Abstract
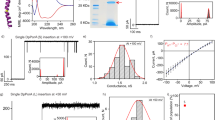
By using an engineered, self-assembling, proteinaceous, 2-nm pore equipped with a metal-actuated switch, a technique to reversibly permeabilize the plasma membrane to small molecules (∼1000 Da) has been developed. We have demonstrated the dose-dependent permeabilization of fibroblasts by pores designed to be blocked and unblocked by the addition and removal of μM concentrations of Zn2+. Further, we have shown that the activity of the switch allows permeabilized cells to maintain viability and ultrastructural integrity following the unconstrained flux of small molecules. This ability to control the transmembrane influx and efflux of molecules and thereby vary the intracellular environment yet maintain cell viability will impact an array of biological and medical problems.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhakdi, S., Weller, U., Walev, U., Martin, E., Jonas, D., and Palmer, M. 1993. A guide to use of pore-forming toxins for controlled permeabilization of cell membranes. Med. Microb. Immunol. 182: 167–175.
Wilmsen, H.U., Pattus, R., and Buckley, J.T., 1990. lysin, a hemolysin from Aeromonas hydrophilia, forms voltage-gated channels in planar lipid bilayers. J. Membrane Biol. 115: 71–82.
Menestrina, G., 1986. Ionic channels formed by Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin: voltage-dependent inhibition by divalent and trivalent cations. J. Membrane Biol. 90: 177–190.
Tsong, Y.T. 1991. Electroporation of cell membranes. Biophys. J. 60: 297–306.
Morris, A.P. and Frizzell, R.A. 1993. Calcium-dependent chloride channels in undifferentiated human colonic cells HT-29 II. Am. J. Physiol. 264: C977–C985.
Kubisch, H.M., Hernandez-Ledezma, J.J., Larson, M.A., and Sikes, J.D. 1995. Expression of two transgenes in in vitro matured and fertilized bovine zygotes after DMA microinjection. J. Reprod. and Fertil. 104: 133–139.
Walker, B., Kasianowicz, J., Krishnasastry, M., and Bayley, H. 1994. A pore-forming protein with a metal-actuated switch. Protein Eng. 7: 655–662.
Bhakdi, S. and Tranum-Jensen, J. 1991. Alpha-toxin of Staphylococcus aureus. Microbiol. Rev. 55: 733–751.
Hildebrand, A., Pohl, M., and Bhakdi, S. 1991. Staphylococcus aureus α-toxin: dual mechanism of binding to target cells. J. Biol. Chem. 266: 17195–17200.
Bayley, H. 1995. Pore-forming proteins with built-in triggers and switches. Bioorg. Chem. 23: 340–345.
Walker, B., Braha, O., Cheley, S., and Bayley, H. 1995. An intermediate in the assembly of a pore-forming protein trapped with a genetically engineered switch. Chem. Biol. 2: 99–105.
Bashford, C.L., Alder, G.M., Fulford, L.G., Korchev, Y.E., Kovacs, E. et al. 1996. Pore formation by S.aureus alpha-toxin in liposomes and planar lipid bilayers: effects of non-electrolytes. J. Membr. Biol. 150: 37–45.
Sunzel, B., Holm, S., Reuterving, C., Söderberg, T., et al. 1995. The effect of zinc on bacterial phagocytosis, killing, and cytoprotection in human polymorphonuclear leucocytes. APMIS 103: 633–644.
Walker, B., Krishnasastry, J., Zorn, L., and Bayley, H. 1992. Assembly of the oligomeric membrane pore formed by staphylococcal α-hemolys in examined by truncation mutagenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 267: 21782–21786.
Palmer, M., Weller, U., MeBner, M., and Bhakdi, S. 1993. Altered pore-forming properties of proteolytically nicked staphylococcal α-toxin. J. Biol. Chem. 268: 11963–11967.
Gouaux, J.E., Braha, O., Hobaugh, M., Song, L., Cheley, S., Shustak, C. et al. 1994. Subunit stoichiometry of staphylococcal α-hemolysin in crystals and on membranes: a heptameric transmembrane pore. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91: 12828–12831.
Panchal, R. and Bayley, H. 1995. Interactions between residues in staphylococcal α-hemolysin revealed by reversion mutagenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 270: 23072–23076.
Johnson, H.L. and Sauberlich, H.E. Trace element analysis in biological systems. pp. 405–426 in Current topics in nutrition and disease, volume 6. A.S. Prasad (ed.). Alan R. Liss, Inc., New York.
Levin, R.L. and Miller, T.M. 1981. An optimum method for the introduction or removal of permeable cryoprotectants: isolated cells. Cryobiology 18: 32–48.
Walev, I., Palmer, M., Martin, E., Jonas, D., Weller, U., and Bhakdi, S. 1994. Recovery of human fibroblasts from attack by the pore-forming α-toxin of Staphylococcus aureus. Microb. Path. 17: 187–201.
Panchal, R.G., Cusack, E., Cheley, S., and Bayley, H. 1995. Tumor pro-tease-activated, pore-forming toxins from a combinatorial library. Nature Biotechnology 14: 852–856.
Walkr, B. and Bayley, H. 1994. A pore-forming protein with a protease-activated trigger. Protein Eng. 7: 91–97.
Chang, C., Niblack, B., Walker, B., and Bayley, H. 1995. A photogenerated pore-forming protein. Chem. Biol. 2: 391–400.
Bischof, J.C., Padanilam, J., Holmes, W.H., Ezzell, R.M., Lee, R.C., et al 1995. Dynamics of cell membrane permeability changes at supraphysiological temperatures. Biophys. J. 68: 2608–2614.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Russo, M., Bayley, H. & Toner, M. Reversible permeabilization of plasma membranes with an engineered switchable pore. Nat Biotechnol 15, 278–282 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0397-278
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0397-278