Abstract
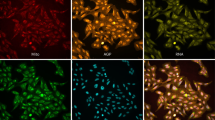
With the publication of the sequence of the human genome, we are challenged to identify the functions of an estimated 70,000 human genes1,2 and the much larger number of proteins encoded by these genes. Of particular interest is the identification of gene products that play a role in human disease pathways, as these proteins include potential new targets that may lead to improved therapeutic strategies. This requires the direct measurement of gene function on a genomic scale in cell-based, functional assays. We have constructed and validated an individually arrayed, replication-defective adenoviral library harboring human cDNAs, termed PhenoSelect library. The adenoviral vector guarantees efficient transduction of diverse cell types, including primary cells. The arrayed format allows screening of this library in a variety of cellular assays in search for gene(s) that, by overexpression, induce a particular disease-related phenotype. The great majority of phenotypic assays, including morphological assays, can be screened with arrayed libraries. In contrast, pooled-library approaches often rely on phenotype-based isolation or selection of single cells by employing a flow cytometer or screening for cell survival. An arrayed placental PhenoSelect library was screened in cellular assays aimed at identifying regulators of osteogenesis, metastasis, and angiogenesis. This resulted in the identification of known regulators, as well as novel sequences that encode proteins hitherto not known to play a role in these pathways. These results establish the value of the PhenoSelect platform, in combination with cellular screens, for gene function discovery.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wright, F.A. et al. A draft annotation and overview of the human genome. Genome Biol. 2, 0025.1–0025.18 (2001).
Hogenesch, J.B. et al. A comparison of the Celera and Ensembl predicted gene sets reveals little overlap in novel genes. Cell 106, 413–415 (2001).
Fallaux, F.J. et al. Means and methods for nucleic acid delivery vehicle design and nucleic acid transfer. US 6,395,519 (2002).
Schouten, G., Vogels, R., Bout, A. & Van Es, H. High-throughput screening of gene function using libraries for functional genomics applications. US 6,430,595 (2002).
Ma, L. et al. Rapid determination of adenoviral vector titres by quantitative real-time PCR. J. Virol. Methods 93, 181–188 (2001).
Bergelson, J.M. et al. Isolation of a common receptor for Coxsackie B viruses and adenoviruses 2 and 5. Science 275, 1320–1323 (1997).
Rodan, G.A. & Harada, S. The missing bone. Cell 89, 677–680 (1997).
Service, R.F. Tissue engineers build new bone. Science 289, 1498–1500 (2000).
Sabatakos, G. et al. Overexpression of DeltaFosB transcription factor(s) increases bone formation and inhibits adipogenesis. Nat. Med. 6, 985–990 (2000).
Behrens, J., Mareel, M.M., Van Roy, F.M. & Birchmeier, W. Dissecting tumor cell invasion: epithelial cells acquire invasive properties after the loss of uvomorulin-mediated cell–cell adhesion. J. Cell Biol. 108, 2435–2447 (1989).
Demunter, A., De Wolf-Peeters, C., Degreef, H., Stas, M. & van den Oord, J.J. Expression of the endothelin-B receptor in pigment cell lesions of the skin. Evidence for its role as tumor progression marker in malignant melanoma. Virchows Arch. 438, 485–491 (2001).
Vournakis, J.N., Finkielsztein, S. & Pariser, E.R. Methods and compositions for treatment of cell proliferative disorders. Patent Application US 6,063,911 (2000).
Nahagara, H. et al. Transduction of full-length TAT fusion proteins into mammalian cells: TAT-p27Kip1 induces cell migration. Nat. Med. 4, 1449–1452 (1998).
Babic, A.M., Kireeva, M.L., Kolesnikova, T.V. & Lau, L.F. CYR61, a product of a growth factor-inducible immediate early gene, promotes angiogenesis and tumor growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 6355–6360 (1998).
Sambrook, J. & Russel, D.W. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY, 2001).
Montesano, R. & Orci, L. Tumor-promoting phorbol esters induce angiogenesis in vitro. Cell 42, 469–477 (1985).
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the gift of mesenchymal stem cells by IsoTis (Bilthoven, The Netherlands). We thank John Collard for providing the MDCK cells. This work was supported in part by an IWT grant from the Flemish government.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
All authors are employed by Galapagos Genetics, and the research described in this article was funded by Galapagos Genetics.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Michiels, F., van Es, H., van Rompaey, L. et al. Arrayed adenoviral expression libraries for functional screening. Nat Biotechnol 20, 1154–1157 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt746
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt746
This article is cited by
-
AAV-mediated in vivo functional selection of tissue-protective factors against ischaemia
Nature Communications (2015)
-
Loss-of-function genetic screens as a tool to improve the diagnosis and treatment of cancer
Oncogene (2009)
-
A novel reverse transduction adenoviral array for the functional analysis of shRNA libraries
BMC Genomics (2008)
-
An empty E1−, E3−, E4− adenovirus vector protects photoreceptors from light-induced degeneration
Journal of Ocular Biology, Diseases, and Informatics (2008)
-
Embryonic stem-cell culture as a tool for developmental cell biology
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2007)