Abstract
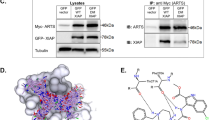
The inhibitors of apoptosis (IAPs) suppress apoptosis through the inhibition of the caspase cascade and thus are key proteins in the control of cell death. Here we have isolated the protein XIAP-associated factor 1 (XAF1) on the basis of its ability to bind XIAP, a member of the IAP family. XIAP suppresses caspase activation and cell death in vitro, and XAF1 antagonizes these XIAP activities. Expression of XAF1 triggers a redistribution of XIAP from the cytosol to the nucleus. XAF1 is ubiquitously expressed in normal tissues, but is present at low or undetectable levels in many different cancer cell lines. Loss of control over apoptotic signalling is now recognized as a critical event in the development of cancer. Our results indicate that XAF1 may be important in mediating the apoptosis resistance of cancer cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roy, N. et al. The gene for neuronal apoptosis inhibitory protein is partially deleted in individuals with spinal muscular atrophy. Cell 80, 167–178 (1995).
Rothe, M., Pan, M., Henzel, W. L. ., Ayres, T. M. & Goeddel, D. V. The TNFR2-TRAF signaling complex contains two novel proteins related to baculoviral inhibitor of apoptosis proteins. Cell 83, 1243–1252 (1995).
Liston, P. et al. Suppression of apoptosis in mammalian cells by NAIP and a related family of IAP genes. Nature 379, 349–353 (1996).
Duckett, C. S. et al. A conserved family of cellular genes related to the baculovirus iap gene and encoding apoptosis inhibitors. EMBO J. 15, 2685–2694 (1996).
Uren, A. G., Pakusch, M., Hawkins, C. J., Puls, K. L. & Vaux, D. L. Cloning and expression of apoptosis inhibitory protein homologues that function to inhibit apoptosis and/or bind tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factors. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 93, 4974–4978 (1996).
Ambrosini, G., Adida, C. & Altieri, D.C. A novel anti-apoptosis gene, survivin, expressed in cancer and lymphoma. Nature Med. 3, 917–921 (1997).
Deveraux, Q. L., Takahashi, R., Salvesen, G. S. & Reed, J. C. X-linked IAP is a direct inhibitor of cell death proteases. Nature 388, 300–304 (1997).
Roy, N., Deveraux, Q. L., Takahashi, R., Salvesen, G. S. & Reed, J. C. The c-IAP-1 and c-IAP-2 proteins are direct inhibitors of specific caspases. EMBO J. 16, 6914–6925 (1997).
Deveraux, Q. L. et al. IAPs block apoptotic events induced by caspase-8 and cytochrome c by direct inhibition of distinct caspases. EMBO J. 17, 2215–2223 (1998).
Takahashi, R. et al. A single BIR domain of XIAP sufficient for inhibiting caspases. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 7787–7790 (1998).
Kobayashi, K., Hatano, M., Otaki, M., Ogasawara, T. & Tokuhisa, T. Expression of a murine homologue of the inhibitor of apoptosis protein is related to cell proliferation. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 96, 1457–1462 (1999).
Tamm, I. et al. IAP-family protein survivin inhibits caspase activity and apoptosis induced by Fas (CD95), Bax, caspases, and anticancer drugs. Cancer Res. 58, 5315–5320 (1998).
Deveraux, Q. L. et al. Cleavage of human inhibitor of apoptosis protein XIAP results in fragments with distinct specificities for caspases. EMBO J. 18, 5242–5251 (1999).
Yang, Y., Fang, S., Jensen, J.P., Weissman, A. M. & Ashwell, J. D. Ubiquitin protein ligase activity of IAPs and their degradation in proteosomes in response to apoptotic stimuli. Science 288, 874–877 (2000).
Huang, H.-K. et al. The inhibitor of apoptosis, cIAP2, functions as a ubiquitin-protein ligase and promotes in vitro monoubiquitination of caspases 3 and 7. J. Biol. Sci. 275, 26661–26664 (2000).
Yamaguchi, K. et al. XIAP, a cellular member of the inhibitor of apoptosis protein family, links the receptors to TAB1-TAK1 in the BMP signaling pathway. EMBO J. 18,179–187.
