Abstract
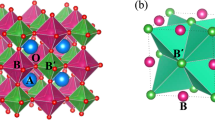
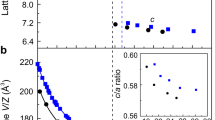
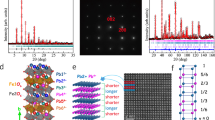
Changes of valence states in transition-metal oxides often cause significant changes in their structural and physical properties1,2. Chemical doping is the conventional way of modulating these valence states. In ABO3 perovskite and/or perovskite-like oxides, chemical doping at the A site can introduce holes or electrons at the B site, giving rise to exotic physical properties like high-transition-temperature superconductivity and colossal magnetoresistance3,4. When valence-variable transition metals at two different atomic sites are involved simultaneously, we expect to be able to induce charge transfer—and, hence, valence changes—by using a small external stimulus rather than by introducing a doping element. Materials showing this type of charge transfer are very rare, however, and such externally induced valence changes have been observed only under extreme conditions like high pressure5,6. Here we report unusual temperature-induced valence changes at the A and B sites in the A-site-ordered double perovskite LaCu3Fe4O12; the underlying intersite charge transfer is accompanied by considerable changes in the material’s structural, magnetic and transport properties. When cooled, the compound shows a first-order, reversible transition at 393 K from LaCu2+3Fe3.75+4O12 with Fe3.75+ ions at the B site to LaCu3+3Fe3+4O12 with rare Cu3+ ions at the A site. Intersite charge transfer between the A-site Cu and B-site Fe ions leads to paramagnetism-to-antiferromagnetism and metal-to-insulator isostructural phase transitions. What is more interesting in relation to technological applications is that this above-room-temperature transition is associated with a large negative thermal expansion.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Imada, M., Fujimori, A. & Tokura, Y. Metal-insulator transitions. Rev. Mod. Phys. 70, 1039–1263 (1998)
Goto, T. & Luthi, B. Charge ordering, charge fluctuations and lattice effects in strongly correlated electron systems. Adv. Phys. 52, 67–118 (2003)
Lee, P. A., Nagaosa, N. & Wen, X. G. Doping a Mott insulator: physics of high-temperature superconductivity. Rev. Mod. Phys. 78, 17–85 (2006)
Salamon, M. B. & Jaime, M. The physics of manganites: structure and transport. Rev. Mod. Phys. 73, 583–628 (2001)
Seda, T. & Hearne, G. R. Pressure induced Fe2++Ti4+→Fe3++Ti3+ intervalence charge transfer and the Fe3+/Fe2+ ratio in natural ilmenite (FeTiO3) minerals. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 16, 2707–2718 (2004)
Azuma, M. et al. Pressure-induced intermetallic valence transition in BiNiO3 . J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 14433–14436 (2007)
Zeng, Z., Greenblatt, M., Subramanian, M. A. & Croft, M. Large low-field magnetoresistance in perovskite-type CaCu3Mn4O12 without double exchange. Phys. Rev. Lett. 82, 3164–3167 (1999)
Subramanian, M. A., Li, D., Duan, N., Reisner, B. A. & Sleight, A. W. High dielectric constant in ACu3Ti4O12 and ACu3Ti3FeO12 phases. J. Solid State Chem. 151, 323–325 (2000)
Homes, C. C., Vogt, T., Shapiro, S. M., Wakimoto, S. & Ramirez, A. P. Optical response of high-dielectric-constant perovskite-related oxide. Science 293, 673–676 (2001)
Takata, K. et al. Magnetoresistance and electronic structure of the half-metallic ferrimagnet BiCu3Mn4O12 . Phys. Rev. B 76, 024429 (2007)
Sánchez-Benítez, J. et al. Preparation, crystal and magnetic structure, and magnetotransport properties of the double perovskite CaCu2. 5Mn4. 5O12 . Chem. Mater. 15, 2193–2200 (2003)
Shimakawa, Y. A-site-ordered perovskites with intriguing physical properties. Inorg. Chem. 47, 8562–8570 (2008)
