Abstract
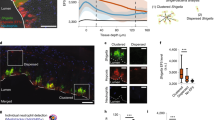
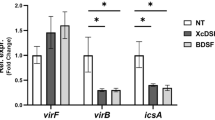
Bacteria coordinate expression of virulence determinants in response to localized microenvironments in their hosts. Here we show that Shigella flexneri, which causes dysentery, encounters varying oxygen concentrations in the gastrointestinal tract, which govern activity of its type three secretion system (T3SS). The T3SS is essential for cell invasion and virulence1. In anaerobic environments (for example, the gastrointestinal tract lumen), Shigella is primed for invasion and expresses extended T3SS needles while reducing Ipa (invasion plasmid antigen) effector secretion. This is mediated by FNR (fumarate and nitrate reduction), a regulator of anaerobic metabolism that represses transcription of spa32 and spa33, virulence genes that regulate secretion through the T3SS. We demonstrate there is a zone of relative oxygenation adjacent to the gastrointestinal tract mucosa, caused by diffusion from the capillary network at the tips of villi. This would reverse the anaerobic block of Ipa secretion, allowing T3SS activation at its precise site of action, enhancing invasion and virulence.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Phalipon, A. & Sansonetti, P. J. Shigella’s ways of manipulating the host intestinal innate and adaptive immune system: a tool box for survival? Immunol. Cell Biol. 85, 119–129 (2007)
Magdalena, J. et al. Spa32 regulates a switch in substrate specificity of the type III secreton of Shigella flexneri from needle components to Ipa proteins. J. Bacteriol. 184, 3433–3441 (2002)
Tamano, K., Katayama, E., Toyotome, T. & Sasakawa, C. Shigella Spa32 is an essential secretory protein for functional type III secretion machinery and uniformity of its needle length. J. Bacteriol. 184, 1244–1252 (2002)
Bahrani, F. K., Sansonetti, P. J. & Parsot, C. Secretion of Ipa proteins by Shigella flexneri: inducer molecules and kinetics of activation. Infect. Immun. 65, 4005–4010 (1997)
West, N. P. et al. Optimization of virulence functions through glucosylation of Shigella LPS. Science 307, 1313–1317 (2005)
Sansonetti, P. J. et al. Alterations in the pathogenicity of Escherichia coli K-12 after transfer of plasmid and chromosomal genes from Shigella flexneri . Infect. Immun. 39, 1392–1402 (1983)
Kiley, P. J. & Beinert, H. The role of Fe–S proteins in sensing and regulation in bacteria. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 6, 181–185 (2003)
Maxwell, P. H. et al. The tumour suppressor protein VHL targets hypoxia-inducible factors for oxygen-dependent proteolysis. Nature 399, 271–275 (1999)
Esteban, M. A. et al. Regulation of E-cadherin expression by VHL and hypoxia-inducible factor. Cancer Res. 66, 3567–3575 (2006)
Tobe, T. et al. Temperature-regulated expression of invasion genes in Shigella flexneri is controlled through the transcriptional activation of the virB gene on the large plasmid. Mol. Microbiol. 5, 887–893 (1991)
Schuch, R. & Maurelli, A. T. Spa33, a cell surface-associated subunit of the Mxi-Spa type III secretory pathway of Shigella flexneri, regulates Ipa protein traffic. Infect. Immun. 69, 2180–2189 (2001)
Hoitink, C. W., Woudt, L. P., Turenhout, J. C., van de Kamp, M. & Canters, G. W. Isolation and sequencing of the Alcaligenes denitrificans azurin-encoding gene: comparison with the genes encoding blue copper proteins from Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Alcaligenes faecalis . Gene 90, 15–20 (1990)
Melican, K. et al. Bacterial infection-mediated mucosal signalling induces local renal ischaemia as a defence against sepsis. Cell. Microbiol. 10, 1987–1998 (2008)
Becker, S., Holighaus, G., Gabrielczyk, T. & Unden, G. O2 as the regulatory signal for FNR-dependent gene regulation in Escherichia coli . J. Bacteriol. 178, 4515–4521 (1996)
Marti, M. A. et al. Dioxygen affinity in heme proteins investigated by computer simulation. J. Inorg. Biochem. 100, 761–770 (2006)
Hansen, M. C., Palmer, R. J. Jr, Udsen, C., White, D. C. & Molin, S. Assessment of GFP fluorescence in cells of Streptococcus gordonii under conditions of low pH and low oxygen concentration. Microbiology 147, 1383–1391 (2001)
Takahashi, E. et al. In vivo oxygen imaging using green fluorescent protein. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 291, C781–C787 (2006)
Ghisla, S., Hastings, J. W., Favaudon, V. & Lhoste, J.-M. Structure of the oxygen adduct intermediate in the bacterial luciferase reaction: 13C nuclear magnetic resonance determination. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 75, 5860–5863 (1978)
Torres Filho, I. P., Leunig, M., Yuan, F., Intaglietta, M. & Jain, R. K. Non-invasive measurement of microvascular and interstitial oxygen profiles in a human tumor in SCID mice. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 91, 2081–2085 (1994)
Tamano, K. et al. Supramolecular structure of the Shigella type III secretion machinery: the needle part is changeable in length and essential for delivery of effectors. EMBO J. 19, 3876–3887 (2000)
