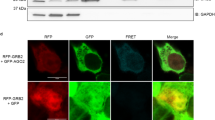
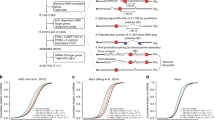
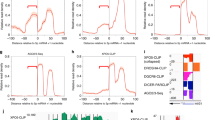
Abstract
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) comprise a large family of small RNA molecules that post-transcriptionally regulate gene expression in many biological pathways1. Most miRNAs are derived from long primary transcripts that undergo processing by Drosha to produce ∼65-nucleotide precursors that are then cleaved by Dicer, resulting in the mature 22-nucleotide forms2,3. Serving as guides in Argonaute protein complexes, mature miRNAs use imperfect base pairing to recognize sequences in messenger RNA transcripts, leading to translational repression and destabilization of the target messenger RNAs4,5. Here we show that the miRNA complex also targets and regulates non-coding RNAs that serve as substrates for the miRNA-processing pathway. We found that the Argonaute protein in Caenorhabditis elegans, ALG-1, binds to a specific site at the 3′ end of let-7 miRNA primary transcripts and promotes downstream processing events. This interaction is mediated by mature let-7 miRNA through a conserved complementary site in its own primary transcript, thus creating a positive-feedback loop. We further show that ALG-1 associates with let-7 primary transcripts in nuclear fractions. Argonaute also binds let-7 primary transcripts in human cells, demonstrating that the miRNA pathway targets non-coding RNAs in addition to protein-coding messenger RNAs across species. Moreover, our studies in C. elegans reveal a novel role for Argonaute in promoting biogenesis of a targeted transcript, expanding the functions of the miRNA pathway in gene regulation. This discovery of autoregulation of let-7 biogenesis establishes a new mechanism for controlling miRNA expression.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Suh, N. & Blelloch, R. Small RNAs in early mammalian development: from gametes to gastrulation. Development 138, 1653–1661 (2011)
Kim, V. N., Han, J. & Siomi, M. C. Biogenesis of small RNAs in animals. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 10, 126–139 (2009)
Krol, J., Loedige, I. & Filipowicz, W. The widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay. Nature Rev. Genet. 11, 597–610 (2010)
Huntzinger, E. & Izaurralde, E. Gene silencing by microRNAs: contributions of translational repression and mRNA decay. Nature Rev. Genet. 12, 99–110 (2011)
Fabian, M. R., Sonenberg, N. & Filipowicz, W. Regulation of mRNA translation and stability by microRNAs. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 79, 351–379 (2010)
Zisoulis, D. G. et al. Comprehensive discovery of endogenous Argonaute binding sites in Caenorhabditis elegans . Nature Struct. Mol. Biol. 17, 173–179 (2010)
Bracht, J., Hunter, S., Eachus, R., Weeks, P. & Pasquinelli, A. E. Trans-splicing and polyadenylation of let-7 microRNA primary transcripts. RNA 10, 1586–1594 (2004)
Van Wynsberghe, P. M. et al. LIN-28 co-transcriptionally binds primary let-7 to regulate miRNA maturation in Caenorhabditis elegans . Nature Struct. Mol. Biol. 18, 302–308 (2011)
Grishok, A. et al. Genes and mechanisms related to RNA interference regulate expression of the small temporal RNAs that control C. elegans developmental timing. Cell 106, 23–34 (2001)
Duchaine, T. F. et al. Functional proteomics reveals the biochemical niche of C. elegans DCR-1 in multiple small-RNA-mediated pathways. Cell 124, 343–354 (2006)
Diederichs, S. & Haber, D. A. Dual role for argonautes in microRNA processing and posttranscriptional regulation of microRNA expression. Cell 131, 1097–1108 (2007)
Tan, G. S. et al. Expanded RNA-binding activities of mammalian Argonaute 2. Nucleic Acids Res. 37, 7533–7545 (2009)
Reinhart, B. J. et al. The 21-nucleotide let-7 RNA regulates developmental timing in Caenorhabditis elegans . Nature 403, 901–906 (2000)
Bagga, S. et al. Regulation by let-7 and lin-4 miRNAs results in target mRNA degradation. Cell 122, 553–563 (2005)
Chatterjee, S., Fasler, M., Bussing, I. & Grosshans, H. Target-mediated protection of endogenous microRNAs in C. elegans . Dev. Cell 20, 388–396 (2011)
Chatterjee, S. & Grosshans, H. Active turnover modulates mature microRNA activity in Caenorhabditis elegans . Nature 461, 546–549 (2009)
Vella, M. C., Choi, E. Y., Lin, S. Y., Reinert, K. & Slack, F. J. The C. elegans microRNA let-7 binds to imperfect let-7 complementary sites from the lin-41 3′ UTR. Genes Dev. 18, 132–137 (2004)
