Abstract
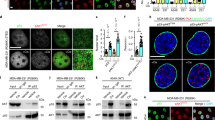
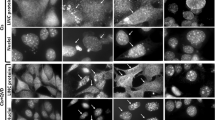
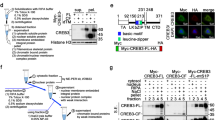
The ubiquitously expressed c-Abl tyrosine kinase localizes to the cytoplasm and nucleus1,2. Nuclear c-Abl is activated by diverse genotoxic agents and induces apoptosis3,4; however, the mechanisms that are responsible for nuclear targeting of c-Abl remain unclear. Here, we show that cytoplasmic c-Abl is targeted to the nucleus in the DNA damage response. The results show that c-Abl is sequestered into the cytoplasm by binding to 14-3-3 proteins. Phosphorylation of c-Abl on Thr 735 functions as a site for direct binding to 14-3-3 proteins. We also show that, in response to DNA damage, activation of the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (Jnk) induces phosphorylation of 14-3-3 proteins and their release from c-Abl. Together with these results, expression of an unphosphorylated 14-3-3 mutant attenuates DNA-damage-induced nuclear import of c-Abl and apoptosis. These findings indicate that 14-3-3 proteins are pivotal regulators of intracellular c-Abl localization and of the apoptotic response to genotoxic stress.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wen, S. T., Jackson, P. K. & Van Etten, R. A. The cytostatic function of c-Abl is controlled by multiple nuclear localization signals and requires the p53 and Rb tumor suppressor gene products. EMBO J. 15, 1583–1595 (1996).
Taagepera, S. et al. Nuclear-cytoplasmic shuttling of c-ABL tyrosine kinase. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 7457–7462 (1998).
Kharbanda, S. et al. Activation of the c-Abl tyrosine kinase in the stress response to DNA-damaging agents. Nature 376, 785–788 (1995).
Yuan, Z. M. et al. Regulation of DNA damage-induced apoptosis by the c-Abl tyrosine kinase. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 94, 1437–1440 (1997).
Wetzler, M. et al. Subcellular localization of Bcr, Abl, and Bcr-Abl proteins in normal and leukemic cells and correlation of expression with myeloid differentiation. J. Clin. Invest. 92, 1925–1939 (1993).
Raitano, A. B., Whang, Y. E. & Sawyers, C. L. Signal transduction by wild-type and leukemogenic Abl proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1333, F201–F216 (1997).
Vigneri, P. & Wang, J. Y. Induction of apoptosis in chronic myelogenous leukemia cells through nuclear entrapment of BCR–ABL tyrosine kinase. Nature Med. 7, 228–234 (2001).
Sun, X., Wu, F., Datta, R., Kharbanda, S. & Kufe, D. Interaction between protein kinase C delta and the c-Abl tyrosine kinase in the cellular response to oxidative stress. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 7470–7473 (2000).
Druker, B. J. et al. Effects of a selective inhibitor of the Abl tyrosine kinase on the growth of Bcr–Abl positive cells. Nature Med. 2, 561–566 (1996).
Yoshida, K., Komatsu, K., Wang, H. G. & Kufe, D. c-Abl tyrosine kinase regulates the human Rad9 checkpoint protein in response to DNA damage. Mol. Cell. Biol. 22, 3292–3300 (2002).
Gong, J. G. et al. The tyrosine kinase c-Abl regulates p73 in apoptotic response to cisplatin-induced DNA damage. Nature 399, 806–809 (1999).
Agami, R., Blandino, G., Oren, M. & Shaul, Y. Interaction of c-Abl and p73α and their collaboration to induce apoptosis. Nature 399, 809–813 (1999).
Yuan, Z. M. et al. p73 is regulated by tyrosine kinase c-Abl in the apoptotic response to DNA damage. Nature 399, 814–817 (1999).
