Abstract
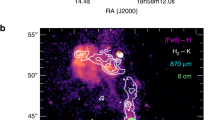
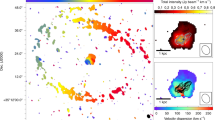
Massive outflows driven by active galactic nuclei are widely recognized to have a key role in the evolution of galaxies1,2,3,4, by heating the ambient gas, expelling it from the nuclear regions, and thereby affecting the star-formation histories of the galaxy bulges. It has been proposed that the powerful jets of relativistic particles (such as electrons) launched by some active nuclei can both accelerate5,6,7 and heat8 the molecular gas, which often dominates the mass budgets of the outflows5,9. Clear evidence for this mechanism, in the form of detailed associations between the molecular gas kinematics and features in the radio-emitting jets, has however been lacking. Here we report that the warm molecular hydrogen gas in the western radio lobe of the Seyfert galaxy IC 5063 is moving at high velocities—up to about 600 kilometres per second—relative to the galaxy disk. This suggests that the molecules have been accelerated by fast shocks driven into the interstellar medium by the expanding radio jets. These results demonstrate the general feasibility of accelerating molecular outflows in fast shocks driven by active nuclei.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fabian, A. Observational evidence of active galactic nuclei feedback. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 50, 455–489 (2012)
Silk, J. & Rees, M. Quasars and galaxy formation. Astron. Astrophys. 331, L1–L4 (1998)
Fabian, A. The obscured growth of massive black holes. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 308, L39–L43 (1999)
di Matteo, T. et al. Energy input from quasars regulates the growth and activity of black holes and their host galaxies. Nature 433, 604–607 (2005)
Morganti, R., Frieswijk, W., Oonk, R. J. B., Osterloo, T. & Tadhunter, C. Tracing the extreme interplay between radio jets and the ISM in IC 5063. Astron. Astrophys. 552, L4–L7 (2013)
Dasyra, K. M. & Combes, F. Cold and warm molecular gas in the outflow of 4C 12.50. Astron. Astrophys. 541, L7–L11 (2012)
Morganti, R., Fogasy, J., Paragi, Z., Oosterloo, T. & Orienti, M. Radio jets clearing the way through a galaxy: watching feedback in action. Science 341, 1082–1085 (2013)
Guillard, P. et al. Strong molecular hydrogen emission and kinematics of the multiphase gas in radio galaxies with fast jet-driven outflows. Astrophys. J. 747, 95–120 (2012)
Alatalo, K. et al. Discovery of an active galactic nucleus driven molecular outflow in the early-type galaxy NGC1266. Astrophys. J. 735, 88–100 (2011)
Morganti, R. et al. A radio study of the Seyfert galaxy IC 5063: evidence for fast gas outflow. Astron. J. 115, 915–927 (1998)
Oosterloo, T. A. et al. A strong jet-cloud interaction in the Seyfert galaxy IC 5063: VLBI observations. Astron. J. 119, 2085–2091 (2000)
Morganti, R., Holt, J., Saripalli, L., Oosterloo, T. A. & Tadhunter, C. N. IC 5063: AGN driven outflow of warm and cold gas. Astron. Astrophys. 476, 735–743 (2007)
Kulkarni, V. et al. Unveiling the hidden nucleus of IC 5063 with NICMOS. Astrophys. J. 492, L121–L124 (1998)
Oonk, J. B. R., Jaffe, W., Bremer, M. N. & van Weeren, R. J. The distribution and condition of the warm molecular gas in Abell 2597 and Sersic 159–03. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 405, 898–932 (2010)
Mellema, G., Kurk, J. D. & Rottgering, H. J. A. Evolution of clouds in radio galaxy cocoons. Astron. Astrophys. 395, L13–L16 (2002)
Wagner, A. Y., Bicknell, G. V. & Umemura, M. Driving outflows with relativistic jets and the dependence of active galactic nucleus feedback efficiency on interstellar medium inhomogeneity. Astrophys. J. 757, 136–160 (2012)
Hollenbach, D. & McKee, C. F. Molecule formation and infrared emission in fast interstellar shocks. I. Physical processes. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 41, 555–592 (1979)
