Abstract
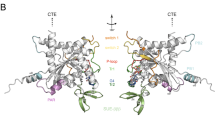
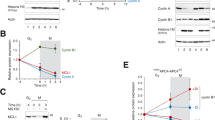
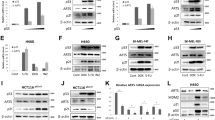
Here we describe a protein product of the human septin H5/PNUTL2/CDCrel2b gene, which we call ARTS (for apoptosis-related protein in the TGF-β signalling pathway). ARTS is expressed in many cells and acts to enhance cell death induced by TGF-β or, to a lesser extent, by other apoptotic agents. Unlike related septin gene products, ARTS is localized to mitochondria and translocates to the nucleus when apoptosis occurs. Mutation of the P-loop of ARTS abrogates its competence to activate caspase 3 and to induce apoptosis. Taken together, these observations expand the functional attributes of septins previously described as having roles in cytokinesis and cellular morphogenesis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thompson, C. B. Apoptosis in the pathogenesis and treatment of disease. Science 267, 1456–1462 ( 1995).
Vaux, D. L. & Korsmeyer, S. J. Cell death in development. Cell 96, 245– 254 (1999).
Nicholson, W. D. & Thornberry, N. A. Caspases: killer proteases. Trends Biochem. Sci. 257, 299–306 (1997).
Thornberry, N. A. & Lazebnik, Y. Caspases: enemies within. Science 281, 1312– 1316 (1998).
Zou, H., Henzel, W. J., Liu, X., Lutschg, A. & Wang, X. Apaf-1, a human protein homologous to C. elegans CED-4, participates in cytochrome c-dependent activation of caspase-3. Cell 90, 405– 413 (1997).
Liu, X., Zou, H., Slaughter, C. & Wang, X. DFF, a heterodimeric protein that functions downstream of caspase-3 to trigger DNA fragmentation during apoptosis. Cell 89, 175– 184 (1997).
Li, P. et al. Cytochrome c and dATP-dependent formation of Apaf-1/caspase-9 complex initiates an apoptotic protease cascade. Cell 91, 479–489 (1997).
Susin, S. A. et al. Molecular characterization of mitochondrial apoptosis-inducing factor. Nature 397, 441– 446 (1999).
Hsing, A. Y., Kadomatsu, K., Bonham, M. J. & Danielpour, D. Regulation of apoptosis induced by transforming growth factor-beta1 in nontumorigenic rat prostatic epithelial cell lines. Cancer Res. 56 , 5146–5149 (1996).
Haufel, T., Dormann, S., Hanusch, J., Schwieger, A. & Bauer, G. Three distinct roles for TGF-beta during intercellular induction of apoptosis: a review. Anticancer Res. 19,105–111 (1999).
Flanders, K. C. & Roberts, A. B. Transforming growth factor-β. Cytokine Reference (eds Oppenheim, J. J. et al.) (Academic, New York, 2000).
Massagué, J. & Chen, Y. G. Controlling TGF-beta signaling. Genes Dev. 14, 627– 644 (2000).
Hartsough, M. T. & Mulder, K. M. Transforming growth factor-beta signaling in epithelial cells. Pharmacol Ther. 75, 21–41 ( 1997).
Engel, M. E., McDonnell, M. A., Law, B. K. & Moses, H. L. Interdependent SMAD and JNK signaling in transforming growth factor-beta-mediated transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 37413 –37420 (1999).
Larisch-Bloch, S. et al. Selective loss of the transforming growth factor-beta apoptotic signaling pathway in mutant NRP-154 rat prostatic epithelial cells. Cell Growth Diferf. 11, 1–10 (2000).
Field, C. M. & Kellogg, D. Septins: cytoskeletal polymers or signalling GTPases? Trends Cell Biol. 9 , 387–394 (1999).
Xie, H., Surka, M., Howard, J. & Trimble, W. S. Characterization of the mammalian septin H5: distinct patterns of cytoskeletal and membrane association from other septin proteins. Cell Motil. Cytoskel. 43, 52–62 (1999).
McKie, J. M., Sutherland, H. F., Harvey, E., Kim, U. J. & Scambler, P. J. A human gene similar to Drosophila melanogaster peanut maps to the DiGeorge syndrome region of 22q11. Hum. Genet. 101, 6– 12 (1997).
Zieger, B., Hashimoto, Y. & Ware, J. Alternative expression of platelet glycoprotein Ib(beta) mRNA from an adjacent 5′ gene with an imperfect polyadenylation signal sequence. Clin. Invest. 99, 520– 525 (1997).
Saraste, M., Sibbald, P. R. & Wittinghofer, A. The P-loop — a common motif in ATP- and GTP-binding proteins. Trends Biochem. Sci. 11, 430– 434 (1990).
Aravind, L., Dixit, V. M. & Koonin, E. V. The domains of death: evolution of the apoptosis machinery. Trends Biochem. Sci. 24, 47– 53 (1999).
Yuan, J. & Horvitz, H. R. The Caenorhabditis elegans cell death gene ced-4 encodes a novel protein and is expressed during the period of extensive programmed cell death. Development 116, 309–320 ( 1992).
Chaudhary, D., O'Rourke, K., Chinnaiyan, A. M. & Dixit, V. M. The death inhibitory molecules CED-9 and CED-4L use a common mechanism to inhibit the CED-3 death protease. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 17708–17712 ( 1998).
