Abstract
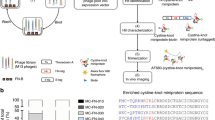
Several lines of evidence suggest that tumor growth, angiogenesis, and metastasis are dependent on matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) activity. However, the lack of inhibitors specific for the type IV collagenase/gelatinase family of MMPs has thus far prevented the selective targeting of MMP-2 (gelatinase A) and MMP-9 (gelatinase B) for therapeutic intervention in cancer. Here, we describe the isolation of specific gelatinase inhibitors from phage display peptide libraries. We show that cyclic peptides containing the sequence HWGF are potent and selective inhibitors of MMP-2 and MMP-9 but not of several other MMP family members. Our prototype synthetic peptide, CTTHWGFTLC, inhibits the migration of human endothelial cells and tumor cells. Moreover, it prevents tumor growth and invasion in animal models and improves survival of mice bearing human tumors. Finally, we show that CTTHWGFTLC–displaying phage specifically target angiogenic blood vessels in vivo. Selective gelatinase inhibitors may prove useful in tumor targeting and anticancer therapies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Birkendal-Hansen, H. Proteolytic remodeling of extracellular matrix. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 7, 728–735 ( 1995).
Stetler-Stevenson, W.G., Aznavoorian, S. & Liotta, L.A. Tumor cell interactions with the extracellular matrix during invasion and metastasis. Annu. Rev. Cell Biol. 9, 541–573 (1993).
Murray, G.I., Duncan, M.E., O'Neil, P., Melvin, W.T. & Fothergill, J.E. Matrix metalloproteinase-1 is associated with poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Nat. Med. 2, 461–462 (1996).
Murphy, G. & Crabbe, T. Gelatinases A and B. Methods Enzymol. 248, 470–484 (1995).
Liotta, L.A. et al. Metastatic potential correlates with enzyme derived from a metastatic murine tumor. Nature 284, 67– 68 (1980).
Karakiulakis, G. et al. Increased type IV collagen-degrading activity in metastases originating from primary tumors of the human colon. Invasion & Metastasis 17, 158–168 1997.
Pyke, C., Ralfkiaer, E., Tryggvason, K. & Dano, K. Messenger RNA for two type IV collagenases is located in stromal cells in human colon cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 142, 359–365 (1993).
Sugiura, Y., Shimada, H., Seeger, R.C., Laung, W.E. & DeClerck, Y. A Matrix metalloproteinases-2 and -9 are expressed in human neuroblastoma: contribution of stromal cells to their production and correlation with metastasis. Cancer Res. 58, 2209–2216 (1998).
Wilhelm, S.M. et al. SV40-transformed human lung fibroblasts secrete a 92 kDa type IV collagenase which is identical to that secreted by normal human macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 264, 17213– 17221 (1989).
Heppner, K.J., Matrisian, L.M., Jensen, R.A. & Rodgers, W.H. Expression of most matrix metalloproteinase family members in breast cancer represents a tumor-induced response. Am. J. Pathol. 149, 273–282 (1996).
Brooks, P.C. et al. Localization of matrix metalloproteinase MMP-2 to the surface of invasive cells by interaction with integrin αvβ3. Cell 85, 683–693 ( 1996).
Haas, T.L., Davis, S.J. & Madri, J.A. Three-dimensional type I collagen lattices induce coordinate expression of matrix metalloproteinases MT1-MMP and MMP-2 in microvascular endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 3604 –3610 (1998).
Vu, T.H. et al. MMP-9/gelatinase B is a key regulator of growth plate angiogenesis and apoptosis of hypertrophic chondrocytes. Cell 93 , 411–422 (1998).
Hanahan, D. & Folkman, J. Patterns and emerging mechanisms of the angiogenic switch during tumorigenesis. Cell 86, 353–364 (1996).
Davies, B., Brown, P.D., East, N., Crimmin, M.J. & Balkwill, F.R. A synthetic matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor decreases tumor burden and prolongs survival of mice bearing human ovarian carcinoma xenografts. Cancer Res. 53, 2087– 2091 (1993).
Taraboletti, G. et al. Inhibition of angiogenesis and murine hemangioma growth by batimastat, a synthetic inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 87, 293–298 (1995).
Volpert, O.V. et al. Captopril inhibits angiogenesis and slows the growth of experimental tumors in rats. J. Clin. Invest. 98, 671 –679 (1996).
