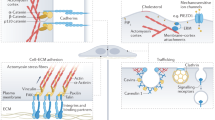
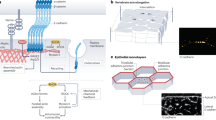
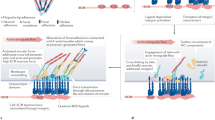
Abstract
Connections between the cytoskeleton and intercellular junctions profoundly influence cell shape and motility. It is becoming increasingly clear that in addition to structural functions, components of the adhesion apparatus also possess signalling capabilities. Recent studies suggest that their dual function may provide the means to integrate changes in morphology and gene expression during tissue and organ development.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hogan, B. L. Morphogenesis. Cell 96, 225–233 (1999).
Yap, A. S., Brieher W. M. & Gumbiner B. M. Molecular and functional analysis of cadherin-based adherens junctions. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 13, 119–146 (1997).
Chen, Y. T., Stewart, D. B. & Nelson, W. J. Coupling assembly of the E-cadherin/beta-catenin complex to efficient endoplasmic reticulum exit and basal-lateral membrane targeting of E-cadherin in polarized MDCK cells. J. Cell Biol. 4, 687–699 (1994).
Aberle, H. et al. Assembly of the cadherin–catenin complex in vitro with recombinant proteins. J. Cell Sci. 107, 3655–3663 (1994).
Huber O., Krohn M. & Kemler R. A specific domain in alpha-catenin mediates binding to beta-catenin or plakoglobin. J. Cell Sci. 110, 1759–1765 (1994).
Vasioukhin, V., Bauer, C., Yin, M. & Fuchs, E. Directed actin polymerization is the driving force for epithelial cell–cell adhesion. Cell 100, 209–219 (2000).
Giancotti, F. G. & Ruoslahti, E. Integrin signalling. Science 285, 1028–1032 (1999).
Reinhard, M., Jarchau, T. & Walter, U. Actin-based motility: stop and go with Ena/VASP proteins. Trends Biochem. Sci. 26, 243–249 (2001).
Taylor, K. A. & Taylor, D. W. Formation of two-dimensional complexes of F-actin and crosslinking proteins on lipid monolayers: demonstration of unipolar α-actinin–F-actin crosslinking. Biophys. J. 67, 1976–1983 (1994).
Reynolds, A. B. et al. Identification of a new catenin: the tyrosine kinase substrate p120cas associates with E-cadherin complexes. Mol. Cell Biol. 14, 8333–8342 (1994).
Anastasiadis, P. Z. & Reynolds, A. B. The p120 catenin family: complex roles in adhesion, signalling and cancer. J. Cell Sci. 113, 1319–1334 (2000).
Kowalczyk, A. P., Bornslaeger, E. A., Norvell, S. M., Palka, H. L. & Green, K. J. Desmosomes: intercellular adhesive junctions specialized for attachment of intermediate filaments. Int. Rev. Cytol. 185, 237–302 (1999).
Stappenbeck, T. S., Lamb, J. A., Corcoran, C. M. & Green, K. J. Phosphorylation of the desmoplakin COOH terminus negatively regulates its interaction with keratin intermediate filament networks. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 29351–29354 (1994).
Kouklis, P. D., Hutton, E. & Fuchs, E. Making a connection: direct binding between keratin intermediate filaments and desmosomal proteins. J. Cell Biol. 127, 1049–1060 (1994).
Smith, E. A. & Fuchs, E. Defining the interactions between intermediate filaments and desmosomes. J. Cell Biol. 141, 1229–1241 (1998).
Bierkamp, C, Schwarz, H., Huber O. & Kemler R. Desmosomal localization of β-catenin in the skin of plakoglobin null-mutant mice. Development 126, 371–381 (1999).
Hatsell, S. & Cowin, P. Deconstructing desmoplakin. Nature Cell Biol. 3, E270–E272 (2001).
