Abstract
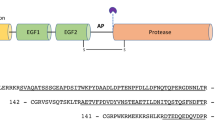
The formation of N-linked oligosaccharides of eukaryotic glycoproteins starts with the attachment of a common precursor at the recognition site Asn-X-Ser/Thr. Subsequent processing, by yet unknown controlling factors, leads to the formation of three different glycans: the high mannose type, the complex type and the hybrid type. In order to gain insight into the processing mechanisms, we studied the glycan pattern of a panel of related molecules constructed by insertion, duplication or deletion of the domains encoded by the cDNA of a fibrinolytic glycoprotein, tissue-type plasminogen activator (t-PA). These variant molecules are identical in regard to the glycosylation sites originally situated in particular domains, but differ with respect to the sequential alignment of the domains. The variant and native t-PA genes were transfected into mouse C127 cells and their carbohydrate structures analyzed by the susceptibility to specific endoglycosidases and by reaction with sugar-specific lectins. We found that with one exception, all mutant activators lack the high mannose glycan found at asn 117 of native t-PA. The exception was a molecule that retains the original domain arrangement up to and through the glycosylation site at asn 117. These results demonstrate for the first time that structural alterations in the primary sequence distal to the actual glycosylation site can result in altered processing of N-linked oligosaccharides.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goto, M., Akai, K., Murakami, A., Hashimoto, C., Tsuda, E., Ueda, M., Kawanishi, G., Takahashi, N., Ishimoto, A., Chiba, H. and Sasaki, R., 1988. Production of recombinant human erythropoietin in mammalian cells: host-cell dependency of the biological activity of the cloned glycoprotein. Biotechnology 6: 67–71.
Moonen, P., Mermod, J.J., Ernst, J.F., Hirshci, M. and DeLamarter, J.F. 1987. Increased biological activity of deglycosylated recombinant human granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor produced by yeast or animals cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84: 4428–4431.
Donahue, R.E., Wang, E.A., Kaufman, R.J., Foutch, L., Leary, A.C., Withe-Giannetti, J.S., Metzger, M., Hewick, R.M., Steinbrink, D.R., Shaw, G. Kamen, R. Clark, S.C. 1986. Effects of N-linked carbohydrate on the in vivo properties of human GM-CSF. Cold Spring Harbor Symp. Quant. Biol. 51: 685–692.
Yet, M.G., Shao, M.C. and Wold, F. 1988. Effects of the protein matrix on glycan processing in glycoproteins. FASEB J 2: 22–31.
Pohl, G., Kenne, L., Nilsson, B. and Einarsson, M. 1987. Isolation and characterization of three different carbohydrate chains from melanoma tissue plasminogen activator. Eur. J. Biochem. 170: 69–75.
Vehar, G.A., Spellman, M.W, Keyt, B.A., Ferguson, C.K., Keck, R.G., Chlouper, R.C., Harris, R., Bennett, W.F., Builder, S.E and Hancock, W.S. 1986. Characterization studies of human tissue-type plasminogen activator produced by recombinant DNA technology. Cold Spring Harbor Symp. Quan. Biol. 51: 551–562.
Kalyan, N.K., Lee, S.G., Wilhelm, J., Fu, K.P., Hum, W.T., Rappaport, R., Hartzell, R.W., Urbano, C., Hung, P.P, 1988. Structure-function analysis with tissue-type plasminogen activator. J. Biol. Chem. 263: 3971–3978.
Lee, S.G., Kalyan, N., Wilhelm, J., Hum, W.T., Rappaport, R., Cheng, S.M., Dheer, S., Urbano, C., Hartzell, R., Ronchetti-Blume, M., Levner, M. and Hung, P.P, 1988. Construction and expression of hybrid plasminogen activators prepared from tissue-type plasminogen activator and urokinase-type plasminogen activator genes. J. Biol. Chem. 263: 2917–2924.
Tarentino, A.L., Plummer, T.H. and Maley, F. 1974. The release of intact oligosaccharides from specific glycoproteins by endo-β-N-acetyl-glucosaminidase H. J. Biol. Chem. 249: 818–824.
Tarentino, A.L., Gomez, C.M. and Plummer, T.H., Jr., 1985. Deglycosylation of asparagine linked glycans by peptide: N-glycosidase F. Biochem. 24: 4665–4671.
Hubbard, S.C. 1988. The regulation of glycosylation. The influence of protein structure on N-linked oligosaccharide processing. J. Biol. Chem. 263: 19303–19317.
Lustbader, J., Birken, S., Pollak, S., Levinson, L., Bernstine, E., Hsiung, N. and Canfield, R. 1987. Characterization of the expression products of recombinant human choriogonadotropin and subunits. J. Biol. Chem. 262: 14204–14212.
Hotchkiss, A., Refino, C.J., Leonard, C.K., O'Connor, J.V., Crowley, C., McCabe, J., Tate, K., Nakamura, G., Powers, D., Levinson, A., Mohler, A. and Spellman, M.W. 1988. The influence of carbohydrate structure on the clearance of recombinant t-PA. Thromb. Haemostas. 60: 255–261.
Zoller, M.J. and Smith, M. 1984. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis: A simple method using two oligonucleotide primers and a single-stranded DNA template. DNA 3: 479–488.
Kalyan, N.L., Hung, P.P., Levner, M.H., Dheer, S.K. and Lee, S.G. 1986. Site-specific DNA splicing: a general procedure for the creation of a restriction site at a predetermined position in a DNA sequence. Gene 42: 331–337.
Kijimoto-Ochiai, S., Katagiri, Y.U. and Ochiai, H. 1985. Analysis of N-linked oligosaccharide chains of glycoproteins on nitrocellulose sheets using lectin-peroxidase reagents. Analytical Biochem. 147: 222–229.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wilhelm, J., Lee, S., Kalyan, N. et al. Alterations in the Domain Structure of Tissue-Type Plasminogen Activator Change the Nature of Asparagine-Linked Glycosylation. Nat Biotechnol 8, 321–325 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0490-321
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0490-321
This article is cited by
-
Functional characterization of Schistosoma mansoni fucosyltransferases in Nicotiana benthamiana plants
Scientific Reports (2020)