Anderson, I.C., Shipp, M.A., Docherty, A.J.P. & Teicher, B.A. Combination therapy including a gelatinase inhibitor and a cytotoxic agent reduced local invasion and metastasis of murine Lewis lung carcinoma. Cancer Res. 56, 715–710 (1996).
Ecclels, S.A. et al. Control of lymphatic and hematogenous metastasis of a rat mammary carcinoma by the matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor batimastat (BB-94). Cancer Res. 56, 2815–2822 (1996).
Talbot, D.C. & Brown, P.D. Experimental and clinical studies on the use of matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors for the treatment of cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 32, 2528– 2533 (1996).
Beckett, R.P., Davidson, A.H., Drummond, A.H., Huxley, P. & Whittaker, M. Recent advances in matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor research. Drug Design Today 1, 16–26 (1996).
Santos, O., McDermott, C.D., Daniels, R.G. & Appelt, K. Rodent pharmacokinetic and anti-tumor efficacy studies with a series of synthetic inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 15, 499–508 ( 1997).
Pulli, T., Koivunen, E. & Hyypia, T. Cell-surface interactions of echovirus 22. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 21176–21180 (1997).
Goldberg, G.I., Strongin, A., Collier, I.E., Genrich, L.T. & Marmer, B.L. Interaction of 92-kDa type IV collagenase with the tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases prevents dimerization, complex formation with interstitial collagenase, and activation of the proenzyme with stromelysin. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 4583– 4591 (1992).
Brooks, P.C., Silletti, S., von Schalscha, T.L., Friedlander, M. & Cheresh, D.A. Disruption of angiogenesis by PEX, a noncatalytic metalloproteinase fragment with integrin binding activity. Cell 92, 391–400 (1998).
Pasqualini, R., Koivunen, E. & Ruoslahti, E. αv integrins as receptors for tumor targeting by circulating ligands. Nat. Biotechnol. 245, 346–369 (1997).
Arap, W., Pasqualini, R. & Ruoslahti, E. Cancer treatment by targeted drug delivery to tumor vasculature in a mouse model. Science 279, 377–380 (1998).
Wojtowicz-Praga, S. et al. Phase I trial of Marimastat, a novel matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor, administered orally to patients with advanced lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 16, 2150–2156 (1998).
Goetzl, E.J., Banda, M.J. & Leppert, D. Matrix metalloproteinases in immunity. J. Immunol. 156, 1–4 ( 1996).
Sorsa, T. et al. Activation of type IV procollagenases by human tumor-associated trypsin-2. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 21067– 21074 (1997).
Nagase, H., Enghild, J.J., Suzuki, K. & Salvesen, G. Stepwise activation mechanisms of the precursor of matrix metalloproteinase 3 (stromelysin) by proteinases and (4-aminophenyl) mercuric acetate. Biochemistry 29, 5783–5790 (1990).
Stocker, W. & Bode, W. Structural features of a superfamily of zinc-endopeptidases: the metzincins. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 5, 383–390 ( 1995).
Ferry, G., Boutin, J.A., Atassi, G., Fauchere, J.-L. & Tucker, G.C. Selection of histidine-containing inhibitor of gelatinases through deconvolution of combinatorial tetrapeptide libraries. Molecular Diversity 2, 135–146 (1996).
Matthews, D.J. & Wells, J.A. Substrate phage: selection of protease substrates by monovalent display. Science 260, 1113–1117 ( 1993).
Ke, S.H. et al. Distinguishing the specificities of closely related proteases. Role of P3 in substrate and inhibitor discrimination between tissue type plasminogen activator and urokinase. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 16603–16609 (1997).
Smith M.M., Shi, L. & Navre, M. Rapid identification of highly active and selective substrates for stromelysin and matrilysin using bacteriophage peptide display libraries. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 6440–6449 (1995).
Krook, M., Lindbladh, C., Eriksen, J.A. & Mosbach, K. Selection of a cyclic nonapeptide inhibitor to α-chymotrypsin using a phage display peptide library. Molecular Diversity 3, 149–159 (1998).
Rui, F., Jie, Q., Zhi-bin, L., Hui, Z., Wei, L. & Jiacong, S. Selection of trypsin inhibitors in a phage peptide library. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 220, 53–56 ( 1996).