Adams, C. L., Chen, Y. T., Smith, S. J. & Nelson, W. J. Mechanisms of epithelial cell–cell adhesion and cell compaction revealed by high-resolution tracking of E-cadherin–green fluorescent protein. J. Cell Biol. 142, 1105–1119 (1998).
Yonemura, S., Itoh, M., Nagafuchi, A. & Tsukita, S. Cell-to-cell adherens junction formation and actin filament organization: similarities and differences between non-polarized fibroblasts and polarized epithelial cells. J. Cell Sci. 108, 127–142 (1995).
Vasioukhin, V., Bauer, C., Degenstein, L., Wise, B. & Fuchs, E. Hyperproliferation and defects in epithelial polarity upon conditional ablation of α-catenin in skin. Cell 104, 605–617 (2001).
Raich, W. B., Agbunag, C. & Hardin, J. Rapid epithelial-sheet sealing in the Caenorhabditis elegans embryo requires cadherin-dependent filopodial priming. Curr. Biol. 9, 1139–1146 (1999).
Martin-Blanco, E., Pastor-Pareja, J. C. & Garcia-Bellido, A. JNK and decapentaplegic signalling control adhesiveness and cytoskeleton dynamics during thorax closure in Drosophila. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 97, 7888–7893 (2000).
Tanaka-Matakatsu, M., Uemura, T., Oda, H., Takeichi, M. & Hayashi, S. Cadherin-mediated cell adhesion and cell motility in Drosophila trachea regulated by the transcription factor Escargot. Development 122, 3697–3705 (1996).
Vasioukhin, V., Bowers, E., Bauer, C., Degenstein, L. & Fuchs, E. Desmoplakin is essential in epidermal sheet formation. Nature Cell Biol. 3, 1076–1085 (2001).
Hall, A. & Nobes, C. D. Rho GTPases: molecular switches that control the organization and dynamics of the actin cytoskeleton. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B. 355, 965–970 (2000).
Nakagawa, M., Fukata, M., Yamaga, M., Itoh, N. & Kaibuchi, K. Recruitment and activation of Rac1 by the formation of E-cadherin-mediated cell–cell adhesion sites. J. Cell Sci. 114, 1829–1838 (2001).
Fukata, M. et al. Cdc42 and Rac1 regulate the interaction of IQGAP1 with β-catenin. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 26044–26050 (1999).
Sander, E. E. et al. Matrix-dependent Tiam1/Rac signalling in epithelial cells promotes either cell–cell adhesion or cell migration and is regulated by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. J. Cell Biol. 143, 1385–1398 (1998).
Kovacs, E. M, Ali, R. G., McCormack, A. J. & Yap, A. S. E-cadherin Homophilic Ligation Directly Signals through Rac and Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase to Regulate Adhesive Contacts. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 6708–6718 (2002).
Kodama, A., Takaishi, K., Nakano, K., Nishioka, H. & Takai, Y. Involvement of Cdc42 small G protein in cell–cell adhesion, migration and morphology of MDCK cells. Oncogene 18, 3996–4006 (1999).
Kim, S. H., Li, Z. & Sacks, D. B. E-cadherin-mediated cell–cell attachment activates Cdc42. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 36999–37005 (2000).
Jacinto, A. et al. Dynamic actin-based epithelial adhesion and cell matching during Drosophila dorsal closure. Curr. Biol. 10, 1420–1426 (2000).
Izumi, Y. et al. An atypical PKC directly associates and colocalizes at the epithelial tight junction with ASIP, a mammalian homologue of Caenorhabditis elegans polarity protein PAR-3. J. Cell Biol. 143, 95–106 (1998).
Ohno, S. Intercellular junctions and cellular polarity: the PAR–aPKC complex, a conserved core cassette playing fundamental roles in cell polarity. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 13, 641–648 (2001).
Pollard, T. D., Blanchoin, L. & Mullins, R. D. Molecular mechanisms controlling actin filament dynamics in nonmuscle cells. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 29, 545–576 (2000).