Büssing, I., Yang, J. S., Lai, E. C. & Grosshans, H. The nuclear export receptor XPO-1 supports primary miRNA processing in C. elegans and Drosophila . EMBO J. 29, 1830–1839 (2010)
Castanotto, D., Lingeman, R., Riggs, A. D. & Rossi, J. J. CRM1 mediates nuclear-cytoplasmic shuttling of mature microRNAs. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 106, 21655–21659 (2009)
Tang, R. et al. Mouse miRNA-709 directly regulates miRNA-15a/16–1 biogenesis at the posttranscriptional level in the nucleus: evidence for a microRNA hierarchy system. Cell Res 22, 504–515 (2012)
Heo, I. et al. Lin28 mediates the terminal uridylation of let-7 precursor microRNA. Mol. Cell 32, 276–284 (2008)
Lehrbach, N. J. et al. LIN-28 and the poly(U) polymerase PUP-2 regulate let-7 microRNA processing in Caenorhabditis elegans . Nature Struct. Mol. Biol. 16, 1016–1020 (2009)
Michlewski, G. & Caceres, J. F. Antagonistic role of hnRNP A1 and KSRP in the regulation of let-7a biogenesis. Nature Struct. Mol. Biol. 17, 1011–1018 (2010)
Newman, M. A., Thomson, J. M. & Hammond, S. M. Lin-28 interaction with the Let-7 precursor loop mediates regulated microRNA processing. RNA 14, 1539–1549 (2008)
Rybak, A. et al. A feedback loop comprising lin-28 and let-7 controls pre-let-7 maturation during neural stem-cell commitment. Nature Cell Biol. 10, 987–993 (2008)
Trabucchi, M. et al. The RNA-binding protein KSRP promotes the biogenesis of a subset of microRNAs. Nature 459, 1010–1014 (2009)
Viswanathan, S. R., Daley, G. Q. & Gregory, R. I. Selective blockade of microRNA processing by Lin28. Science 320, 97–100 (2008)
Büssing, I., Slack, F. J. & Grosshans, H. let-7 microRNAs in development, stem cells and cancer. Trends Mol. Med. 14, 400–409 (2008)
Hendrickson, D. G., Hogan, D. J., Herschlag, D., Ferrell, J. E. & Brown, P. O. Systematic identification of mRNAs recruited to argonaute 2 by specific microRNAs and corresponding changes in transcript abundance. PLoS ONE 3, e2126 (2008)
Frøkjaer-Jensen, C. et al. Single-copy insertion of transgenes in Caenorhabditis elegans . Nature Genet. 40, 1375–1383 (2008)
Acknowledgements
We thank J. Lykke-Andersen and members of the Pasquinelli lab for reading the manuscript, and we thank D. Hogan for discussions. We thank F. Slack for originally pointing out the let-7 complementary site in pri-let-7; the M. David lab for sharing their real-time PCR machine; P. Van Wynsberghe for the Δalg-1 primary let-7 plasmid; C. Mello for the worm fractionation protocol; E. Moss for LIN-28 antibodies; and A. Gorin, H. Jenq and S. Verma for technical assistance. Funding was provided by a Leukemia & Lymphoma Society Special Fellow Award 3611-11 (D.G.Z.); US National Institutes of Health (NIH) CMG and NIH/NCI T32 CA009523 Training Grants (Z.S.K.); the Swedish Board of Study Support (R.K.C.); and NIH grant GM071654, the Keck Foundation and the Peter Gruber Foundation (A.E.P.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.E.P., D.G.Z. and Z.S.K. designed the project and wrote the paper. D.G.Z. (Figs 1b, c, 2a, 3b, g and 4b–e and Supplementary Figs 2, 3a–c, 4a and 6a), Z.S.K. (Figs 1d, 2c, d and 3c and Supplementary Figs 3d, 4c, d, g and 6b), R.K.C. (Figs 2b, 3g and 4a and Supplementary Fig. 4b) and A.E.P. (Fig. 4a and Supplementary Fig. 7) performed the experiments and analysed the data. A.E.P. supervised the studies.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
This file contains Supplementary Tables 1-2 and Supplementary Figures 1-7. (PDF 11404 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zisoulis, D., Kai, Z., Chang, R. et al. Autoregulation of microRNA biogenesis by let-7 and Argonaute. Nature 486, 541–544 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11134
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11134
This article is cited by
-
Selective inhibition of miRNA processing by a herpesvirus-encoded miRNA
Nature (2022)
-
MicroRNA: Could It Play a Role in Bovine Endometritis?
Inflammation (2021)
-
Mitochondrial noncoding RNA-regulatory network in cardiovascular disease
Basic Research in Cardiology (2020)
-
Regulation of microRNA function in animals
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2019)
-
Microglial-derived miRNA let-7 and HMGB1 contribute to ethanol-induced neurotoxicity via TLR7
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2017)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.