Natsume, T. et al. A direct nanoflow liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry system for interaction proteomics. Anal. Chem. 74, 4725–4733 (2002).
Tzivion, G. & Avruch, J. 14-3-3 proteins: active cofactors in cellular regulation by serine/threonine phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 3061–3064 (2002).
Muslin, A. J. & Xing, H. 14-3-3 proteins: regulation of subcellular localization by molecular interference. Cell Signal. 12, 703–709 (2000).
Tsuruta, F. et al. JNK promotes Bax translocation to mitochondria through phosphorylation of 14-3-3 proteins. EMBO J. 23, 1889–1899 (2004).
Zha, J., Harada, H., Yang, E., Jockel, J. & Korsmeyer, S. J. Serine phosphorylation of death agonist BAD in response to survival factor results in binding to 14-3-3 not BCL-X(L). Cell 87, 619–628 (1996).
Zhang, L., Chen, J. & Fu, H. Suppression of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1-induced cell death by 14-3-3 proteins. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 96, 8511–8515 (1999).
Masuyama, N. et al. Akt inhibits the orphan nuclear receptor Nur77 and T-cell apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 32799–32805 (2001).
Muslin, A. J., Tanner, J. W., Allen, P. M. & Shaw, A. S. Interaction of 14-3-3 with signaling proteins is mediated by the recognition of phosphoserine. Cell 84, 889–897 (1996).
Yaffe, M. B. et al. The structural basis for 14-3-3:phosphopeptide binding specificity. Cell 91, 961–971 (1997).
Nomura, M. et al. 14-3-3 interacts directly with and negatively regulates pro-apoptotic Bax. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 2058–2065 (2003).
Aitken, A. et al. Specificity of 14-3-3 isoform dimer interactions and phosphorylation. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 30, 351–360 (2002).
Won, J. et al. Cleavage of 14-3-3 protein by caspase-3 facilitates bad interaction with Bcl-x(L) during apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 19347–19351 (2003).
Yoshida, K., Weichselbaum, R., Kharbanda, S. & Kufe, D. Role for Lyn tyrosine kinase as a regulator of stress-activated protein kinase activity in response to DNA damage. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20, 5370–5380 (2000).
Yoshida, K., Wang, H. G., Miki, Y. & Kufe, D. Protein kinase Cδ is responsible for constitutive and DNA damage-induced phosphorylation of Rad9. EMBO J. 22, 1431–1441 (2003).
Deng, Y., Ren, X., Yang, L., Lin, Y. & Wu, X. A JNK-dependent pathway is required for TNFα-induced apoptosis. Cell 115, 61–70 (2003).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the Ministry of Education, Science and Culture of Japan (K.Y. and Y.M.), the Mitsubishi Pharma Research Foundation (K.Y.), the Tokyo Biochemical Research Foundation (K.Y.), Uehara Memorial Foundation (K.Y.) and also by grants CA29431 and CA98628 from the National Cancer Institute (D.K.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Figures S1, S2, S3, S4 (PDF 111 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoshida, K., Yamaguchi, T., Natsume, T. et al. JNK phosphorylation of 14-3-3 proteins regulates nuclear targeting of c-Abl in the apoptotic response to DNA damage. Nat Cell Biol 7, 278–285 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1228
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1228
This article is cited by
-
FOXO transcription factors as mediators of stress adaptation
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2024)
-
MEK1/2 regulate normal BCR and ABL1 tumor-suppressor functions to dictate ATO response in TKI-resistant Ph+ leukemia
Leukemia (2023)
-
Exposure of the cytoplasm to low-dose X-rays modifies ataxia telangiectasia mutated-mediated DNA damage responses
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
PPIP5K2 promotes colorectal carcinoma pathogenesis through facilitating DNA homologous recombination repair
Oncogene (2021)
-
Combating acquired resistance to MAPK inhibitors in melanoma by targeting Abl1/2-mediated reactivation of MEK/ERK/MYC signaling
Nature Communications (2020)