Abstract
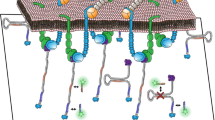
Focal adhesions are integrin-based multiprotein complexes, several micrometres in diameter, that mechanically link the extracellular matrix with the termini of actin bundles. The molecular diversity of focal adhesions and their role in cell migration and matrix sensing has been extensively studied, but their ultrastructural architecture is still unknown. We present the first three-dimensional structural reconstruction of focal adhesions using cryo-electron tomography. Our analyses reveal that the membrane–cytoskeleton interaction at focal adhesions is mediated through particles located at the cell membrane and attached to actin fibres. The particles have diameters of 25 ± 5 nm, and an average interspacing of approximately 45 nm. Treatment with the Rho-kinase inhibitor Y-27632 induces a rapid decrease in particle diameter, suggesting that they are highly mechanosensitive. Our findings clarify the internal architecture of focal adhesions at molecular resolution, and provide insights into their scaffolding and mechanosensory functions.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
17 August 2010
In the version of this letter initially published online, Vera Hirschfeld-Warneken was incorrectly spelled in the author list. This error has been corrected in both the HTML and PDF versions of the letter.
References
Abercrombie, M. & Dunn, G. A. Adhesions of fibroblasts to substratum during contact inhibition observed by interference reflection microscopy. Exp. Cell. Res. 92, 57–62 (1975).
Wiesner, S., Lange, A. & Fässler, R. Local call: from integrins to actin assembly. Trends Cell Biol. 16, 327–329 (2006).
Ginsberg, M., Pierschbacher, M. D., Ruoslahti, E., Marguerie, G. & Plow, E. Inhibition of fibronectin binding to platelets by proteolytic fragments and synthetic peptides which support fibroblast adhesion. J. Biol. Chem. 260, 3931–3936 (1985).
Burridge, K., Fath, K., Kelly, T., Nuckolls, G. & Turner, C. Focal adhesions: transmembrane junctions between the extracellular matrix and the cytoskeleton. Annu. Rev. Cell Biol. 4, 487–525 (1988).
Campbell, I. D. Studies of focal adhesion assembly. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 36, 263–266 (2008).
Zamir, E. & Geiger, B. Molecular complexity and dynamics of cell–matrix adhesions. J. Cell Sci. 114, 3583–3590 (2001).
Zaidel-Bar, R., Itzkovitz, S., Ma'ayan, A., Iyengar, R. & Geiger, B. Functional atlas of the integrin adhesome. Nat. Cell Biol. 9, 858–867 (2007).
Legate, K. R., Wickstrom, S. A. & Fässler, R. Genetic and cell biological analysis of integrin outside–in signaling. Genes Dev. 23, 397–418 (2009).
Geiger, B., Spatz, J. P. & Bershadsky, A. D. Environmental sensing through focal adhesions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 10, 21–33 (2009).
Winograd-Katz, S. E., Itzkovitz, S., Kam, Z. & Geiger, B. Multiparametric analysis of focal adhesion formation by RNAi-mediated gene knockdown. J. Cell Biol. 186, 423–436 (2009).
Delon, I. & Brown, N. H. Integrins and the actin cytoskeleton. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 19, 43–50 (2007).
Feltkamp, C. A., Pijnenburg, M. A. & Roos, E. Organization of talin and vinculin in adhesion plaques of wet-cleaved chicken embryo fibroblasts. J. Cell Sci. 100, 579–587 (1991).
Nicol, A. et al. Labeling of structural elements at the ventral plasma membrane of fibroblasts with the immunogold technique. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 35, 499–506 (1987).
Rinnerthaler, G., Geiger, B. & Small, J. V. Contact formation during fibroblast locomotion: involvement of membrane ruffles and microtubules. J. Cell Biol. 106, 747–760 (1988).
Turner, C. E. & Miller, J. T. Primary sequence of paxillin contains putative SH2 and SH3 domain binding motifs and multiple LIM domains: identification of a vinculin and pp125Fak-binding region. J. Cell Sci. 107, 1583–1591 (1994).
Salgia, R. et al. Molecular cloning of human paxillin, a focal adhesion protein phosphorylated by P210BCR/ABL. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 5039–5047 (1995).
Medalia, O. et al. Macromolecular architecture in eukaryotic cells visualized by cryoelectron tomography. Science 298, 1209–1213 (2002).
Vogel, V. & Sheetz, M. Local force and geometry sensing regulate cell functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 7, 265–275 (2006).
Riveline, D. et al. Focal contacts as mechanosensors: externally applied local mechanical force induces growth of focal contacts by an mDia1-dependent and ROCK-independent mechanism. J. Cell Biol. 153, 1175–1186 (2001).
Chrzanowska-Wodnicka, M. & Burridge, K. Rho-stimulated contractility drives the formation of stress fibers and focal adhesions. J. Cell Biol. 133, 1403–1415 (1996).
Lo, S. H. Focal adhesions: what's new inside. Dev. Biol. 294, 280–291 (2006).
Petit, V. & Thiery, J. P. Focal adhesions: structure and dynamics. Biol. Cell 92, 477–494 (2000).
Singer, I. I. The fibronexus: a transmembrane association of fibronectin-containing fibers and bundles of 5 nm microfilaments in hamster and human fibroblasts. Cell 16, 675–685 (1979).
Waterman-Storer, C. M., Salmon, W. C. & Salmon, E. D. Feedback interactions between cell–cell adherens junctions and cytoskeletal dynamics in newt lung epithelial cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 11, 2471–2483 (2000).