Chausovsky, A., Bershadsky, A. D. & Borisy, G. G. Cadherin-mediated regulation of microtubule dynamics. Nature Cell Biol. 2, 797–804 (2000).
Le Borgne, R., Bellaiche, Y. & Schweisguth, F. Drosophila E-cadherin regulates the orientation of asymmetric cell division in the sensory organ lineage. Curr. Biol. 12, 95–104 (2002).
Munemitsu, S. et al. The APC gene product associates with microtubules in vivo and promotes their assembly in vitro. Cancer Res. 54, 3676–3681 (1994).
Karakesisoglou, I., Yang, Y. & Fuchs, E. An epidermal plakin that integrates actin and microtubule networks at cellular junctions. J. Cell Biol. 149, 195–208 (2000).
Lu, B., Roegiers, F., Jan, L. Y. & Jan, Y. N. Adherens junctions inhibit asymmetric division in the Drosophila epithelium. Nature 409, 522–525 (2001).
Ligon, L. A., Karki, S., Tokito, M. & Holzbaur, E. L. Dynein binds to β-catenin and may tether microtubules at adherens junctions. Nature Cell Biol. 3, 913–917 (2001).
Larue, L., Ohsugi, M., Hirchenhain, J. & Kemler, R. E-cadherin null mutant embryos fail to form a trophectoderm epithelium. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 91, 8263–8267 (1994).
Torres, M. et al. An α-E-catenin gene trap mutation defines its function in preimplantation development. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 94, 901–906 (1997).
Haegel, H. et al. Lack of β-catenin affects mouse development at gastrulation. Development 121, 3529–3537 (1995).
Cadigan, K. M. & Nusse, R. Wnt signalling: a common theme in animal development. Genes Dev. 11, 3286–305 (1997).
Garcia-Castro, M. I., Vielmetter, E. & Bronner-Fraser, M. N-Cadherin, a cell adhesion molecule involved in establishment of embryonic left–right asymmetry. Science 288, 1047–1051 (2000).
Huelsken, J., Vogel, R., Erdmann, B., Cotsarelis, G. & Birchmeier, W. β-Catenin controls hair follicle morphogenesis and stem cell differentiation in the skin. Cell 105, 533–545 (2001).
Ruiz, P, et al. Targeted mutation of plakoglobin in mice reveals essential functions of desmosomes in the embryonic heart. J. Cell Biol. 135, 215–225 (1996).
Koch, P. J. et al. Targeted disruption of the pemphigus vulgaris antigen (desmoglein 3) gene in mice causes loss of keratinocyte cell adhesion with a phenotype similar to pemphigus vulgaris. J. Cell Biol. 137, 1091–1102 (1997).
Chidgey M, et al. Mice lacking desmocollin 1 show epidermal fragility accompanied by barrier defects and abnormal differentiation. J. Cell Biol. 155, 821–832 (2001).
Gallicano, G. I. et al. Desmoplakin is required early in development for assembly of desmosomes and cytoskeletal linkage. J. Cell Biol. 143, 2009–2022 (1998).
Gallicano, G. I., Bauer, C. & Fuchs, E. Rescuing desmoplakin function in extra-embryonic ectoderm reveals the importance of this protein in embryonic heart, neuroepithelium, skin and vasculature. Development 128, 929–941 (2001).
Runswick, S. K., O'Hare, M. J., Jones, L., Streuli, C. H. & Garrod, D. R. Desmosomal adhesion regulates epithelial morphogenesis and cell positioning. Nature Cell Biol. 3, 823–830 (2001).
Heasman, J. et al. Overexpression of cadherins and underexpression of β-catenin inhibit dorsal mesoderm induction in early Xenopus embryos. Cell 79, 791–803 (1994).
Fagotto, F., Funayama, N., Gluck, U. & Gumbiner, B. M. Binding to cadherins antagonizes the signalling activity of β-catenin during axis formation in Xenopus. J. Cell Biol. 132, 1105–1114 (1996).
