Abstract
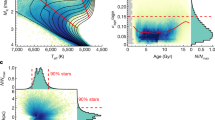
NGC 6791 is a well studied open cluster1 that it is so close to us that can be imaged down to very faint luminosities2. The main-sequence turn-off age (∼8 Gyr) and the age derived from the termination of the white dwarf cooling sequence (∼6 Gyr) are very different. One possible explanation is that as white dwarfs cool, one of the ashes of helium burning, 22Ne, sinks in the deep interior of these stars3,4,5. At lower temperatures, white dwarfs are expected to crystallize and phase separation of the main constituents of the core of a typical white dwarf (12C and 16O) is expected to occur6,7. This sequence of events is expected to introduce long delays in the cooling times8,9, but has not hitherto been proven. Here we report that, as theoretically anticipated5,6, physical separation processes occur in the cores of white dwarfs, resolving the age discrepancy for NGC 6791.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bedin, L. R. et al. The white dwarf cooling sequence in NGC 6791. Astrophys. J. 624, L45–L48 (2005)
Bedin, L. R. et al. Reaching the end of the white dwarf cooling sequence in NGC 6791. Astrophys. J. 678, 1279–1291 (2008)
Bravo, E., Isern, J., Labay, J. & Canal, R. On the contribution of Ne22 to the synthesis of Fe54 and Ni58 in thermonuclear supernovae. Astron. Astrophys. 257, 534–538 (1992)
Bildsten, L. & Hall, D. M. Gravitational settling of 22Ne in liquid white dwarf interiors. Astrophys. J. 549, L219–L223 (2001)
Deloye, C. J. & Bildsten, L. Gravitational settling of 22Ne in liquid white dwarf interiors: cooling and seismological effects. Astrophys. J. 580, 1077–1090 (2002)
García-Berro, E., Hernanz, M., Mochkovitch, R. & Isern, J. Theoretical white-dwarf luminosity functions for two phase diagrams of the carbon-oxygen dense plasma. Astron. Astrophys. 193, 141–147 (1988)
García-Berro, E., Hernanz, M., Isern, J. & Mochkovitch, R. Properties of high-density binary mixtures and the age of the universe from white dwarf stars. Nature 333, 642–644 (1988)
Segretain, L. et al. Cooling theory of crystallized white dwarfs. Astrophys. J. 434, 641–651 (1994)
García-Berro, E., Althaus, L. G., Córsico, A. H. & Isern, J. Gravitational settling of 22Ne and white dwarf evolution. Astrophys. J. 677, 473–482 (2008)
Bedin, L. R. et al. The puzzling white dwarf cooling sequence in NGC 6791: a simple solution. Astrophys. J. 679, L29–L32 (2008)
Kalirai, J. S. et al. Stellar evolution in NGC 6791: mass loss on the red giant branch and the formation of low-mass white dwarfs. Astrophys. J. 671, 748–760 (2007)
Althaus, L. G. et al. New evolutionary sequences for hot H-deficient white dwarfs on the basis of a full account of progenitor evolution. Astrophys. J. 704, 1605–1615 (2009)
Isern, J., Mochkovitch, R., García-Berro, E. & Hernanz, M. The physics of crystallizing white dwarfs. Astrophys. J. 485, 308–312 (1997)
Isern, J., García-Berro, E., Hernanz, M. & Chabrier, G. The energetics of crystallizing white dwarfs revisited again. Astrophys. J. 528, 397–400 (2000)
Segretain, L. Three-body crystallization diagrams and the cooling of white dwarfs. Astron. Astrophys. 310, 485–488 (1996)
Segretain, L. & Chabrier, G. Crystallization of binary ionic mixtures in dense stellar plasmas. Astron. Astrophys. 271, L13–L16 (1993)
García-Berro, E., Torres, S., Isern, J. & Burkert, A. Monte Carlo simulations of the disc white dwarf population. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 302, 173–188 (1999)
Torres, S., García-Berro, E., Burkert, A. & Isern, J. High-proper-motion white dwarfs and halo dark matter. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 336, 971–978 (2002)
García-Berro, E., Torres, S., Isern, J. & Burkert, A. Monte Carlo simulations of the halo white dwarf population. Astron. Astrophys. 418, 53–65 (2004)
Weiss, A. & Ferguson, J. W. New asymptotic giant branch models for a range of metallicities. Astron. Astrophys. 508, 1343–1358 (2009)
Ferrario, L., Wickramasinghe, D., Liebert, J. & Williams, K. A. The open-cluster initial-final mass relationship and the high-mass tail of the white dwarf distribution. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 361, 1131–1135 (2005)
Grundahl, F., Clausen, J. V., Hardis, S. & Frandsen, S. A new standard: age and distance for the open cluster NGC 6791 from the eclipsing binary member V20. Astron. Astrophys. 492, 171–184 (2008)
Gratton, R., Bragaglia, A., Carretta, E. & Tosi, M. The metallicity of the old open cluster NGC 6791. Astrophys. J. 642, 462–469 (2006)
Bedin, L. R. et al. The white dwarf cooling sequence in NGC 6791. Astrophys. J. 624, L45–L48 (2005)
Catalán, S., Isern, J., García-Berro, E. & Ribas, I. The initial-final mass relationship of white dwarfs revisited: effect on the luminosity function and mass distribution. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 387, 1693–1706 (2008)
Pietrinferni, A., Cassisi, S., Salaris, M. & Castelli, F. A large stellar evolution database for population synthesis studies. I. Scaled solar models and isochrones. Astrophys. J. 612, 168–190 (2004)
Acknowledgements
This research was partially supported by MCINN, AGENCIA, the Generalitat de Catalunya, STFC and CONICET. L.G.A. also acknowledges a PIV grant from the AGAUR of the Generalitat de Catalunya. We are indebted to L. Bedin and co-authors for providing the observational colour–magnitude diagram of Fig. 1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
E.G.-B. and L.G.A. conceived the study. E.G.-B. wrote the paper. J.I., P.L.-A. and E.G.-B. computed the theoretical expressions for the time delays introduced by the different separation processes. L.G.A., I.R., A.H.C. and E.G.-B. computed the cooling sequences. R.D.R. provided the appropriate colours. S.T., E.G.-B. and J.I. did the Monte Carlo simulations. M.S. computed the main-sequence evolutionary ages and errors. All authors discussed the results and made substantial contributions to the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
PowerPoint slides
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
García-Berro, E., Torres, S., Althaus, L. et al. A white dwarf cooling age of 8 Gyr for NGC 6791 from physical separation processes. Nature 465, 194–196 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09045
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09045
This article is cited by
-
Buoyant crystals halt the cooling of white dwarf stars
Nature (2024)
-
Searching for a secular variation of the gravitational constant using strong gravitational fields
General Relativity and Gravitation (2023)
-
Dynamics of ion-acoustic waves in multi-species quantum plasmas with arbitrary degeneracy
Indian Journal of Physics (2023)
-
Nonlinear excitation of large-amplitude ion acoustic solitary waves in a multispecies warm ion plasma with ultra-relativistic degenerate electrons
Journal of the Korean Physical Society (2022)
-
Arbitrary-amplitude self-gravitational solitary potential in a degenerate quantum plasma system
Journal of the Korean Physical Society (2022)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.