Abstract
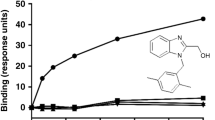
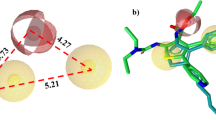
Exocyclic small peptidomimetics corresponding to three critical binding sites of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-receptor(l) have been designed based on atomic features deduced from the crystal structures of TNFα and the TNFβ/TNF-receptor(l) complex and a model of an anti-TNFα monoclonal antibody. TNFα antagonistic activities were evaluated by binding assays using soluble receptor or intact receptor on cells as well as an apoptosis/cytotoxicity assay. The most critical interaction site for rational design of peptidomimetics was localized to the Ioop1/domain3 of the TNF-receptor. The best antagonist showed 5 μM inhibition in the binding assay. Biologically, the mimetics inhibited TNFα-mediated apoptosis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carswell, E.A., Old, L.J., Kassel, R.L., Green, S., Fiore, N., and Williamson, B. 1975. An endotoxin-induced serum factor that causes necrosis of tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 72: 3666–3670.
Beutler, B. 1995. TNF, immunity and inflammatory disease: lessons of the past decade. J. Investig. Med. 43: 227–235.
Hotamisligil, G.S. and Spiegelman, B.M. 1994. Tumor necrosis factor a: a key component of the obesity-diabetes link. Diabetes 43: 1271–1278.
Williams, R.O., Feldmann, M., and Maini, R.N. 1992. Anti-tumor necrosis factor ameliorates joint disease in murine collagen-induced arthritis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89: 9784–9788.
Baker, D., Butler, D., Scallon, B.J., O'Neil, J.K., Turk, J.L., and Feldmann, M. 1994. Control of established experimental allergic encephalomyelitis by inhibition of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) activity within the central nervous system using monoclonal antibodies and TNF receptor-immunoglobulin fusion proteins. Eur. J. Immunol. 24: 2040–2048.
Suitters, A.J., Foulkes, R., Opal, S.M., Palardy, J.E., Emtage, S., Rolfe, M., et al. 1994. Differential effect of isotype on efficacy of anti-tumor necrosis factor a chimeric antibodies in experimantal septic shock. J. Exp. Med. 179: 849–856.
Knight, D.M., Trinh, H., Le, J., Siegel, S., Shealy, D., McDonough, M., et al. 1993. Construction and initial characterization of a mouse-human chimeric anti-TNF antibody. Mol. Immun. 30: 1443–1453.
Maini, R.N., Elliott, M.J., Brennan, F.M., Williams, R.O., Chu, C.Q., Paleolog, E., et al. 1995. Monoclonal anti-TNFα antibody as a probe of pathogenesis and therapy of rheumatoid disease. Immunol. Rev. 144: 195–223.
Lorenz, H.-M., Antoni, C., Valerius, T., Repp, R., Grunke, M., Schwardtner, N., et al. 1996. In vivo blockade of TNF-α by intravenous infusion of a chimeric monoclonal TNF-α antibody in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: short term cellular and molecular effects. J. Immunol. 156: 1646–53.
Walker, R.E., Spooner, K.M., Kelly, G., McCloskey, R.V., Woody, J.N., Falloon, J., et al. 1996. Inhibition of immunoreactive tumor necrosis factor-α by a chimeric antibody in patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J. Infect. Dis. 174: 63–68.
Tak, P.P., Taylor, P.C., Breedveld, F.C., Smeets, T.M., Daha, M.R., Kluin, P.M., et al. 1996. Decrease in cellularity and expression of adhesion molecules by anti-tumor necrosis factor α monoclonal antibody treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 39: 1077–1081.
Schall, T.J., Lewis, M., Koller, K.J., Lee, A., Rice, G.C., Wong, G.H.W., et al. 1990. Molecular cloning and expression of a receptor for human tumor necrosis factor. Cell 61: 361–370.
Smith, C.A., Davis, T., Anderson, D., Solam, L., Beckmann, M.P., Jerzy, R., et al. 1990. A receptor for tumor necrosis factor defines an unusual family of cellular and viral proteins. Science 248: 1019–1023.
Peppel, K., Crawford, D., and Beutler, B. 1991. A tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor-IgG heavy chain chimeric protein as a bivalent antagonist of TNF activity. J. Exp. Med. 174: 1483–1489.
