Abstract
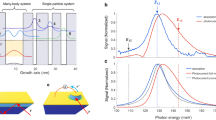
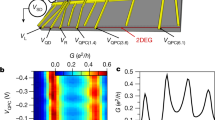
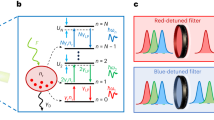
The interaction between a single confined spin and the spins of an electron reservoir leads to one of the most remarkable phenomena of many-body physics—the Kondo effect1,2. Electronic transport measurements on single artificial atoms, or quantum dots, have made it possible to study the effect in great detail3,4,5. Here we report optical measurements on a single semiconductor quantum dot tunnel-coupled to a degenerate electron gas which show that absorption of a single photon leads to an abrupt change in the system Hamiltonian and a quantum quench of Kondo correlations. By inferring the characteristic power-law exponents from the experimental absorption line shapes, we find a unique signature of the quench in the form of an Anderson orthogonality catastrophe6,7, induced by a vanishing overlap between the initial and final many-body wavefunctions. We show that the power-law exponent that determines the degree of orthogonality can be tuned using an external magnetic field8, which unequivocally demonstrates that the observed absorption line shape originates from Kondo correlations. Our experiments demonstrate that optical measurements on single artificial atoms offer new perspectives on many-body phenomena previously studied using transport spectroscopy only.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kondo, J. Resistance minimum in dilute magnetic alloys. Prog. Theor. Phys. 32, 37–49 (1964)
Kouwenhoven, L. P. & Glazman, L. Revival of the Kondo effect. Phys. World 14, 33–38 (January 2001)
Goldhaber-Gordon, D. et al. Kondo effect in a single-electron transistor. Nature 391, 156–159 (1998)
Cronenwett, S. M., Oosterkamp, T. H. & Kouwenhoven, L. P. A tunable Kondo effect in quantum dots. Science 281, 540–544 (1998)
van der Wiel, W. G. et al. The Kondo effect in the unitary limit. Science 289, 2105–2108 (2000)
Mahan, G. Many-Particle Physics 612–621 (Kluwer, 2000)
Anderson, P. W. Infrared catastrophe in Fermi gases with local scattering potentials. Phys. Rev. Lett. 18, 1049–1051 (1967)
Türeci, H. E. et al. Many-body dynamics of exciton creation in a quantum dot by optical absorption: a quantum quench towards Kondo correlations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 107402 (2011)
Michler, P. et al. A quantum dot single-photon turnstile device. Science 290, 2282–2285 (2000)
Dousse, A. et al. Ultrabright source of entangled photon pairs. Nature 466, 217–220 (2010)
Press, D., Ladd, T. D., Zhang, B. & Yamamoto, Y. Complete quantum control of a single quantum dot spin using ultrafast optical pulses. Nature 456, 218–221 (2008)
Kim, D. et al. Ultrafast optical control of entanglement between two quantum-dot spins. Nature Phys. 7, 223–229 (2011)
Yilmaz, S. T., Fallahi, P. & Imamoglu, A. Quantum-dot-spin single-photon interface. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 033601 (2010)
Claassen, M., Türeci, H. & Imamoglu, A. Solid-state spin-photon quantum interface without spin-orbit coupling. Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 177403 (2010)
Dalgarno, P. A. et al. Optically induced hybridization of a quantum dot state with a filled continuum. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100, 176801 (2008)
Hilario, L. M. L. & Aligia, A. A. Photoluminescence of a quantum dot hybridized with a continuum of extended states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 156802 (2009)
Kleemans, N. A. J. M. et al. Many-body exciton states in self-assembled quantum dots coupled to a Fermi sea. Nature Phys. 6, 534–538 (2010)
Latta, C. et al. Confluence of resonant laser excitation and bidirectional quantum-dot nuclear-spin polarization. Nature Phys. 5, 758–763 (2009)
Xu, X. et al. Optically controlled locking of the nuclear field via coherent dark-state spectroscopy. Nature 459, 1105–1109 (2009)
Högele, A. et al. Voltage-controlled optics of a quantum dot. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 217401 (2004)
Atatüre, M. et al. Quantum-dot spin-state preparation with near-unity fidelity. Science 312, 551–553 (2006)
Shahbazyan, T. V., Perakis, I. E. & Raikh, M. E. Spin correlations in nonlinear optical response: light-induced Kondo effect. Phys. Rev. Lett. 84, 5896–5899 (2000)
Kikoin, K. & Avishai, Y. Many-particle resonances in excited states of semiconductor quantum dots. Phys. Rev. B 62, 4647–4655 (2000)
Govorov, A. O., Karrai, K. & Warburton, R. J. Kondo excitons in self-assembled quantum dots. Phys. Rev. B 67, 241307(R) (2003)
Helmes, R. W., Sindel, M., Borda, L. & von Delft, J. Absorption and emission in quantum dots: Fermi surface effects of Anderson excitons. Phys. Rev. B 72, 125301 (2005)
Gunnarsson, O. & Schönhammer, K. Electron spectroscopies for Ce compounds in the impurity model. Phys. Rev. B 28, 4315–4341 (1983)
Warburton, R. J. et al. Optical emission from a charge-tunable quantum ring. Nature 405, 926–929 (2000)
Anderson, P. W. Localized magnetic states in metals. Phys. Rev. 124, 41–53 (1961)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Swiss NSF under grant no. 200021-121757 and an ERC Advanced Investigator Grant (A.I.). J.v.D. acknowledges support from the DFG (SFB631, SFB-TR12, De730/3-2, De730/4-1), the Cluster of Excellence ‘Nanosystems Initiative Munich’. H.E.T. acknowledges support from the Swiss NSF under grant no. PP00P2-123519/1. L.G. acknowledges support from NSF DMR under grant no. 0906498.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C.L., F.H., W.W. and P.F. carried out the experiments. M.H. and A.W. performed the numerical analysis. The samples were grown by S.F. C.L. and A.I. planned the experiment. H.E.T., M.C., L.G., A.I. and J.v.D. developed the theoretical framework. C.L., J.v.D. and A.I. supervised the project, carried out the analysis of the data and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
The file contains Supplementary Text and Data, Supplementary Figures 1-10 with legends and additional references. (PDF 1590 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Latta, C., Haupt, F., Hanl, M. et al. Quantum quench of Kondo correlations in optical absorption. Nature 474, 627–630 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10204
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10204
This article is cited by
-
Electrical monitoring of photoisomerization of block copolymers intercalated into graphene sheets
Nature Communications (2020)
-
Coulomb blockade in an atomically thin quantum dot coupled to a tunable Fermi reservoir
Nature Nanotechnology (2019)
-
Range of the Kondo Cloud in Weakly Disordered Hosts
Journal of Superconductivity and Novel Magnetism (2015)
-
Temperature-dependent photoluminescence in light-emitting diodes
Scientific Reports (2014)
-
Single spins in self-assembled quantum dots
Nature Materials (2013)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.