Abstract
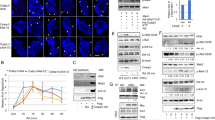
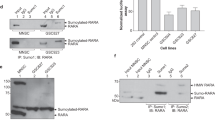
The retinoid–X receptor (RXR) regulates multiple hormonal pathways through heterodimerization with nuclear receptors such as the all-trans retinoic acid receptor (RAR). The orphan nuclear receptor NGFI-B (also called Nur77) can heterodimerize with RXR. Here we show that nerve growth factor (NGF) induces the phosphorylation of Ser 105 of NGFI-B in PC12 phaeochromocytoma cells, resulting in translocation of the NGFI-B–RXR heterodimer complex out of the nucleus using nuclear export signals within NGFI-B. As a consequence of the redistribution of RXR, the transcriptional activity of RXR–RAR is reduced. NGFI-B-mediated nuclear export of receptors may serve as a mechanism for crosstalk between NGF and retinoid pathways.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mangelsdorf, D. J. et al. The nuclear receptor superfamily: The second decade. Cell 83, 835–839 ( 1995).
Mangelsdorf, D. J. & Evans, R. M. The RXR heterodimers and orphan receptors. Cell 83, 841– 850 (1995).
Chambon, P. A decade of molecular biology of retinoic acid receptors. FASEB. J. 10, 940–954 ( 1996).
Milbrandt, J. Nerve growth factor induces a gene homologous to the glucocorticoid receptor gene. Neuron 1, 183–188 (1988).
Hazel, T. G., Nathans, D. & Lau, L. F. A gene inducible by serum growth factors encodes a member of the steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 85, 8444–8448 (1988).
Fahrner, T. J., Carroll, S. L. & Milbrandt, J. The NGFI-B protein, an inducible member of the thyroid/steroid receptor family, is rapidly modified posttranslationally. Mol. Cell. Biol. 10, 6454–6459 (1990).
Hazel, T. G., Misra, R., Davis, I. J., Greenberg, M. E. & Lau, L. F. Nur77 is differentially modified in PC12 cells upon membrane depolarization and growth factor treatment. Mol. Cell. Biol. 11, 3239–3246 ( 1991).
Wilson, T. E., Fahrner, T. J., Johnston, M. & Milbrandt, J. Identification of the DNA binding site for NGFI-B by genetic selection in yeast. Science 252, 1296– 1300 (1991).
Philips, A. et al. Novel dimeric Nur77 signaling mechanism in endocrine and lymphoid cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 17, 5946– 5951 (1997).
Forman, B. M., Umesono, K., Chen, J. & Evans, R. M. Unique response pathways are established by allosteric interactions among nuclear hormone receptors. Cell 81, 541– 550 (1995).
Perlmann, T. & Jansson, L. A novel pathway for vitamin A signaling mediated by RXR heterodimerization with NGFI-B and NURR1. Genes Dev. 9, 769–782 ( 1995).
Katagiri, Y., Hirata, Y., Milbrandt, J. & Guroff, G. Differential regulation of the transcriptional activity of the orphan nuclear receptor NGFI-B by membrane depolarization and NGF. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 31278–31284 ( 1997).
Wilson, T. E., Paulsen, R. E., Padgett, K. A. & Milbrandt, J. Participation of non-zinc finger residues in DNA binding by two nuclear orphan receptors. Science 256, 107– 110 (1992).
Wen, W., Meinkoth, J. L., Tsien, R. Y. & Taylor, S. S. Identification of a signal for rapid export of proteins from the nucleus. Cell 82, 463–473 ( 1995).
Fischer, U., Huber, J., Boelens, W. C., Mattaj, I. W. & Luhrmann, R. The HIV-1 Rev activation domain is a nuclear export signal that accesses an export pathway used by specific cellular RNAs. Cell 82, 475– 483 (1995).
Fukuda, M., Gotoh, I., Adachi, M., Gotoh, Y. & Nishida, E. A novel regulatory mechanism in the mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase cascade. Role of nuclear export signal of MAP kinase kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 32642– 32648 (1997).
Nishi, K. et al. Leptomycin B targets a regulatory cascade of crm1, a fission yeast nuclear protein, involved in control of higher order chromosome structure and gene expression. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 6320–6324 (1994).
Greene, L. A. & Kaplan, D. R. Early events in neurotrophin signalling via Trk and p75 receptors. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 5 , 579–587 (1995).
Koizumi, S. et al. K-252 a: a specific inhibitor of the action of nerve growth factor on PC 12 cells. J. Neurosci. 8, 715 –721 (1988).
Thomas, S. M., DeMarco, M., D’Arcangelo, G., Halegoua, S. & Brugge, J. S. Ras is essential for nerve growth factor-and phorbol ester-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of MAP kinases. Cell 68, 1031–1040 (1992).
