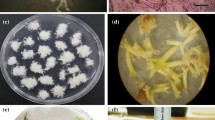
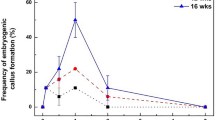
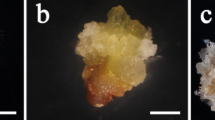
Abstract
The ability to control plant somatic embryogenesis is a necessary prelude to its development as an efficient biotechnological tool. The influence of different suspension culture techniques on the maturation of caraway (Carum carvi) somatic embryos and the effect of growth hormones in controlling development were studied. The three types of culture vessels (tumble tubes, test tubes, and Erlenmeyer flasks), each providing contrasting techniques of agitation, generated populations differing significantly in the frequencies of normal and abnormal embryos. Abscisic acid (ABA), at the appropriate concentrations, effectively normalized development in all systems, inhibiting abnormal proliferations and precocious germination and fostering normal maturation. For those cultures where embryos failed to develop on unsupplemented medium, zeatin in combination with ABA fostered growth and normal maturation. Carrot (Daucus carota) somatic embryo development could be similarly controlled. Such regulation of maturation would facilitate future efforts to manipulate somatic embryos for large scale propagation in batch cultures, mechanized planting, artificial induction of dormancy, and incorporation into artificial seeds.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Steward, F.C., Mapes, M.O. and Meats, K. 1958. Growth and organized development of cultured cells, II. Organization in cultures grown from freely suspended cells. Am. J. Bot. 45: 704–708.
Reinert, J. 1958. Morphogenese und ihre Kontrolle an Gewebekulturen aus Carotten. Nalurwissenschaften 45: 344–345.
Tisserat, B., Esan, B.R. and Murashige, T. 1979. Somatic embryogenesis in angiosperms. Hortic. Rev. 1: 1–78.
Ammirato, P.V. 1983. Embryogenesis. In: Handbook of Plant Cell Culture. Vol. 1. D.A. Evans, W. R. Sharp. P. V. Ammirato, and Y. Yamada (ed.). Macmillan, New York, in press.
Currah, I.E., Gray, D. and Thomas, I.H. 1974. The sowing of germinated plant seeds using a fluid drill. Ann. Appl. Biol. 76: 311–318.
Gray, D. 1981. Fluid drilling of vegetable seeds. Hortic. Rev. 1: 1–27.
Evans, D.A., Sharp, W.R. and Flick, C.E. 1981. p. 45–113. Growth and behavior in cell cultures: Embryogenesis and organogenesis. In: Plant Tissue Culture: Methods and Applications in Agriculture. T. A. Thorpe (ed) Academic Press, New York.
Durzan, D.J. 1980. p. 31–60. Progress and promise in forest genetics. In: Paper Science and Technology—The Cutting Edge. The Institute of Paper Chemistry, Appleton, Wisconsin.
Murashige, T. 1980. p. 426–434. Plant growth substances in commercial use of tissue culture. In: Plant Growth Substances. F. Skoog (ed) Springer-Verlag, New York.
Ammirato, P.V. 1974. The effects of abscisic acid on the development of somatic embryos from cells of caraway (Carum carvi). Bot. Gaz. 135: 328–337.
Ammirato, P.V. 1977. Hormonal control of somatic embryo development from cultured cells of caraway: Interactions of abscisic acid, zeatin, and gibberellic acid. Plant Physiol. 59: 579–586.
Steward, F.C., Caplin, S.M. and Millar, F.K. 1952. Investigations on growth and metabolism of plant cells. I. New techniques for the investigation of metabolism, nutrition, and growth in undifferentiated cells. Ann. Bot. 16: 58–77.
Halperin, W. and Wetherell, D.R. 1964. Adventive embryony in tissue cultures of the wild carrot, Daucus carota . Am. J. Bot. 51: 274–283.
Halperin, W. 1966. Alternative morphogenetic events in cell suspensions. Am. J. Bot. 53: 443–453.
Kessel, R.H.J. and Carr, A.H. 1972. The effect of dissolved oxygen concentration on growth and differentiation of carrot (Daucus carota) tissue. J. Exp. Bot. 23: 996–1007.
Street, H.E. 1977. p. 61–102. Cell (suspension) cultures—Techniques. In: Plant Tissue and Cell Culture. 2nd ed. H. E. Street (ed) Univ. of California Press, Berkeley.
Steward, F.C. and Shantz, E.M. 1956. p. 165–187. The chemical induction of growth in plant tissue cultures. In: The Chemistry and Mode of Action of Plant Growth Substances. R. L. Wain, and F. Wightman (cd) Academic Press, New York.
White, P.R. 1963. A Handbook of Plant and Animal Tissue Culture, (Jacques Cattel Press, Lancaster, Pennsylvania).
Murashige, T. and Skoog, F. 1962. A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 15: 473–492.
Kessel, R.H.J., Goodwin, C. and Philip, J. 1977. The relationship between dissolved oxygen concentration, ATP and embryogenesis in carrot (Daucus carota) tissue cultures. Plant Sci. Let. 10: 265–274.