Nicolas, A., Besser, A. & Safran, S. A. Dynamics of cellular focal adhesions on deformable substrates: consequences for cell force microscopy. Biophys. J. 95, 527–539 (2008).
Beningo, K. A. & Wang, Y. L. Flexible substrata for the detection of cellular traction forces. Trends Cell Biol. 12, 79–84 (2002).
Wolfenson, H. et al. A role for the juxtamembrane cytoplasm in the molecular dynamics of focal adhesions. PLoS One 4, e4304 (2009).
Zamir, E., Geiger, B. & Kam, Z. Quantitative multicolor compositional imaging resolves molecular domains in cell–matrix adhesions. PLoS ONE 3, e1901 (2008).
Frank, J. Electron Tomography (ed. Frank, J.) 1–13 (Plenum, 1992).
van Heel, M. Multivariate statistical classification of noisy images (randomly oriented biological macromolecules). Ultramicroscopy 13, 165–183 (1984).
Wolfenson, H., Henis, Y. I., Geiger, B. & Bershadsky, A. D. The heel and toe of the cell's foot: a multifaceted approach for understanding the structure and dynamics of focal adhesions. Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton 66, 1017–1029 (2009).
Jimenez, J., Santisteban, A., Carazo, J. M. & Carrascosa, J. L. Computer graphic display method for visualizing three-dimensional biological structures. Science 232, 1113–1115 (1986).
Avnur, Z. & Geiger, B. Substrate-attached membranes of cultured cells isolation and characterization of ventral cell membranes and the associated cytoskeleton. J. Mol. Biol. 153, 361–379 (1981).
Slot, J. W. & Geuze, H. J. A new method of preparing gold probes for multiple-labeling cytochemistry. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 38, 87–93 (1985).
Schwartz, M. A. & DeSimone, D. W. Cell adhesion receptors in mechanotransduction. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 20, 551–556 (2008).
Narumiya, S., Ishizaki, T. & Uehata, M. Use and properties of ROCK-specific inhibitor Y-27632. Methods Enzymol. 325, 273–284 (2000).
Katoh, K., Kano, Y. & Ookawara, S. Rho-kinase dependent organization of stress fibers and focal adhesions in cultured fibroblasts. Genes Cells 12, 623–638 (2007).
Cavalcanti-Adam, E. A. et al. Cell spreading and focal adhesion dynamics are regulated by spacing of integrin ligands. Biophys. J. 92, 2964–2974 (2007).
Finer, J. T., Simmons, R. M. & Spudich, J. A. Single myosin molecule mechanics: piconewton forces and nanometre steps. Nature 368, 113–119 (1994).
Betzig, E. et al. Imaging intracellular fluorescent proteins at nanometer resolution. Science 313, 1642–1645 (2006).
Dubochet, J. et al. Cryo-electron microscopy of vitrified specimens. Q. Rev. Biophys. 21, 129–228 (1988).
Sartori, A. et al. Correlative microscopy: bridging the gap between fluorescence light microscopy and cryo-electron tomography. J. Struct. Biol. 160, 135–145 (2007).
Slot, J. W. & Geuze, H. J. A new method of preparing gold probes for multiple-labeling cytochemistry. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 38, 87–93 (1985).
Avnur, Z. & Geiger, B. Substrate-attached membranes of cultured cells isolation and characterization of ventral cell membranes and the associated cytoskeleton. J. Mol. Biol. 153, 361–379 (1981).
Nickell, S. et al. TOM software toolbox: acquisition and analysis for electron tomography. J. Struct. Biol. 149, 227–234 (2005).
Frangakis, A. S. & Hegerl, R. Noise reduction in electron tomographic reconstructions using nonlinear anisotropic diffusion. J. Struct. Biol. 135, 239–250 (2001).
Hegerl, R. The EM Program Package: a platform for image processing in biological electron microscopy. J. Struct. Biol. 116, 30–34 (1996).
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a grant from the German-Israeli Cooperation Project (DIP H.2.2) to O. M., R. F., J. S. and B. G., an NIGMS grant from the National Institutes of Health Cell Migration Consortium (Grant No. U54 GM64346) to B. G. and an ERC Starting Grant to O. M. The authors express gratitude to B. Morgenstern for help in editing the manuscript. B. G. holds the Erwin Neter Professorial Chair in Cell and Tumor Biology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
I. P., N. E., T. V., C. G. and V. H. W. performed experimental work and analysed the data. B. G., J. S., R. F. and O. M. designed the experiments, analysed the data and prepared the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Information (PDF 857 kb)
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Information Movie 1 (MPG 4296 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patla, I., Volberg, T., Elad, N. et al. Dissecting the molecular architecture of integrin adhesion sites by cryo-electron tomography. Nat Cell Biol 12, 909–915 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2095
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2095
This article is cited by
-
Organization, dynamics and mechanoregulation of integrin-mediated cell–ECM adhesions
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2023)
-
A network of mixed actin polarity in the leading edge of spreading cells
Communications Biology (2022)
-
Adhesive-ligand-independent cell-shaping controlled by the lateral deformability of a condensed polymer matrix
Polymer Journal (2022)
-
A cryo-TSEM with temperature cycling capability allows deep sublimation of ice to uncover fine structures in thick cells
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
The cardiac nanoenvironment: form and function at the nanoscale
Biophysical Reviews (2021)