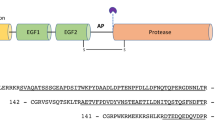
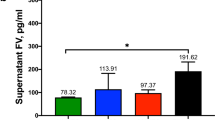
Abstract
Protein C, a vitamin K–dependent plasma protease involved in the regulation of hemostasis, has potent anticoagulant activity and may be useful as an effective antithrombotic agent. Because of the risk of infection by blood–borne viruses, such as HIV, a source of protein C other than from human plasma is desirable. We constructed a vector for the expression of recombinant human protein C (rHPC) using a hybrid promoter that could be activated in trans by the early region 1A (E1A) proteins of adenovirus. Stable cell lines secreting rHPC were isolated by introducing expression vectors into the adenovirus–transformed human kidney cell line 293 with a dominant selectable marker. The protein C was purified to homogeneity using a conformation (Ca2+) specific anti–HPC monoclonal antibody. Like plasma–derived HPC, the purified rHPC was 90% two chain and 10% one chain, and N–terminal sequence analysis indicated that the molecule was processed correctly. Upon activation of the recombinant zymogen with thrombomodulin–thrombin, the purified rHPC expressed anticoagulant activity at a level above that of plasma–derived human HPC. This high level of activity was reduced when the rHPC was produced in the presence of warfarin, indicating a vitamin K–dependence for the production of fully active rHPC from the 293 cell line. Biochemical analysis confirmed the presence of nine γ–carboxyglutamic acid residues per mole of rHPC.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Esmon, C.T. 1987. The regulation of the natural anticoagulant pathway. Science 235: 1348–1382.
Esmon, N.L., Owen, W.G., and Esmon, C.T. 1982. Isolation of a membrane-bound cofactor for thrombin-catalyzed activation of protein C. J. Biol. Chem. 257: 859–864.
Marlar, R.A., Kleiss, A.J., and Griffin, J. 1982. Mechanism of action of human activated protein C, a thrombin-dependent anticoagulant protein. Blood 59: 1067–1072.
Zolton, R.P. and Seeders, W.H. 1973. Autoprothrombin IIA: Thrombin removal and mechanisms of induction of fibrinolysis. Thromb. Res. 3: 23.
Comp, P.C. and Esmon, C.T. 1981. Generation of fibrinolytic activity by infusion of activated protein C into dogs. J. Clin. Invest. 68: 1221–1228.
Gardner, J.E. and Griffin, J.H. 1983. Human protein C and thromboembolic disease, p. 265–278. In: Progress in Hematology Vol 13. E. D. Brown (ed.). Grune and Stratton, New York.
Clouse, L.H. and Comp, P.C. 1986. The regulation of hemostasis: The protein C system. New Engl. J. Med. 314: 1298–1304.
Kisiel, W. 1979. Human plasma protein C: Isolation, characterization, and mechanism of activation by alpha-thrombin. J. Clin. Invest. 64: 761–769.
Drakenberg, T. et al. 1983. Beta-hydroxyaspartic acid in vitamin K-dependent protein C. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 80: 1802–1806.
Plutzky, J. et al. 1986. Evolution and organization of the human protein C gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 83: 546–550.
Foster, D. and Davie, E.W. 1984. Characterization of a cDNA coding for human protein C. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 81: 4766–4770.
Beckmann, R.J. et al. 1985. The structure and evolution of a 461 amino acid human protein C precursor and its messenger RNA, based upon the DNA sequence of cloned human liver cDNAs, Nucl. Acids Res. 13: 5233–5247.
Pan, L.C. and Price, P.A. 1985. The propeptide of rat bone γ-carboxylic acid protein shares homology with other vitamin K-dependent protein precursors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 82: 6109–6113.
Sutie, J.W. et al. 1987. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylasae: Possible role of the substrate (propeptide) as an intracellular recognition site. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84: 634–638.
Anson, D.S., Austen, D.E.G. and Brownlee, G.G. 1985. Expression of active human clotting factor IX from recombinant DNA clones in mammalian cells. Nature 315: 683–685.
de la Salle, H. et al. 1985. Active γ-carboxylated human factor IX expressed using recombinant DNA techniques. Nature 316: 268–270.
Busby, S. et al. 1985. Expression of active human factor IX in transfected cells. Nature 316: 271–273.
Kaufman, R.J. et al. 1986. Expression, purification and characterization of recombinant γ-carboxylated factor IX synthesized in Chinese Hamster Ovary cells J. Biol. Chem. 261: 9622–9628.
Grinnell, B.W., Berg, D. and Walls, J. 1986. Activation of the adenovirus and BK virus late promoters: Effects of the BK virus enhancer and trans-acting viral early proteins. Mol. Cell. Biol. 6: 3596–3605.
Kisiel, W. and Davie, E.W. 1981. Protein C. Meth. Enzymol. 80: 320–332.
Suzuki, K., Stenflo, J., Dahlback, B. and Teodorsson, B. 1983. Inactivation of human coagulation factor V by activated protein C. J. Biol. Chem. 258: 1914–1920.
Suttie, J.W. 1985. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylase. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 54: 459–477.
Kuwada, M. and Katayama, K. 1983. An improved method for the determination of γ-carboxylic acid in proteins, bone and urine. Anal. Biochem. 131: 173–179.
Grinnell, B.W., Padgett, B.L. and Walker, D.L. 1983. Comparison of infectious JC virus DNAs cloned from human brain. J. Virol. 45: 299–308.
Santerre, R.F. et al. 1984. Expression of prokaryotic genes for hygromycin B and G418 resistance as dominant-selection marker in mouse L cells. Gene 30: 147–156.
Wigler, M. et al. 1979. DNA-mediated transfer of the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase locus into mammalian cells. Proc. Nad. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 76: 1373–1376.
Vagano D'Angelo, S., Comp, P.D., Esmon, C.T. and D'Angelo, A. 1986. Relationship between protein C antigen and anticoagulant activity during oral anticoagulation and in selected disease states. J. Clin. Invest. 77: 416–425.
Comp, P.C. and Esmon, C.T. 1979. Activated protein C inhibits platelet prothrombin-activity. Blood 54: 1272–1278.
Pfleiderer, G. 1970. Particle-bound aminopeptidase from pig kidney. Meth. Enzymol. 19: 514–521.
Laemmli, U.K. 1970. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227: 680–685.
Jorgensen, M., Cantor, A., Furie, B. and Furie, B. 1987. Expression of completely γ-carboxylated recombinant human prothrombin. J. Biol. Chem. 262: 6729–6734.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grinnell, B., Berg, D., Walls, J. et al. Trans–Activated Expression of Fully Gamma–Carboxylated Recombinant Human Protein C, an Antithrombotic Factor. Nat Biotechnol 5, 1189–1192 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1187-1189
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1187-1189
This article is cited by
-
Aryl propanolamines: comparison of activity at human β3 receptors, rat β3 receptors and rat atrial receptors mediating tachycardia
British Journal of Pharmacology (1999)