Jaumouillé, V., Francetic, O., Sansonetti, P. J. & Tran Van Nhieu, G. Cytoplasmic targeting of IpaC to the bacterial pole directs polar type III secretion in Shigella . EMBO J. 27, 447–457 (2008)
Pentecost, M., Otto, G., Theriot, J. A. & Amieva, M. R. Listeria monocytogenes invades the epithelial junctions at sites of cell extrusion. PLoS Pathog. 2, e3 (2006)
Exley, R. M. et al. Available carbon source influences the resistance of Neisseria meningitidis against complement. J. Exp. Med. 201, 1637–1645 (2005)
Podkovyrov, S. M. & Larson, T. J. A new vector-host system for construction of lacZ transcriptional fusions where only low-level gene expression is desirable. Gene 156, 151–152 (1995)
Sasakawa, C., Komatsu, K., Tobe, T., Suzuki, T. & Yoshikawa, M. Eight genes in region 5 that form an operon are essential for invasion of epithelial cells by Shigella flexneri 2a. J. Bacteriol. 175, 2334–2346 (1993)
Farinha, M. A. & Kropinski, A. M. Construction of broad-host-range plasmid vectors for easy visible selection and analysis of promoters. J. Bacteriol. 172, 3496–3499 (1990)
Datsenko, K. A. & Wanner, B. L. One-step inactivation of chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli K-12 using PCR products. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 97, 6640–6645 (2000)
Phalipon, A. et al. Identification and characterization of B-cell epitopes of IpaC, an invasion-associated protein of Shigella flexneri . Infect. Immun. 60, 1919–1926 (1992)
Ménard, R., Sansonetti, P., Parsot, C. & Vasselon, T. Extracellular association and cytoplasmic partitioning of the IpaB and IpaC invasins of S. flexneri . Cell 79, 515–525 (1994)
Warnecke, C. et al. Activation of the hypoxia-inducible factor-pathway and stimulation of angiogenesis by application of prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors. FASEB J. 17, 1186–1188 (2003)
Esteban, M. A. et al. Regulation of E-cadherin expression by VHL and hypoxia-inducible factor. Cancer Res. 66, 3567–3575 (2006)
Darzynkiewicz, Z. et al. Features of apoptotic cells measured by flow cytometry. Cytometry 13, 795–808 (1992)
Browning, D. F., Beatty, C. M., Wolfe, A. J., Cole, J. A. & Busby, S. J. Independent regulation of the divergent Escherichia coli nrfA and acsP1 promoters by a nucleoprotein assembly at a shared regulatory region. Mol. Microbiol. 43, 687–701 (2002)
Miller, J. Experiments in Molecular Genetics. (1972)
D’Hauteville, H. et al. Two msbB genes encoding maximal acylation of lipid A are required for invasive Shigella flexneri to mediate inflammatory rupture and destruction of the intestinal epithelium. J. Immunol. 168, 5240–5251 (2002)
Liss, P., Nygren, A., Revsbech, N. P. & Ulfendahl, H. R. Intrarenal oxygen tension measured by a modified Clark electrode at normal and low blood pressure and after injection of x-ray contrast media. Pflugers Arch. 434, 705–711 (1997)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale, the Royal Society, an ERC Advanced Grant (HOMEOEPITH), and the European Union (QLRT-1999-00938). Work in CMT’s laboratory is supported by the Wellcome Trust and The Medical Research Council, and PJS is a Howard Hughes Medical Institute scholar. Imaging was performed at the PFID station (Institut Pasteur). We are grateful to J. Green for the anti-FNR pAbs and advice. R. Exley, D. Holden and K. Ray provided suggestions and reviewed the manuscript; we thank M.-A. Nicola for technical help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
B.M., N.P.W. and J.M. performed experiments with Shigella. D.F.B. and J.A.C. provided technical support and advice for electrophoretic mobility shift assays and analysis of the fusions. J.G.S. analysed the lipopolysaccharide, M.-C.P. carried out EM, and F.P. performed the oxygen measurements. C.M.T. and P.S. provided advice and overall direction, and wrote the paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
This file contains Supplementary Figures 1-11 with legends, Supplementary Tables S1-S4 and References. (PDF 1264 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marteyn, B., West, N., Browning, D. et al. Modulation of Shigella virulence in response to available oxygen in vivo. Nature 465, 355–358 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08970
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08970
This article is cited by
-
Saccharomyces boulardii promoters for control of gene expression in vivo
Microbial Cell Factories (2024)
-
Nitric oxide is a host cue for Salmonella Typhimurium systemic infection in mice
Communications Biology (2023)
-
Molecular mechanisms of Shigella effector proteins: a common pathogen among diarrheic pediatric population
Molecular and Cellular Pediatrics (2022)
-
Microaerobic conditions enhance laccase production from Rheinheimera sp. in an economical medium
Archives of Microbiology (2022)
-
Adaptive strategies of uropathogenic Escherichia coli CFT073: from growth in lab media to virulence during host cell adhesion
International Microbiology (2022)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.