Sanson, B., White, P. & Vincent, J. P. Uncoupling cadherin-based adhesion from wingless signalling in Drosophila. Nature 383, 627–630 (1996).
Brieher, W. M., Yap, A. S. & Gumbiner, B. M. Lateral dimerization is required for the homophilic binding activity of C-cadherin. J. Cell Biol. 135, 487–496 (1996).
Zhong, Y., Brieher, W. M. & Gumbiner, B. M. Analysis of C-cadherin regulation during tissue morphogenesis with an activating antibody. J. Cell Biol. 144, 351–359 (1999).
Hardy, M. H. The secret life of the hair follicle. Trends Genet. 8, 55–61 (1992).
Fuchs, E., Merrill, B. J., Jamora, C. & DasGupta, R. At the roots of a never-ending cycle. Dev. Cell 1, 13–25 (2001).
Hardy, M. H. & Vielkind, U. Changing patterns of cell adhesion molecules during mouse pelage hair follicle development. 1. Follicle morphogenesis in wild-type mice. Acta Anat. (Basel) 157, 169–82 (1996).
Radice, G. L. et al. Precocious mammary gland development in P-cadherin-deficient mice. J. Cell Biol. 139, 1025–1032 (1997).
Gumbiner, B. M. Regulation of cadherin adhesive activity. J. Cell Biol. 148, 399–404 (2000).
Hinck, L., Nelson, W. J. & Papkoff, J. Wnt-1 modulates cell–cell adhesion in mammalian cells by stabilizing β-catenin binding to the cell adhesion protein cadherin. J. Cell Biol. 124, 729–741 (1994).
Bradley, R. S., Cowin, P. & Brown, A. M. Expression of Wnt-1 in PC12 cells results in modulation of plakoglobin and E-cadherin and increased cellular adhesion. J. Cell Biol. 123, 1857–1865 (1993).
Yanagawa S, et al. Accumulation of Armadillo induced by Wingless, Dishevelled, and dominant-negative Zeste-White 3 leads to elevated DE-cadherin in Drosophila clone 8 wing disc cells. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 25243–25251 (1997).
Wong, M. H., Rubinfeld, B. & Gordon, J. I. Effects of forced expression of an NH2-terminal truncated β-Catenin on mouse intestinal epithelial homeostasis. J. Cell Biol. 141, 765–777 (1998).
Gat, U., DasGupta, R., Degenstein, L. & Fuchs, E. De novo hair follicle morphogenesis and hair tumors in mice expressing a truncated β-catenin in skin. Cell 95, 605–614 (1998).
DasGupta, R. & Fuchs, E. Multiple roles for activated LEF/TCF transcription complexes during hair follicle development and differentiation. Development 126, 4557–4568 (1999).
Imbert, A., Eelkema, R., Jordan, S., Feiner, H. & Cowin, P. Delta N89 β-catenin induces precocious development, differentiation, and neoplasia in mammary gland. J. Cell Biol. 153, 555–568 (2001).
Huber, O. et al. Nuclear localization of β-catenin by interaction with transcription factor LEF-1. Mech. Dev. 59, 3–10 (1996).
Comijn, J. et al. The two-handed E box binding zinc finger protein SIP1 downregulates E-cadherin and induces invasion. Mol. Cell 7, 1267–1278 (2001).
Perez-Moreno, M. A. et al. A new role for E12/E47 in the repression of E-cadherin expression and epithelial–mesenchymal transitions. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 27424–27431 (2001).
Ciruna, B. & Rossant, J. FGF signalling regulates mesoderm cell fate specification and morphogenetic movement at the primitive streak. Dev. Cell 1, 37–49 (2001).
Nieto, M. A., Bennett, M. F., Sargent, M. G. & Wilkinson, D. G. Cloning and developmental expression of Sna, a murine homologue of the Drosophila snail gene. Development 116, 227–237 (1992).