Hofer-Warbinek, R. et al. Activation of NF-Kappa B by XIAP, the X chromosome-linked inhibitor of apoptosis, in endothelial cells involves TAK1. J. Biol. Sci. 275, 22064–22068 (2000).
Fong, W. G. et al. Expression and genetic analysis of XIAP associated factor 1 (XAF1) in cancer cell lines. Genomics 70, 113–122 (2000).
Alam, A., Cohen, L. Y., Aouad, S. & Sekaly, R. P. Early activation of caspases during T lymphocyte stimulation results in selective substrate cleavage in nonapoptotic cells. J. Exp. Med. 190, 1879–1890 (1999).
Kennedy, N. J., Kataoka, T., Tschopp, J. & Budd, R. C. caspase activation is required for T cell proliferation. J. Exp. Med. 190, 1891–1896 (1999).
Shu, H.-B., Takeuchi, M. & Goeddel, D. V. The tumor necrosis factor receptor 2 signal transducers TRAF2 and c-IAP1 are components of the tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 signaling complex. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 93, 13973–13978 (1996).
Vucic, D., Kaiser, W. J. & Miller, L. K. Inhibitor of apoptosis proteins physically interact with and block apoptosis induced by Drosophila proteins HID and GRIM. Mol. Cell Biol. 18, 3300–3309 (1998).
Goyal, L., McCall, K., Apapite, J., Hartwieg, E. & Steller, H. Induction of apoptosis by Drosophila reaper, hid and grim through inhibition of IAP function. EMBO J. 19, 589–597 (2000).
Wang, S. L., Hawkins, C. J., Yoo, S. J., Muller, H. A. J. & Hay, B. A. The Drosophila caspase inhibitor DIAP1 is essential for cell survival and is negatively regulated by HID. Cell 98, 453–463 (1999).
Du, C., Fang, M., Li, Y., Li, L. & Wang, X. Smac, a mitochondrial protein that promotes cytochrome c-dependent caspase activation by eliminating IAP inhibition. Cell 102, 33–42 (2000).
Verhagen, A. M. et al. Identification of DIABLO, a mammalian protein that promotes apoptosis by binding to and antagonizing IAP proteins. Cell 102, 43–53 (2000).
Miyake, S. et al. Efficient generation of recombinant adenoviruses using adenovirus DNA-terminal protein complex and a cosmid bearing the full-length virus genome. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 93, 1320–1324 (1996).
Li, J. et al. Expression of inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (IAPs) in rat granulosa cells during ovarian follicular development and atresia. Endocrinology 139, 1321–1328 (1998).
Xu, D. G. et al. Elevation of neuronal expression of NAIP reduces ischemic damage in the rat hippocampus. Nature Med. 3, 997–1004 (1997).
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank the University of California San Francisco / Neurosurgery Tissue Bank for the SF-295 and SF-539 cell lines. P.L. is a Centennial Fellow of the Medical Research Council of Canada. This work was supported by grants to R.G.K. from the Networks of Centers of Excellence Canadian Genetic Diseases Network (CGDN), the Medical Research Council of Canada (MRC), and the Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI). R.G.K. is a recipient of an MRC senior scientist award, a HHMI International Research Scholar, and a Fellow of the Royal Society of Canada.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liston, P., Fong, W., Kelly, N. et al. Identification of XAF1 as an antagonist of XIAP anti-Caspase activity. Nat Cell Biol 3, 128–133 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/35055027
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/35055027
This article is cited by
-
XAF1 destabilizes estrogen receptor α through the assembly of a BRCA1-mediated destruction complex and promotes estrogen-induced apoptosis
Oncogene (2022)
-
XAF1 drives apoptotic switch of endoplasmic reticulum stress response through destabilization of GRP78 and CHIP
Cell Death & Disease (2022)
-
DCAF12 promotes apoptosis and inhibits NF-κB activation by acting as an endogenous antagonist of IAPs
Oncogene (2022)
-
Comprehensive genomic profiling of EWSR1/FUS::CREB translocation-associated tumors uncovers prognostically significant recurrent genetic alterations and methylation-transcriptional correlates
Modern Pathology (2022)
-
Diverse maturity-dependent and complementary anti-apoptotic brakes safeguard human iPSC-derived neurons from cell death
Cell Death & Disease (2022)