Scallon, B.J., Trinh, H., Nedelman, M., Brennan, F.M., Feldmann, M., and Ghrayeb, J. 1995. Functional comparisons of different tumor necrosis factor receptor/IgG fusion proteins. Cytokine 7: 759–770.
Williams, R.O., Ghrayeb, J., Feldmann, M., and Maini, R.N. 1995. Successful therapy of collagen-induced arthritis with TNF receptor-IgG fusion protein and combination with anti-CD4. Immunology 84: 433–439.
Suffredini, A.F., Reda, D., Banks, S.M., Tropea, M., Agosti, J.M., and Miller, R. 1995. Effects of recombinant dimeric TNF receptor on human inflammatory responses following intravenous endotoxin administration. J. Immunol. 155: 5038–5045.
Baumgartner, S., Moreland, L.W., Schiff, M.H., Tindall, E., Fleischmann, R.M., Weaver, A., et al. 1996. Double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of tumor necrosis factor receptor (p80) fusion protein (TNFR:Fc) in active rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 39(Suppl): S74.
Orfanoudakis, G., Karim, B., Bourel, D., and Weiss, E. 1993. Bacterially expressed Fabs of monoclonal antibodies neutralizing tumor necrosis factor a in vitro retain full binding and biological activity. Mol. Immun. 30: 1519–1528.
Jespers, L.S., Roberts, A., Mahler, S.M., Winter, G., and Hoogenboom, H.R. 1994. Guiding the selection of human antibodies from phage display repertoires to a single epitope of an antigen. Bio/Technology 12: 899–903.
Reinhart, K., Wiegand-Lohnert, C., Grimminger, F., Kaul, M., Withington, S., Treacher, D., et al. 1996. Assessment of the safety and efficacy of the monoclonal anti-tumor necrosis factor antibody-fragment, MAK 195F, in patients with sepsis and septic shock: a multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging study. Crit. Care Med. 24: 733–742.
Döring, E., Stigler, R., Grütz, G., Baehr, R., and Schneider-Mergener, J. 1994. Identification and characterization of a TNFα antagonist derived from a monoclonal antibody. Mol. Immun. 31: 1059–1067.
Hwang, C., Gatanga, M., Innins, E.K., Yamamoto, R.S., Granger, G.A., and Gatanga, T. 1991. A 20 amino acid synthetic peptide of a region from the 55 kDa human TNF receptor inhibits cytolytic and binding activities of recombinant human tumor necrosis factor in vitro. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B. 245: 115–119.
Lie, B.-L., Tunemoto, D., Hemmi, H., Mizukami, Y., Fukuda, H., Kikuchi, H., et al. 1992. Identification of the binding site of 55kDa tumor necrosis factor receptor by synthetic peptides. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 188: 503–509.
Saragovi, H.U., Fitzpatrick, D., Raktabutr, A., Nakanishi, H., Kahn, M., and Greene, M.I. 1991. Design and synthesis of a mimetic from an antibody complementarity-determining region. Science 253: 792–795.
Taub, R. and Greene, M.I. 1992. Functional validation of ligand mimicry by anti-receptor antibodies: structural and therapeutic implications. Biochemistry 31: 7431–7435.
Saragovi, H.U. and Greene, M.I. 1992. Constrained peptides and mimetics as probes of protein secondary structure. Immunomethod 1: 5–9.
McDonnell, J.M., Beavil, A.J., Mackay, G.A., Jameson, B.A., Korngold, R., Gould, H.J., and Sutton, B.J. 1996. Structure based design and characterization of peptide that inhibit IgE binding to its high-affinity receptor. Nat. Struct. Biol. 3: 419–426.
Zhang, X., Piatier-Tonneau, P., Auffray, C., Murali, R., Mahapatra, A., Zhang, F., et al. 1996. Synthetic CD4 exocyclic peptides antagonize CD4 holoreceptor binding and T cell activation. Nature Biotechnology 14: 472–475.
Zhang, X., Gaubin, M., Briant, L., Srikantan, V., Murali, R., Saragovi, M.H., et al. 1997. Synthetic CD4 exocyclics inhibit binding of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope to CD4 and virus replication in T lymphocytes. Nature Biotechnology 15: 150–154.
Banner, D.W., D'Arcy, A., Janes, W., Gentz, R., Schoenfeld, H.-J., Broger, C., et al. 1993. Crystal structure of the soluble human 55 kd TNF receptor-human TNFp complex: implications for TNF receptor activation. Cell 73: 431–445.
