Abstract
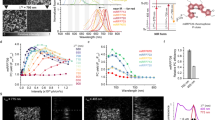
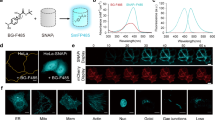
We have developed a method for visualizing phosphorylation of proteins in living cells using a novel fluorescent indicator composed of two green fluorescent protein (GFP) variants joined by the kinase-inducible domain (KID) of the transcription factor cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP)-responsive element binding protein (CREB). Phosphorylation of KID by the cAMP-dependent protein kinase A (PKA) decreased the fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) among the flanking GFPs. By transfecting COS-7 cells with an expression vector encoding this indicator protein (termed ART for cAMP-responsive tracer), we were able to visualize activation dynamics of PKA in living cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hagiwara, M. et al. Coupling of hormonal stimulation and transcription via the cyclic AMP-responsive factor CREB is rate limited by nuclear entry of protein kinase A. Mol. Cell. Biol. 13, 4852– 4859 (1993).
Sakaguchi, H., Wada, K., Maekawa, M., Watsuji, T. & Hagiwara, M. Song-induced phosphorylation of cAMP response element-binding protein in the songbird brain. J. Neurosci. 19, 3973–3981 (1999).
Ng, T. et al. Imaging protein kinase C alpha activation in cells. Science 283, 2085–2089 ( 1999).
Lee, C.L., Linton, J., Soughayer, J.S., Sims, C.E. & Allbritton, N.L. Localized measurement of kinase activation in oocytes of Xenopus laevis. Nat. Biotechnol. 17, 759–762 ( 1999).
Adams, S.R., Harootunian, A.T., Buechler, Y.J., Taylor, S.S. & Tsien, R.Y. Fluorescence ratio imaging of cyclic AMP in single cells. Nature 349, 694– 697 (1999).
Morise, H., Shimomura, O., Johnson, F.H. & Winant, J. Intermolecular energy transfer in the bioluminescent system of Aequorea. Biochemistry 13, 2656– 2662 (1974).
Prasher, D.C., Eckenrode, V.K., Ward, W., Prendergast, F.G. & Cormier, M.J. Primary structure of the Aequorea victoria green-fluorescent protein. Gene 111, 229–233 (1992).
Chalfie, M., Tu, Y., Euskirchen, G., Ward, W.W. & Prasher, D.C. Green fluorescent protein as a marker for gene expression. Science 263, 802–805 (1994).
Inouye, S. & Tsuji, F.I. Aequorea green fluorescent protein. Expression of the gene and fluorescence characteristics of the recombinant protein. FEBS Lett. 341, 277– 280 (1994).
Romoser, V.A., Hinkle, P.M. & Persechini, A. Detection in living cells of Ca2+-dependent changes in the fluorescence emission of an indicator composed of two green fluorescent protein variants linked by a calmodulin-binding sequence. A new class of fluorescent indicators. J. Biol. Chem. 272 , 13270–13274 (1997).
Miyawaki, A. et al. Fluorescent indicators for Ca2+ based on green fluorescent proteins and calmodulin. Nature 388, 882–887 (1997).
Mahajan, N.P. et al. Bcl-2 and Bax interactions in mitochondria probed with green fluorescent protein and fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Nat. Biotechnol. 16, 547–552 (1998).
Suzuki, Y., Yasunaga, T., Ohkura, R., Wakabayashi, T. & Sutoh, K. Swing of the lever arm of a myosin motor at the isomerization and phosphate-release steps. Nature 396, 380–383 (1998).
Kemp, B.E. Phosphorylation of acyl and dansyl derivatives of the peptide Leu-Arg-Arg-Ala-Ser-Leu-Gly by the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 255, 2914–2918 (1980).
Chrivia, J.C. et al. Phosphorylated CREB binds specifically to the nuclear protein CBP. Nature 365, 855–859 (1993).
Mitra, R.D., Silva, C.M. & Youvan, D.C. Fluorescence resonance energy transfer between blue-emitting and red-shifted excitation derivatives of the green fluorescent protein. Gene 173, 13–17 ( 1996).
Hagiwara, M. et al. Transcriptional attenuation following cAMP induction requires PP-1-mediated dephosphorylation of CREB. Cell 70, 105–113 (1992).
Hagiwara, M., Inagaki, M. & Hidaka, H. Specific binding of a novel compound, N-[2-(methylamino)ethyl]-5-isoquinolinesulfonamide (H-8) to the active site of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Mol. Pharmacol. 31, 523–528 ( 1987).
Chijiwa, T. et al. Inhibition of forskolin-induced neurite outgrowth and protein phosphorylation by a newly synthesized selective inhibitor of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase, N-[2-(p-bromocinnamylamino)ethyl]-5-isoquinolinesulfonamide (H-89), of PC12D pheochromocytoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 265, 5267–5272 (1990).
Tokumitsu, H. et al. KN-62, 1-[N,O-bis(5-isoquinolinesulfonyl)-N-methyl-L-tyrosyl]-4-phenylpiperazine, a specific inhibitor of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. J. Biol. Chem. 265, 4315– 4320 (1990).
Chijiwa, T., Hagiwara, M. & Hidaka, H. A newly synthesized selective casein kinase I inhibitor, N-(2-aminoethyl)-5-chloroisoquinoline-8-sulfonamide, and affinity purification of casein kinase I from bovine testis. J. Biol. Chem. 264, 4924–4927 (1989).
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Anthony Persechini (University of Rochester) for pETIC-1 plasmid and Grace M. Lopresto-Mizuno for English correction. This work was supported by Research for the Future Program, the Inamori Foundation, Nissan Science Foundation, The Mitsubishi Foundation, Project Research Program (Cell Fate Modulation Research Unit) of the Medical Research Institute, Tokyo Medical and Dental University, and grants from the Ministry of Education, Science and Culture in Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagai, Y., Miyazaki, M., Aoki, R. et al. A fluorescent indicator for visualizing cAMP-induced phosphorylation in vivo. Nat Biotechnol 18, 313–316 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/73767
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/73767
This article is cited by
-
Electron transfer in protein modifications: from detection to imaging
Science China Chemistry (2023)
-
In vivo imaging of CREB phosphorylation in awake-mouse brain
Scientific Reports (2015)
-
Visualization of the spatial and temporal dynamics of MAPK signaling using fluorescence imaging techniques
The Journal of Physiological Sciences (2015)