Smith, D. E., Franco del Amo, F. & Gridley, T. Isolation of Sna, a mouse gene homologous to the Drosophila genes snail and escargot: its expression pattern suggests multiple roles during postimplantation development. Development 116, 1033–1039 (1992).
Huelsken, J. & Birchmeier, W. New aspects of Wnt signalling pathways in higher vertebrates. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 11, 547–553 (2001).
Sandoval, R. et al. Ca(2+) signalling and PKCα activate increased endothelial permeability by disassembly of VE-cadherin junctions. J. Physiol. 533, 433–445 (2001).
Winklbauer, R., Medina, A., Swain, R. K. & Steinbeisser, H. Frizzled-7 signalling controls tissue separation during Xenopus gastrulation. Nature 413, 856–860 (2001).
Medina, A., Reintsch, W. & Steinbeisser, H. Xenopus Frizzled 7 can act in canonical and non-canonical Wnt signalling pathways: implications on early patterning and morphogenesis. Mech. Dev. 92, 227–237 (2000).
Willert, K., Brink, M., Wodarz, A., Varmus, H. & Nusse, R. Casein kinase 2 associates with and phosphorylates dishevelled. EMBO J. 16, 3089–3096 (1997).
Lickert, H., Bauer, A., Kemler, R. & Stappert, J. Casein kinase II phosphorylation of E-cadherin increases E-cadherin–β-catenin interaction and strengthens cell–cell adhesion. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 5090–5095 (2000).
Gao, Z. H., Seeling, J. M., Hill, V., Yochum, A. & Virshup, D. M. Casein kinase I phosphorylates and destabilizes the β-catenin degradation complex. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 99, 1182–1187 (2002).
Hoschuetzky, H., Aberle, H. & Kemler, R. β-catenin mediates the interaction of the cadherin–catenin complex with epidermal growth factor receptor. J. Cell Biol. 127, 1375–1380 (1994).
Brady-Kalnay, S. M., Rimm, D. L. & Tonks, N. K. Receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase PTPmu associates with cadherins and catenins in vivo. J. Cell Biol. 130, 977–986 (1995).
Shibamoto, S. et al. Tyrosine phosphorylation of β-catenin and plakoglobin enhanced by hepatocyte growth factor and epidermal growth factor in human carcinoma cells. Cell Adhes. Commun. 1, 295–305 (1994).
Reynolds, A. B., Roesel, D. J., Kanner, S. B. & Parsons, J. T. Transformation-specific tyrosine phosphorylation of a novel cellular protein in chicken cells expressing oncogenic variants of the avian cellular src gene. Mol. Cell Biol. 9, 629–638 (1989).
Vleminckx, K. & Kemler, R. Cadherins and tissue formation: integrating adhesion and signalling. Bioessays 21, 211–220 (1999).
Hermiston, M. L., Wong, M. H. & Gordon, J. I. Forced expression of E-cadherin in the mouse intestinal epithelium slows cell migration and provides evidence for nonautonomous regulation of cell fate in a self-renewing system. Genes Dev. 10, 985–996 (1996).
Perl, A. K., Wilgenbus, P., Dahl, U., Semb, H. & Christofori, G. A causal role for E-cadherin in the transition from adenoma to carcinoma. Nature 392, 190–193 (1998).
Orsulic, S., Huber, O., Aberle, H., Arnold, S. & Kemler, R. E-cadherin binding prevents β-catenin nuclear localization and β-catenin/LEF-1-mediated transactivation. J. Cell Sci. 112, 1237–1245 (1999).
Gottardi, C. J., Wong, E. & Gumbiner, B. M. E-cadherin suppresses cellular transformation by inhibiting β-catenin signalling in an adhesion-independent manner. J. Cell Biol. 153, 1049–1060 (2001).
Stockinger, A., Eger, A., Wolf, J., Beug, H. & Foisner, R. E-cadherin regulates cell growth by modulating proliferation-dependent β-catenin transcriptional activity. J. Cell Biol. 154, 1185–1196 (2001).