Beites, C. L., Xie, H., Bowser, R. & Trimble, W. S. The septin CDCrel-1 binds syntaxin and inhibits exocytosis. Nature Neurosci. 2, 434–439 ( 1999).
Choi, K. S., Lim, I. K., Brady, J. N. & Kim, S. J. ICE-like protease (caspase) is involved in transforming growth factor beta1-mediated apoptosis in FaO rat hepatoma cell line. Hepatology 27, 415–421 (1998).
Tewari, M., Beidler, D. R. & Dixit, V. M. CrmA-inhibitable cleavage of the 70-kDa protein component of the U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein during Fas- and tumor necrosis factor-induced apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 18738– 18741 (1995).
Duckett, C. S. et al. Human IAP-like protein regulates programmed cell death downstream of Bcl-xL and cytochrome c. Mol. Cell Biol. 18, 608–615 (1998).
Atfi, A., Buisine, M., Mazars, A. & Gespach, C. Induction of apoptosis by DPC4, a transcriptional factor regulated by transforming growth factor-beta through stress-activated protein kinase/c-Jun N-terminal kinase (SAPK/JNK) signaling pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 24731–24734 (1997).
Landstrom, M. et al. Smad7 mediates apoptosis induced by transforming growth factor beta in prostatic carcinoma cells. Curr. Biol. 10, 535–538 (2000).
Yanagisawa, K. et al. Induction of apoptosis by Smad3 and down-regulation of Smad3 expression in response to TGF-beta in human normal lung epithelial cells. Oncogene 17, 1743–1747 ( 1998).
Chen, R. H., Su, Y. H., Chuang, R. L. & Chang, T. Y. Suppression of transforming growth factor-beta-induced apoptosis through a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt-dependent pathway. Oncogene 17, 1959–1968 (1998).
Wang, X. et al. Effect of truncated forms of the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein on intramitochondrial cholesterol transfer. Endocrinology 139, 3903–3912 ( 1998).
Verhagen, A. M. et al. Identification of DIABLO, a mammalian protein that promotes apoptosis by binding to and antagonizing IAP proteins. Cell 102, 43–53 (2000).
Du, C., Fang, M., Li, Y., Li, L. & Wang, X. Smac, a mitochondrial protein that promotes cytochrome c-dependent caspase activation by eliminating IAP inhibition. Cell 102, 33–42 ( 2000).
Deveraux, Q. L. & Reed, J. C. IAP family proteins — suppressors of apoptosis. Genes Dev. 13, 239–252 (1999).
Green, D. R. & Reed, J. C. Mitochondria and apoptosis . Science 281, 1309–1312 (1998).
Kinoshita M. et al. Nedd5, a mammalian septin, is a novel cytoskeletal component interacting with actin-based structures. Genes Dev. 11, 1535–1547 (1997).
Neufeld, T. P. & Rubin, G. M. The Drosophila peanut gene is required for cytokinesis and encodes a protein similar to yeast putative bud neck filament proteins. Cell 77, 371–379 (1994).
McCall, K. A. & Steller, H. Facing death in the fly: genetic analysis of apoptosis in Drosophila. Trends Genet. 13, 222–226 ( 1997).
Guo, M. & Hay, B. A. Cell proliferation and apoptosis . Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 11, 745– 752 (1999).
Rubin, Y., Kessler-Icekson, G. & Navon, G. The effect of furosemide on calcium ion concentration in myocardial cells. Cell Calcium 18,135 –139 (1995).
Acknowledgements
We thank M. Bloch for help and encouragement; D. Barzilai and Z. Ben-Ishai for support; Y. Ben-Neriah, A. Yaron, S. Gutkind and M. Zohar for discussions and advice; G. Yaniv and O. Binah for providing the neonatal ventricular myocytes; and N. Frumkin and A. H. Hsing for technical assistance. We thank D. B. Hales and K. H. Hales for providing the antiserum to recombinant murine StAR; the AU5–tag expression vector was provided by S. Gutkind; TGF-β receptor constructs were provided by J. Wrana and L. Attisano; and the p3TP–Lux construct was provided by J. Massagué. This work was supported by the Erna D. Leir Foundation for Research of Degenerative Brain Diseases, the National Alliance for Research of Schizophrenia and Depression, the National Parkinson Foundation Inc., the Israel Science Foundation funded by the Israel Academy of Sciences and Humanities (J.O.), and the NIH. H.S. is an investigator of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Larisch, S., Yi, Y., Lotan, R. et al. A novel mitochondrial septin-like protein, ARTS, mediates apoptosis dependent on its P-loop motif. Nat Cell Biol 2, 915–921 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/35046566
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/35046566
This article is cited by
-
DCAF12 promotes apoptosis and inhibits NF-κB activation by acting as an endogenous antagonist of IAPs
Oncogene (2022)
-
p53 induces ARTS to promote mitochondrial apoptosis
Cell Death & Disease (2021)
-
SEPTIN12 c.474 G > A polymorphism as a risk factor in teratozoospermic patients
Molecular Biology Reports (2021)
-
A small-molecule ARTS mimetic promotes apoptosis through degradation of both XIAP and Bcl-2
Cell Death & Disease (2020)
-
The pro-apoptotic ARTS protein induces neutrophil apoptosis, efferocytosis, and macrophage reprogramming to promote resolution of inflammation
Apoptosis (2020)