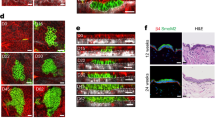
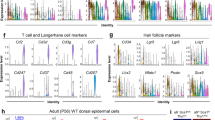
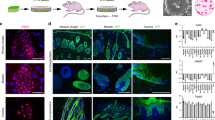
Abstract
Basal cell carcinoma, the most frequent human skin cancer, arises from activating hedgehog (HH) pathway mutations; however, little is known about the temporal changes that occur in tumour-initiating cells from the first oncogenic hit to the development of invasive cancer. Using an inducible mouse model enabling the expression of a constitutively active Smoothened mutant (SmoM2) in the adult epidermis, we carried out transcriptional profiling of SmoM2-expressing cells at different times during cancer initiation. We found that tumour-initiating cells are massively reprogrammed into a fate resembling that of embryonic hair follicle progenitors (EHFPs). Wnt/ β-catenin signalling was very rapidly activated following SmoM2 expression in adult epidermis and coincided with the expression of EHFP markers. Deletion of β-catenin in adult SmoM2-expressing cells prevents EHFP reprogramming and tumour initiation. Finally, human basal cell carcinomas also express genes of the Wnt signalling and EHFP signatures.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Epstein, E. H. Basal cell carcinomas: attack of the hedgehog. Nat. Rev. Cancer 8, 743–754 (2008).
Pasca di Magliano, M. & Hebrok, M. Hedgehog signalling in cancer formation and maintenance. Nat. Rev. Cancer 3, 903–911 (2003).
Xie, J. et al. Activating Smoothened mutations in sporadic basal-cell carcinoma. Nature 391, 90–92 (1998).
Mao, J. et al. A novel somatic mouse model to survey tumorigenic potential applied to the Hedgehog pathway. Cancer Res. 66, 10171–10178 (2006).
Youssef, K. K. et al. Identification of the cell lineage at the origin of basal cell carcinoma. Nat. Cell Biol. 12, 299–305 (2010).
Wong, S. Y. & Reiter, J. F. Wounding mobilizes hair follicle stem cells to form tumors. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 108, 4093–4098 (2011).
Shirahama, S., Furukawa, F., Wakita, H. & Takigawa, M. E- and P-cadherin expression in tumor tissues and soluble E-cadherin levels in sera of patients with skin cancer. J. Dermatol. Sci. 13, 30–36 (1996).
Yoshikawa, K., Katagata, Y. & Kondo, S. Biochemical and immunohistochemical analyses of keratin expression in basal cell carcinoma. J. Dermatol. Sci. 17, 15–23 (1998).
Markey, A. C., Lane, E. B., Macdonald, D. M. & Leigh, I. M. Keratin expression in basal cell carcinomas. Br. J. Dermatol. 126, 154–160 (1992).
Vidal, V. P. et al. Sox9 is essential for outer root sheath differentiation and the formation of the hair stem cell compartment. Curr. Biol. 15, 1340–1351 (2005).
Vidal, V. P., Ortonne, N. & Schedl, A. SOX9 expression is a general marker of basal cell carcinoma and adnexal-related neoplasms. J. Cutan. Pathol. 35, 373–379 (2008).
Tanese, K. et al. G-protein-coupled receptor GPR49 is up-regulated in basal cell carcinoma and promotes cell proliferation and tumor formation. Am. J. Pathol. 173, 835–843 (2008).
Yang, S. H. et al. Pathological responses to oncogenic Hedgehog signaling in skin are dependent on canonical Wnt/ β3-catenin signaling. Nat. Genet. 40, 1130–1135 (2008).
Blanpain, C., Lowry, W. E., Geoghegan, A., Polak, L. & Fuchs, E. Self-renewal, multipotency, and the existence of two cell populations within an epithelial stem cell niche. Cell 118, 635–648 (2004).
Rhee, H., Polak, L. & Fuchs, E. Lhx2 maintains stem cell character in hair follicles. Science 312, 1946–1949 (2006).
Subramanian, A. et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 102, 15545–15550 (2005).
Osorio, K. M. et al. Runx1 modulates developmental, but not injury-driven, hair follicle stem cell activation. Development 135, 1059–1068 (2008).
Osorio, K. M., Lilja, K. C. & Tumbar, T. Runx1 modulates adult hair follicle stem cell emergence and maintenance from distinct embryonic skin compartments. J. Cell Biol. 193, 235–250 (2011).