Seftor, R.E.B. et al. Chemically modified tetracyclines inhibit human melanoma cell invasion and metastasis. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 16, 217–225 (1998).
Kim, J., Yu, W., Kovalski, K. & Ossowski, L. Requirement for specific proteases in cancer cell intravasation as revealed by a novel semiquantitative PCR-based assay. Cell 94, 353– 362 (1998).
Itoh, T. et al. Reduced angiogenesis and tumor progression in gelatinase A-deficient mice. Cancer Res. 58, 1048– 1051 (1998).
Arap, W., Pasqualini., R. & Ruoslahti, E. Chemotherapy targeted to tumor vasculature. Current Opinion in Oncology 10, 560– 565 (1998).
Rajotte, D. & Ruoslahti, E. Membrane dipeptidase is the receptor for a lung-targeting peptide identified by in vivo phage display. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 11593–11598 (1999).
Pasqualini, R., Arap, W., Rajotte, D. & Ruoslahti, E. in Phage display of proteins and peptides (eds Barbas, C., Burton, D., Silverman, G., & Scott, J.) (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, 1999). In press.
Sorsa, T. et al. Effects of tetracyclines on neutrophil, gingival, and salivary collagenases. A functional and Western blot assessment with special reference to their cellular sources in periodontal diseases. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 732, 112–131 ( 1994).
Koivunen, E. et al. Human colon carcinoma, fibrosarcoma and leukemia cell lines produce tumor-associated trypsinogen. Int. J. Cancer 47, 592–596 (1991).
Domingo, G.J., Leatherbarrow, R.J., Freeman, N., Patel, S. & Weir, M. Synthesis of a mixture of cyclic peptides based on the Bowman-Birk reactive site loop to screen for serine protease inhibitors. International Journal of Peptide and Protein Research 46, 79–87 ( 1995).
Koivunen, E., Wang, B. & Ruoslahti, E. . Phage libraries displaying cyclic peptides with different ring sizes: ligand specificities of of the RGD-directed integrins. Bio/Technology 13, 265–270 (1995).
Smith, G.P. & Scott, J.K. Libraries of peptides and proteins displayed in filamentous phage. Methods Enzymol. 217 , 228–257 (1993).
Teronen, O. et al. Human neutrophil collagenase MMP-8 in peri-implant sulcus fluid and its inhibition by clodronate. J. Dent. Res. 76, 1529–1537 (1997).
Edgell, C.-J.S., McDonald, C.C. & Graham, J.B. Permanent cell line expressing human factor VIII-related antigen established by hybridization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 80, 3734–3737 ( 1983).
Herndier, B.G. et al. Characterization of a human Kaposi's sarcoma cell line that induces angiogenic tumors in animals. AIDS 8, 575–581 (1996).
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs. Guy Salvesen and Jeffrey W. Smith for critical reading of the manuscript, and Dr. Daniel Rajotte and Jason A. Hoffman for helpful suggestions. This work was supported by grant CA74238 (E.R.) and Cancer Center Support grant CA30199 from the National Cancer Institute, grants DAMD17-98-1-8041 (R.P.) and DAMD17-98-1-8164 (W.A.) from the Department of Defense, and grants from the Academy of Finland, Finnish Dental Society, Finnish Cancer Society, and Sigrid Juselius Foundation (E.K. and C.G.G.). W.A. is the recipient of a CaP CURE award.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koivunen, E., Arap, W., Valtanen, H. et al. Tumor targeting with a selective gelatinase inhibitor. Nat Biotechnol 17, 768–774 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/11703
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/11703
This article is cited by
-
The immune-chemo-embolization effect of temperature sensitive gold nanomedicines against liver cancer
Nano Research (2023)
-
Tumor Homing Peptides as Fusion Partners of Therapeutic Proteins for Efficient Delivery to Cancer Cells
Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering (2023)
-
JP3, an antiangiogenic peptide, inhibits growth and metastasis of gastric cancer through TRIM25/SP1/MMP2 axis
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2020)
-
A Screening Algorithm for Gastric Cancer-Binding Peptides
International Journal of Peptide Research and Therapeutics (2020)
-
Phage Display Libraries: From Binders to Targeted Drug Delivery and Human Therapeutics
Molecular Biotechnology (2019)