Eck, M.J. and Sprang, S.R. 1989. The structure of tumor necrosis factor-α at 2.6 Å resolution. J. Biol. Chem. 264: 17595–17605.
Habeeb, F.F. 1973. A sensitive method for localization of disulfide containing peptides in column effluents. Anal. Bioch. 56: 60–65.
Angeletti, R.H., Bibbs, L., Bonewald, L.F., Fields, G.B., McMurray, J.S., Moore, W.T., and Stults, J.T. 1996. Formation of a disulfide bond in an octreotide-like peptide: a multicenter study, pp. 81–91 in Techniques in protein chemistry VII. Marsak, D.R. (ed.) Academic Press, Inc., San Diego, CA.
Espevik, T., Brockhaus, M., Loetscher, H., Nonstad, U., and Shalaby, R. 1990. Characterization of binding and biological effects of monoclonal antibodies against a human tumor necrosis factor receptor. J. Exp. Med. 171: 415–426.
Larrick, J.W. and Wright, S.C. 1990. Cytotoxic mechanism of tumor necrosis factor-α. FASEB J. 4: 3215–3223.
Hennet, T., Richter, C., and Peterhans, E. 1993. Tumor necrosis factor-α induces superoxide anion generation in mitochondria of L929 cells. Biochem. J. 289: 587–592.
Hansen, M.B., Nielsen, S.E., and Berg, K. 1989. Re-examination and further development of a precise and rapid dye method for measuring cell growth/cell kill. J. Immunol. Methods 119: 203–210.
Yamagishi, J., Kawashima, H., Matsuo, N., Ohue, M., Yamayoshi, M., Fukui, T., et al. 1990. Mutational analysis of structure-activity relationship in human tumor necrosis factor-α. Protein Eng. 3: 713–719.
Van Ostade, X., Tavernier, J., Prange, T., and Fiers, W. 1991. Localization of the active site of human tumor necrosis factor (hTNF) by mutational analysis. EMBO J. 10: 827–836.
Jones, E.Y., Stuart, D.I., and Walker, N.P.C. 1992. Crystal structure of TNF. Immunology Series 56: 93–127.
Zhang, X.-M., Weber, I., and Chen, M.-J. 1992. Site-directed mutational analysis of human tumor necrosis factor-α receptor binding site and structure-functional relationship. J. Biol. Chem. 267: 24069–24075.
Yone, K., Bajard, S., Tsunekawa, N., and Suzuki, J. 1995. Epitopic regions for antibodies against tumor necrosis factor α: analysis by synthetic peptide mapping. J. Biol. Chem. 270: 19509–19515.
Eck, M.J., Ultsch, M., Rinderknecht, E. de Vos, A.M., and Sprang, S.R. 1992. The structure of human lymphotoxin (tumor necrosis factor-β) at 1.9-Å resolution. J. Biol. Chem. 267: 2119–2122.
Ponder, J.W., and Richards, F.M. Tertiary templates for proteins: use of packing criteria in the enumeration of allowed sequences for different structural classes. J. Mol. Biol. 193: 775–791 (1987).
Bernstein, F.C., Koetzle, T.F., Williams, G.J., Meyer, E.E., Jr., Brice, M.D., Rodgers, J.R., Kennard, O., Shimanouchi, T., and Tasumi, M. The protein data bank: a computer-based archiral file for macromolecular structures. J. Mol. Biol. 112: 535–42 (1977).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takasaki, W., Kajino, Y., Kajino, K. et al. Structure–based design and characterization of exocyclic peptidomimetics that inhibit TNFα binding to its receptor. Nat Biotechnol 15, 1266–1270 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1197-1266
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1197-1266
This article is cited by
-
The W9 peptide inhibits osteoclastogenesis and osteoclast activity by downregulating osteoclast autophagy and promoting osteoclast apoptosis
Journal of Molecular Histology (2022)
-
Osteoclast differentiation by RANKL and OPG signaling pathways
Journal of Bone and Mineral Metabolism (2021)
-
Discovery of the RANKL/RANK/OPG system
Journal of Bone and Mineral Metabolism (2021)
-
Effects of TNF receptor blockade on in vitro cell survival and response to negative energy balance in dairy cattle
Journal of Animal Science and Biotechnology (2018)
-
A vitronectin-derived peptide reverses ovariectomy-induced bone loss via regulation of osteoblast and osteoclast differentiation
Cell Death & Differentiation (2018)