Wu, Q. et al. Modulation of retinoic acid sensitivity in lung cancer cells through dynamic balance of orphan receptors nur77 and COUP-TF and their heterodimerization . EMBO J. 16, 1656–1669 (1997).
Nigg, E. A. Nucleocytoplasmic transport: signals, mechanisms and regulation. Nature 386, 779–787 ( 1997).
Jans, D. A. & Hubner, S. Regulation of protein transport to the nucleus: central role of phosphorylation. Physiol. Rev. 76, 651–685 (1996).
Kaffman, A., Rank, N. M., O’Neill, E. M., Huang, L. S. & O’Shea, E. K. The receptor Msn5 exports the phosphorylated transcription factor Pho4 out of the nucleus . Nature 396, 482–486 (1998).
Ben-Levy, R., Hooper, S., Wilson, R., Paterson, H. F. & Marshall, C. J. Nuclear export of the stress–activated protein kinase p38 mediated by its substrate MAPKAP kinase-2. Curr. Biol. 8, 1049–1057 ( 1998).
Torchia, J., Glass, C. & Rosenfeld, M. G. Co-activators and co-repressors in the integration of transcriptional responses. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 10, 373–383 (1998).
Blanco, J. C. et al. The histone acetylase PCAF is a nuclear receptor coactivator . Genes Dev. 12, 1638–1651 (1998).
Blumberg, B. & Evans, R. M. Orphan nuclear receptors-new ligands and new possibilities. Genes Dev. 12, 3149 –3155 (1998).
Chan, F. K., Zhang, J., Cheng, L., Shapiro, D. N. & Winoto, A. Identification of human and mouse p19, a novel CDK4 and CDK6 inhibitor with homology to p16 ink4. Mol. Cell Biol. 15, 2682–2688 (1995).
Jehn, B. M., Bielke, W., Pear, W. S. & Osborne, B. A. Protective effects of notch-1 on TCR-induced apoptosis. J. Immunol. 162, 635–638 (1999).
Rivest, S. & Rivier, C. Stress and interleukin-1 beta-induced activation of c-fos, NGFI-B and CRF gene expression in the hypothalamic PVN: comparison between Sprague-Dawley, Fisher-344 and Lewis rats. J. Neuroendocrinol. 6, 101–117 (1994).
Honkaniemi, J., Kononen, J., Kainu, T., Pyykonen, I. & Pelto-Huikko, M. Induction of multiple immediate early genes in rat hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus after stress. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 25, 234–241 ( 1994).
Zetterstrom, R. H., Williams, R., Perlmann, T. & Olson, L. Cellular expression of the immediate early transcription factors Nurr1 and NGFI-B suggests a gene regulatory role in several brain regions including the nigrostriatal dopamine system. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 41, 111–120 (1996).
Hamada, K. et al. H-2 RIIBP, a member of the nuclear hormone receptor superfamily that binds to both the regulatory element of major histocompatibility class I genes and the estrogen response element. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 86, 8289–8293 ( 1989).
Acknowledgements
We thank S. S. Simons (NIDDK, NIH), Y. Hirata (RIKEN, Japan), X. W. Liu (NICHD, NIH), and K. Ingham (American Red Cross) for helpful discussion and support. We are grateful to J. Milbrandt (Washington University, St Louis) for NGFI–B plasmid and monoclonal antibody, and to M. Yoshida (University of Tokyo, Japan) for leptomycin B. We also thank E. Mills and D. Balasundaram (NICHD, NIH) for critical comments for this manuscript.
This article is dedicated to G. Guroff, who died on 9 July 1999 as the result of an automobile accident.
Correspondence should be addressed to Y.K.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Katagiri, Y., Takeda, K., Yu, ZX. et al. Modulation of retinoid signalling through NGF-induced nuclear export of NGFI-B. Nat Cell Biol 2, 435–440 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/35017072
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/35017072
This article is cited by
-
RNA N6-methyladenosine modification mediates downregulation of NR4A1 to facilitate malignancy of cervical cancer
Cell & Bioscience (2022)
-
The orphan nuclear receptor NUR77 promotes trophoblast invasion at early pregnancy through paracrine placental growth factor
Journal of Molecular Medicine (2019)
-
Overview of the structure-based non-genomic effects of the nuclear receptor RXRα
Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters (2018)
-
Modulation of nongenomic activation of PI3K signalling by tetramerization of N-terminally-cleaved RXRα
Nature Communications (2017)
-
Nur77 exacerbates PC12 cellular injury in vitro by aggravating mitochondrial impairment and endoplasmic reticulum stress
Scientific Reports (2016)