Abstract
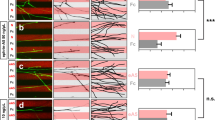
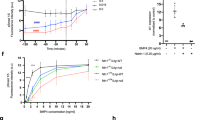
Neuronal growth cones are guided to their targets by attractive and repulsive guidance cues1. In mammals, netrin-1 is a bifunctional cue, attracting some axons and repelling others2,3,4,5. Deleted in colorectal cancer (Dcc) is a receptor for netrin-1 that mediates its chemoattractive effect on commissural axons6,7, but the signalling mechanisms that transduce this effect are poorly understood. Here we show that Dcc activates mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signalling, by means of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)-1 and -2, on netrin-1 binding in both transfected cells and commissural neurons. This activation is associated with recruitment of ERK-1/2 to a Dcc receptor complex. Inhibition of ERK-1/2 antagonizes netrin-dependent axon outgrowth and orientation. Thus, activation of MAPK signalling through Dcc contributes to netrin signalling in axon growth and guidance.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tessier-Lavigne, M. & Goodman, C. S. The molecular biology of axon guidance. Science 274, 1123–1133 (1996)
Serafini, T. et al. The netrins define a family of axon outgrowth-promoting proteins homologous to C. elegans UNC-6. Cell 78, 409–424 (1994)
Kennedy, T. E., Serafini, T., de la Torre, J. R. & Tessier-Lavigne, M. Netrins are diffusible chemotropic factors for commissural axons in the embryonic spinal cord. Cell 78, 425–435 (1994)
Serafini, T. et al. Netrin-1 is required for commissural axon guidance in the developing vertebrate nervous system. Cell 87, 1001–1014 (1996)
Hong, K. et al. A ligand-gated association between cytoplasmic domains of UNC5 and DCC family receptors converts netrin-induced growth cone attraction to repulsion. Cell 97, 927–941 (1999)
Keino-Masu, K. et al. Deleted in Colorectal Cancer (DCC) encodes a netrin receptor. Cell 87, 175–185 (1996)
Fazeli, A. et al. Phenotype of mice lacking functional Deleted in colorectal cancer (Dcc) gene. Nature 386, 796–804 (1997)
Corset, V. et al. Netrin-1-mediated axon outgrowth and cAMP production requires interaction with adenosine A2b receptor. Nature 407, 747–750 (2000)
Stein, E. & Tessier-Lavigne, M. Hierarchical organization of guidance receptors: silencing of netrin attraction by slit through a Robo/DCC receptor complex. Science 291, 1928–1938 (2001)
Mehlen, P. et al. The DCC gene product induces apoptosis by a mechanism requiring receptor proteolysis. Nature 395, 801–804 (1998)
Chang, L. & Karin, M. Mammalian MAP kinase signalling cascades. Nature 410, 37–40 (2001)
Alessi, D. R., Cuenda, A., Cohen, P., Dudley, D. T. & Saltiel, A. R. PD 098059 is a specific inhibitor of the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase in vitro and in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 27489–27494 (1995)
Garrington, T. P. & Johnson, G. L. Organization and regulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase signalling pathways. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 11, 211–218 (1999)
Birkenkamp, K. U. et al. p38MAP kinase inhibitor SB203580 enhances nuclear factor-κB transcriptional activity by a non-specific effect upon the ERK pathway. Br. J. Pharmacol. 131, 99–107 (2000)
de la Torre, J. R. et al. Turning of retinal growth cones in a netrin-1 gradient mediated by the netrin receptor DCC. Neuron 19, 1211–1224 (1997)
Stein, E., Zou, Y., Poo, M.-M. & Tessier-Lavigne, M. Binding of DCC by netrin-1 to mediate axon guidance independent of adenosine A2B receptor activation. Science 291, 1976–1982 (2001)
Fukuda, M. et al. Induction of neurite outgrowth by MAP kinase in PC12 cells. Oncogene 11, 239–244 (1995)
Kolkova, K., Novitskaya, V., Pedersen, N., Berezin, V. & Bock, E. Neural cell adhesion molecule-stimulated neurite outgrowth depends on activation of protein kinase C and the Ras-mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. J. Neurosci. 20, 2238–2246 (2000)
Schmid, R. S. et al. NCAM stimulates the Ras-MAPK pathway and CREB phosphorylation in neuronal cells. J. Neurobiol. 38, 542–558 (1999)
Schmid, R. S., Pruitt, W. M. & Maness, P. F. A MAP kinase-signalling pathway mediates neurite outgrowth on L1 and requires Src-dependent endocytosis. J. Neurosci. 20, 4177–4188 (2000)
Yamashita, H., Avraham, S., Jiang, S., Dikic, I. & Avraham, H. The Csk homologous kinase associates with TrkA receptors and is involved in neurite outgrowth of PC12 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 15059–15065 (1999)
Elowe, S., Holland, S. J., Kulkarni, S. & Pawson, T. Downregulation of the Ras-mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway by the EphB2 receptor tyrosine kinase is required for ephrin-induced neurite retraction. Mol. Cell Biol. 21, 7429–7441 (2001)
Miao, H. et al. Activation of EphA receptor tyrosine kinase inhibits the Ras/MAPK pathway. Nature Cell Biol. 3, 527–530 (2001)
Gundersen, G. G. & Cook, T. A. Microtubules and signal transduction. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 11, 81–94 (1999)
Schaefer, A. W. et al. Activation of the MAPK signal cascade by the neural cell adhesion molecule L1 requires L1 internalization. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 37965–37973 (1999)
Kamiguchi, H. & Lemmon, V. Recycling of the cell adhesion molecule L1 in axonal growth cones. J. Neurosci. 20, 3676–3686 (2000)
Sgambato, V. et al. In vivo expression and regulation of Elk-1, a target of the extracellular-regulated kinase signalling pathway, in the adult rat brain. J. Neurosci. 18, 214–226 (1998)
Campbell, D. S. & Holt, C. E. Chemotropic responses of retinal growth cones mediated by rapid local protein synthesis and degradation. Neuron 32, 1013–1026 (2001)
Herbert, T. P., Tee, A. R. & Proud, C. G. The extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway regulates the phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 at multiple sites. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 11591–11596 (2002)
Acknowledgements
We thank J. Pouyssegur for reagents and discussions; V. Fafeur and E. Bloch-Gallego for providing reagents; C. Guix for technical assistance; and S. Dazy for preliminary observations on ERK-1/2 activation. This work was supported by the Ligue Contre le Cancer and the ARC (P.M.). L.P. is supported by a post-doctoral fellowship from the Ligue Contre le Cancer. E.S. is an Associate and M.T.-L. an Investigator of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Forcet, C., Stein, E., Pays, L. et al. Netrin-1-mediated axon outgrowth requires deleted in colorectal cancer-dependent MAPK activation. Nature 417, 443–447 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature748
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature748
This article is cited by
-
DCC/netrin-1 regulates cell death in oligodendrocytes after brain injury
Cell Death & Differentiation (2023)
-
Sensory innervation in porous endplates by Netrin-1 from osteoclasts mediates PGE2-induced spinal hypersensitivity in mice
Nature Communications (2019)
-
Egr-1 increases angiogenesis in cartilage via binding Netrin-1 receptor DCC promoter
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2018)
-
Neuronal microRNA regulation in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Reciprocal antagonism between the netrin-1 receptor uncoordinated-phenotype-5A (UNC5A) and the hepatitis C virus
Oncogene (2017)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.