Ellis, T. et al. The transcriptional repressor CDP (Cutl1) is essential for epithelial cell differentiation of the lung and the hair follicle. Genes Dev. 15, 2307–2319 (2001).
Wang, G. Y., Wang, J., Mancianti, M. L. & Epstein, E. H. Jr Basal cell carcinomas arise from hair follicle stem cells in Ptch1(+/-) mice. Cancer Cell 19, 114–124 (2011).
Kasper, M. et al. Wounding enhances epidermal tumorigenesis by recruiting hair follicle keratinocytes. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 108, 4099–4104 (2011).
Uhmann, A. et al. The Hedgehog receptor Patched controls lymphoid lineage commitment. Blood 110, 1814–1823 (2007).
Lowry, W. E. et al. Defining the impact of β-catenin/Tcf transactivation on epithelial stem cells. Genes Dev. 19, 1596–1611 (2005).
DasGupta, R. & Fuchs, E. Multiple roles for activated LEF/TCF transcription complexes during hair follicle development and differentiation. Development 126, 4557–4568 (1999).
Enshell-Seijffers, D., Lindon, C., Kashiwagi, M. & Morgan, B. A. β-catenin activity in the dermal papilla regulates morphogenesis and regeneration of hair. Dev. Cell 18, 633–642 (2010).
Rendl, M., Lewis, L. & Fuchs, E. Molecular dissection of mesenchymal-epithelial interactions in the hair follicle. PLoS Biol. 3, e331 (2005).
Maretto, S. et al. Mapping Wnt/ β-catenin signaling during mouse development and in colorectal tumors. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 100, 3299–3304 (2003).
Tumbar, T. et al. Defining the epithelial stem cell niche in skin. Science 303, 359–363 (2004).
Morris, R. J. et al. Capturing and profiling adult hair follicle stem cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 22, 411–417 (2004).
Harada, N. et al. Intestinal polyposis in mice with a dominant stable mutation of the β-catenin gene. EMBO J. 18, 5931–5942 (1999).
Vasioukhin, V., Bauer, C., Degenstein, L., Wise, B. & Fuchs, E. Hyperproliferation and defects in epithelial polarity upon conditional ablation of α-catenin in skin. Cell 104, 605–617 (2001).
Grachtchouk, V. et al. The magnitude of hedgehog signaling activity defines skin tumor phenotype. EMBO J. 22, 2741–2751 (2003).
Huelsken, J., Vogel, R., Erdmann, B., Cotsarelis, G. & Birchmeier, W. β-Catenin controls hair follicle morphogenesis and stem cell differentiation in the skin. Cell 105, 533–545 (2001).
Andl, T., Reddy, S. T., Gaddapara, T. & Millar, S. E. WNT signals are required for the initiation of hair follicle development. Dev. Cell 2, 643–653 (2002).
Enshell-Seijffers, D., Lindon, C., Wu, E., Taketo, M. M. & Morgan, B. A. β-catenin activity in the dermal papilla of the hair follicle regulates pigment-type switching. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 107, 21564–21569 (2010).
Collins, C. A., Kretzschmar, K. & Watt, F. M. Reprogramming adult dermis to a neonatal state through epidermal activation of β-catenin. Development 138, 5189–5199 (2011).
Crowson, A. N. Basal cell carcinoma: biology, morphology and clinical implications. Mod. Pathol. 19 (Suppl 2), S127–S147 (2006).
El-Bahrawy, M., El-Masry, N., Alison, M., Poulsom, R. & Fallowfield, M. Expression of β-catenin in basal cell carcinoma. Br. J. Dermatol. 148, 964–970 (2003).
Saldanha, G., Ghura, V., Potter, L. & Fletcher, A. Nuclear β-catenin in basal cell carcinoma correlates with increased proliferation. Br. J. Dermatol. 151, 157–164 (2004).
Kriegl, L., Horst, D., Kirchner, T. & Jung, A. LEF-1 expression in basal cell carcinomas. Br. J. Dermatol. 160, 1353–1356 (2009).
Wong, D. J. et al. Module map of stem cell genes guides creation of epithelial cancer stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 2, 333–344 (2008).