Riffel, R. A., Storchi-Bergman, T. & Winge, C. Feeding versus feedback in AGNs from near-infrared IFU observations: the case of Mrk 79. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 430, 2249–2261 (2013)
Schmitt, H. R., Donley, J. L., Antonucci, R. R. J., Hutchings, J. B. & Kinney, A. L. A Hubble Space Telescope survey of extended [OIII] emission in a far-infrared selected sample of Seyfert galaxies: observations. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 148, 327 (2003)
Zubovas, K. & King, A. Galaxy-wide outflows: cold gas and star formation at high speeds. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 439, 400 (2014)
Veilleux, S. et al. Fast molecular outflows in luminous galaxy mergers: evidence for quasar feedback from Herschel. Astrophys. J. 776, 27–48 (2013)
Cicone, C. et al. Massive molecular outflows and evidence for feedback from CO observations. Astron. Astrophys. 562, 21–46 (2014)
McCarthy, P. J., van Breugel, W., Spinrad, H. & Djorgovski, S. A correlation between the radio and optical morphologies of distant 3CR radio galaxies. Astrophys. J. 321, L29–L33 (1987)
Rees, M. J. The radio/optical alignment of high-z radio galaxies—Triggering of star formation in radio lobes. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 239, P1–P4 (1989)
Gaibler, V., Khochfar, S., Krause, M. & Silk, J. Jet-induced star formation in gas-rich galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 425, 438–449 (2012)
di Serego Alighieri, S., Fosbury, R. A. E., Tadhunter, C. N. & Quinn, P. J. Polarized light in high-redshift radio galaxies. Nature 341, 307–309 (1989)
Dickson, R., Tadhunter, C., Shaw, M., Clark, N. & Morganti, R. The nebular contribution to the extended UV continua of powerful radio galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 273, L29–L33 (1995)
Croft, S. et al. Minkowski's object: a starburst triggered by a radio jet, revisited. Astron. J. 647, 1040–1055 (2006)
Crockett, R. et al. Triggered star formation in the inner filament of Centaurus A. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 421, 1603–1623 (2012)
Griersmith, D., Hyland, A. R. & Jones, T. J. Photometric properties of bright early-type spiral galaxies. IV—Multiaperture UBVJHK photometry for the inner/bulge regions of 65 galaxies. Astron. J. 1982, 1106–1126 (1982)
Acknowledgements
This work is based on observations collected at the European Southern Observatory, Chile (programme 290.B-5162). C.T. and M.R. acknowledge financial support from the UK Science and Technology Research Council. R.M. acknowledges support from the European Research Council under the European Union’s Seventh Framework Programme (FP/2007-2013)/ERC Advanced Grant RADIOLIFE-320745.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C.T. and R.M. led the project and the scientific interpretation of the data, and C.T. wrote the text of the paper. M.R. reduced the near-infrared spectroscopic data. R.O. and T.O. contributed equally to the analysis and interpretation of the results.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tadhunter, C., Morganti, R., Rose, M. et al. Jet acceleration of the fast molecular outflows in the Seyfert galaxy IC 5063. Nature 511, 440–443 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13520
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13520
This article is cited by
-
Cool outflows in galaxies and their implications
The Astronomy and Astrophysics Review (2020)
-
The largely unconstrained multiphase nature of outflows in AGN host galaxies
Nature Astronomy (2018)
-
The interstellar and circumnuclear medium of active nuclei traced by H i 21 cm absorption
The Astronomy and Astrophysics Review (2018)
-
Wind from the black-hole accretion disk driving a molecular outflow in an active galaxy
Nature (2015)
-
Stellar feedback as the origin of an extended molecular outflow in a starburst galaxy
Nature (2014)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.