Tisserat, B. and Murashige, T. 1977. Repression of asexual embryogenesis in vitro by some plant growth regulators. In Vitro 13: 799–805.
Kochba, J., Spiegel-Roy, P., Neumann, H. and Saad, S. 1978. Stimulation of embryogenesis in Citrus ovular callus by ABA, ethephon, CCC and alar and its suppression by GA. Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 89: 427–432.
Rajasekhar, W., Edwards, M., Wilson, S.B. and Street, H.E. 197l. Studies on the growth in culture of plant cells. V. The influence of shaking rate on the growth of suspension cultures. J. Exp. Bot. 22: 107–117.
Halperin, W. 1967. Population density effects in embryogenesis in carrot cell cultures. Exp. Cell Res. 48: 170–173.
Steward, F.C., Israel, H.W., Molt, R.L., Wilson, H.J. and Krikorian, A.D. 1975. Observations on growth and morphogenesis in cultured cells of carrot (Daucus carota L.). Philos, Trans. R. Soc. London Ser. B. 273: 33–53.
Stuart, R. and Street, H.E. 1969. Studies on the growth in culture of plant cells. IV. The initiation of division in suspensions of stationary-phase cells of Acer pseudoplatanus L. J. Exp. Bot. 20: 556–571.
Earle, E.D. and Torrey, J.C. 1965. Colony formation by isolated Convolvulus cells plated on defined media. Plant Physiol. 40: 520–528.
Stuart, R. and Street, H.E. 1971. Studies on the growth in culture of plant cells. X. Further studies on the conditioning of culture media by suspensions of Acer pseudoplatanus L. J. Exp. Bot. 22: 96–106.
Vasil, I.K. and Hildebrandt, A.C. 1966. Variations of morphogenetic behavior in plant tissue cultures. II. Petroselium hortense . Am. J. Bot. 53: 869–874.
Steward, F.C., Ammirato, P.V. and Mapes, M.O. 1970. Growth and development of totipotent cells: Some problems, procedures and perspectives, Ann. Bot. 34: 761–787.
Williams, L. and Collin, H.A. 1976. Embryogenesis and plantlet formation in tissue cultures of celery. Ann. Bot. 40: 325–332.
Ammirato, P.V. and Steward, F.C. 1971. Some effects of the development of embryos from cultured free cells. Bot. Gaz. 132: 149–158.
Kamada, H. and Harada, H. 1981. Changes in the endogenous levels and effects of abscisic: acid during somatic embryogenesis of Daucus carota L. Plant Cell Physiol. 22: 1423–1429.
Nitsch, J.P. and Nitsch, C. 1969. Haploid plants from pollen grains, Science 163: 85–87.
Ammirato, P.V. 1978. Somatic embryogenesis and plantlet development in suspension cultures of the medicinal vain, Dioscorea floribunda . Am. J. Bot. (suppl) 65: 89.
Ammirato, P.V. 1982. Growth and morphogenesis in cultures of the monocot yam, Dioscorea . p. 169–170. In: Plant Tissue Culture, 1982. Proc. 5th Intl. Cong. Plant Tissue and Cell Culture. A. Fujiwara, (ed) (Jap. Ass. Plant Tissue Culture, Tokyo, Japan).
Vasil, V. and Vasil, I.K. 1981. Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from tissue cultures of Pennisetum americanum and P. purpureum hybrid. Am. J. Bot. 68: 864–872.
Vasil, V. and Vasil, I.K. 1981. Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from suspension cultures of pearl millet (Pennisetum americanum). Ann. Bot. 47: 669–678.
Norstog, K. and Blume, D. 1974. Abscisic acid promotion of development of excised immature barley embryos. In: Haploids in Higher Plants: Advances and Potential. K. J. Kasha, (ed) Proc. First International Symposium, Univ. Guelph, Ontario.
Umbeck, P.F. and Norstog, K. 1979. Effects of abscisic acid and ammonium ions on morphogenesis of cultured barley embryos. Bull. Torrey Bot. Club 106: 110–116.
Murashige, T. 1974. Plant propagation through tissue cultures. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. 25: 135–166.
Narayanaswamy, S., 1977. Regeneration of plants from tissue cultures. In: Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Cultures, p. 179–206. J. Reinert and Y. P. S. Bajaj, (Springer-Verlag, New York).
Raghavan, V. 1976. Experimental Embryogenesis in Vascular Plants. Academic Press, New York.
Al-Abta, S., Galpin, I.J., and Collin, H.A. 1979. Flavour compounds in tissue cultures of celery. Plant Sci. Lett. 16: 129–134.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ammirato, P. The Regulation of Somatic Embryo Development in Plant Cell Cultures: Suspension Culture Techniques and Hormone Requirements. Nat Biotechnol 1, 68–73 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0383-68
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0383-68
This article is cited by
-
Direct somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from leaf sheath explants of mango ginger (Curcuma amada Roxb.)
In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology - Plant (2014)
-
Somatic embryogenesis in the medicinal legume Desmodium motorium (Houtt.) Merr.
Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture (PCTOC) (2011)
-
Direct somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from immature explants of chickpea
Biologia plantarum (2010)
-
Acquisition of embryogenic competence during somatic embryogenesis
Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture (2007)