Ben-Porath, I. et al. An embryonic stem cell-like gene expression signature in poorly differentiated aggressive human tumors. Nat. Genet. 40, 499–507 (2008).
Kim, J. et al. A Myc network accounts for similarities between embryonic stem and cancer cell transcription programs. Cell 143, 313–324 (2010).
Gat, U., DasGupta, R., Degenstein, L. & Fuchs, E. De Novo hair follicle morphogenesis and hair tumors in mice expressing a truncated β-catenin in skin. Cell 95, 605–614 (1998).
St-Jacques, B. et al. Sonic hedgehog signaling is essential for hair development. Curr. Biol. 8, 1058–1068 (1998).
Silva-Vargas, V. et al. β-catenin and Hedgehog signal strength can specify number and location of hair follicles in adult epidermis without recruitment of bulge stem cells. Dev. Cell 9, 121–131 (2005).
Zhang, Y. et al. Activation of {β}-catenin signaling programs embryonic epidermis to hair follicle fate. Development 135, 2161–2172 (2008).
Krahl, D. & Sellheyer, K. Basal cell carcinoma and pilomatrixoma mirror human follicular embryogenesis as reflected by their differential expression patterns of SOX9 and β-catenin. Br. J. Dermatol. 162, 1294–1301 (2010).
Vasioukhin, V., Degenstein, L., Wise, B. & Fuchs, E. The magical touch: genome targeting in epidermal stem cells induced by tamoxifen application to mouse skin. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 96, 8551–8556 (1999).
Means, A. L., Xu, Y., Zhao, A., Ray, K. C. & Gu, G. A CK19(CreERT) knockin mouse line allows for conditional DNA recombination in epithelial cells in multiple endodermal organs. Genesis 46, 318–323 (2008).
Gentleman, R. C. et al. Bioconductor: open software development for computational biology and bioinformatics. Genome Biol. 5, R80 (2004).
McCall, M. N., Bolstad, B. M. & Irizarry, R. A. Frozen robust multiarray analysis (fRMA). Biostatistics 11, 242–253 (2010).
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank those who provided us with reagents and who are acknowledged in the text. C.B. is an investigator of WELBIO. C.B. is a chercheur qualifié, S.B. is a chargé de recherche and G.L. is a collaborateur scientifique of the FRS/FNRS; K.K.Y. is supported by TELEVIE. This work was supported by the FNRS, the program d’excellence CIBLES of the Wallonia Region, a research grant from the Fondation Contre le Cancer, the Fondation ULB, the Fond Yvonne Boël and the Fond Gaston Ithier, a starting grant of the European Research Council (ERC) and the EMBO Young Investigator Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C.B. and K.K.Y. designed the experiments and carried out the data analysis; K.K.Y., G.L., K.B., O.A., J.C.L., V.S., B.V.S., S.D., S.A. and D.P. carried out most of the experiments; S.B. carried out bioinformatic analysis of the microarray; S.R. and I.S. carried out immunohistochemistry analysis on human BCCs; J.V.B. and V.D.M. provided human biopsy materials; C.B. and K.K.Y. wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Information (PDF 4047 kb)
Supplementary Table 1
Supplementary Information (XLSX 48 kb)
Supplementary Table 2
Supplementary Information (XLSX 52 kb)
Supplementary Table 3
Supplementary Information (XLSX 45 kb)
Supplementary Tables 4 and 5
Supplementary Information (XLS 34 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Youssef, K., Lapouge, G., Bouvrée, K. et al. Adult interfollicular tumour-initiating cells are reprogrammed into an embryonic hair follicle progenitor-like fate during basal cell carcinoma initiation. Nat Cell Biol 14, 1282–1294 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2628
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2628
This article is cited by
-
Cellular Heterogeneity and Plasticity of Skin Epithelial Cells in Wound Healing and Tumorigenesis
Stem Cell Reviews and Reports (2022)
-
New insights into the functions of Cox-2 in skin and esophageal malignancies
Experimental & Molecular Medicine (2020)
-
The great escape: tumour cell plasticity in resistance to targeted therapy
Nature Reviews Drug Discovery (2020)
-
Differences in gynecologic tumor development in Amhr2-Cre mice with KRASG12D or KRASG12V mutations
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
STAT3 polymorphisms and IL-6 polymorphism are associated with the risk of basal cell carcinoma in patients from northern Poland
Archives of Dermatological Research (2019)