Morton, R. A., Ewing, C. M., Nagafuchi, A., Tsukita, S. & Isaacs, W. B. Reduction of E-cadherin levels and deletion of the α-catenin gene in human prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 53, 3585–3590 (1993).
Kallakury, B. V. et al. Decreased expression of catenins (α and β), p120 CTN, and E-cadherin cell adhesion proteins and E-cadherin gene promoter methylation in prostatic adenocarcinomas. Cancer 92, 2786–2795 (2001).
Takahashi, N., Ishihara, S., Takada, S., Tsukita, S. & Nagafuchi, A. Posttranscriptional regulation of α-catenin expression is required for Wnt signalling in L cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 277, 691–698 (2000).
van Hengel, J., Vanhoenacker, P., Staes, K. & van Roy, F. Nuclear localization of the p120(ctn) Armadillo-like catenin is counteracted by a nuclear export signal and by E-cadherin expression. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 96, 7980–7985 (1999).
Kim, S. W. et al. Isolation and characterization of XKaiso, a transcriptional repressor that associates with the catenin Xp120ctn in Xenopus laevis. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 8208–8208 (2002).
Beckerle, M. C. Zyxin: zinc fingers at sites of cell adhesion. Bioessays 19, 949–957 (1997).
Bach, I. The LIM domain: regulation by association. Mech. Dev. 91, 5–17 (2000).
Petit M. M. et al. LPP, an actin cytoskeleton protein related to zyxin, harbors a nuclear export signal and transcriptional activation capacity. Mol. Biol. Cell 11, 117–129 (2000).
Kanungo, J., Pratt, S. J., Marie, H. & Longmore, G. D. Ajuba, a cytosolic LIM protein, shuttles into the nucleus and affects embryonalcell proliferation and fate decisions. Mol. Biol. Cell 11, 3299–3313 (2000).
Rajasekaran, A. K., Hojo, M., Huima, T. & Rodriguez-Boulan, E. Catenins and zonula occludens-1 form a complex during early stages in the assembly of tight junctions. J. Cell Biol. 132, 451–463 (1996).
Itoh, M., Nagafuchi, A., Moroi, S. & Tsukita, S. Involvement of ZO-1 in cadherin-based cell adhesion through its direct binding to α catenin and actin filaments. J. Cell Biol. 138, 181–192 (1997).
Balda, M. S. & Matter, K. The tight junction protein ZO-1 and an interacting transcription factor regulate ErbB-2 expression. EMBO J. 19, 2024–2033 (2000).
Miravet S., et al. The transcriptional factor Tcf-4 contains different binding sites for β-catenin and plakoglobin. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 1884–1891 (2002).
Charpentier, E., Lavker, R. M., Acquista, E. & Cowin, P. Plakoglobin suppresses epithelial proliferation and hair growth in vivo. J. Cell Biol. 149, 503–520 (2000).
Acknowledgements
We thank members of the Fuchs lab for comments on the manuscript.
We also thank C. Bauer, S. Raghavan, A. Vaezi, C. Adams and W.J. Nelson for the use of their figures.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jamora, C., Fuchs, E. Intercellular adhesion, signalling and the cytoskeleton. Nat Cell Biol 4, E101–E108 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb0402-e101
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb0402-e101
This article is cited by
-
Creating complex protocells and prototissues using simple DNA building blocks
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Increasing cancer permeability by photodynamic priming: from microenvironment to mechanotransduction signaling
Cancer and Metastasis Reviews (2022)
-
Ovarian microcystic stromal tumor with omental metastasis: the first case report and literature review
Journal of Ovarian Research (2021)
-
The effects of 808-nm near-infrared laser light irradiation on actin cytoskeleton reorganization in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
Cell and Tissue Research (2021)
-
Wnt-driven LARGE2 mediates laminin-adhesive O-glycosylation in human colonic epithelial cells and colorectal cancer
Cell Communication and Signaling (2020)