2282
This article is cited by
-
On-resin multicomponent protocols for biopolymer assembly and derivatization
Nature Protocols (2021)
-
Chemical Synthesis of Proteins Containing 300 Amino Acids
Chemical Research in Chinese Universities (2020)
-
Designing cooperatively folded abiotic uni- and multimolecular helix bundles
Nature Chemistry (2018)
-
Recent developments in peptide ligation independent of amino acid side-chain functional group
Science China Chemistry (2018)
-
Protein chemical synthesis by α-ketoacid–hydroxylamine ligation
Nature Protocols (2016)