Alonso, J. A. et al. Enhanced magnetoresistance in the complex perovskite LaCu3Mn4O12 . Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, 2623–2625 (2003)
Brown, I. D. & Altermatt, D. Bond-valence parameters obtained from a systematic analysis of the Inorganic Crystal Structure Database. Acta Crystallogr. B 41, 244–247 (1985)
Li, X. et al. Mössbauer spectroscopic study on nanocrystalline LaFeO3 materials. Hyperfine Interact. 69, 851–854 (1991)
Blaauw, C. & van der Woude, F. Magnetic and structural properties of BiFeO3 . J. Phys. Chem. 6, 1422–1431 (1973)
Kawasaki, S., Takano, M. & Takeda, Y. Ferromagnetic properties of SrFe1-x Co x O3 synthesized under high pressure. J. Solid State Chem. 121, 174–180 (1996)
Takano, M. et al. Charge disproportionation in CaFeO3 studied with the Mössbauer effect. Mater. Res. Bull. 12, 923–928 (1977)
Yamada, I. et al. A perovskite containing quadrivalent iron as a charge-disproportionated ferrimagnet. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 47, 7032–7035 (2008)
Takano, M., Kawachi, J., Nakanishi, N. & Takeda, Y. Valence state of the Fe ions in Sr1-x La x FeO3 . J. Solid State Chem. 39, 75–84 (1981)
Bocquet, A. E. et al. Electronic structure of SrFe4+O3 and related Fe perovskite oxides. Phys. Rev. B 45, 1561–1570 (1992)
Riesemeier, H., Gärtner, S., Lüders, K., Schmalz, M. & Schöllhorn, R. Susceptibility and NQR investigations on NaCuO2 . J. Phys. Chem. Solids 55, 613–615 (1994)
Imai, K. et al. Preparation, crystal structure, and magnetic property of a new compound LiCuO2 . J. Phys. Soc. Jpn 61, 1819–1820 (1992)
Prodi, A. et al. Charge, orbital and spin ordering phenomena in the mixed valence manganite (NaMn3+ 3)(Mn3+ 2Mn4+ 2)O12 . Nature Mater. 3, 48–52 (2004)
Takenaka, K. & Takagi, H. Giant negative thermal expansion in Ge-doped anti-perovskite manganese nitrides. Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 261902 (2005)
Takenaka, K., Asano, K., Misawa, M. & Takagi, H. Negative thermal expansion in Ge-free antiperovskite manganese nitrides: Tin-doping effect. Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 011927 (2008)
Sleight, A. W. Isotropic negative thermal expansion. Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 28, 29–43 (1998)
Larson, A. C. & von Dreele, R. B. General Structure Analysis System (GSAS). Report No. LAUR 86-748 (Los Alamos National Laboratory, 1994)
Acknowledgements
We thank K. Nishimura and K. Oka for help with the high-pressure synthesis and magnetic measurements, and we thank K. Jungeun for help with the SXRD experiments. Thanks are also due to M. Takano for discussions. This work was partly supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (19GS0207, 18350097, 17038014, 19014010 and 19340098), by the Global COE Program ‘International Center for Integrated Research and Advanced Education in Materials Science’ and by a grant for the Joint Project of Chemical Synthesis Core Research Institutions from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan.
Author Contributions Y.W.L. and Y.S. designed the study; Y.W.L. synthesized the sample and performed X-ray diffraction, thermogravimetric, magnetic and electrical measurements with the help of M.A. and T.S.; N.H. carried out Mössbauer measurements with the help of S.M.; all of the authors discussed the results; and Y.W.L. and Y.S. wrote the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
This file contains Supplementary Tables S1- S2, Supplementary References and Supplementary Figures S1-S2 with Legends (PDF 222 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Long, Y., Hayashi, N., Saito, T. et al. Temperature-induced A–B intersite charge transfer in an A-site-ordered LaCu3Fe4O12 perovskite. Nature 458, 60–63 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07816
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07816
This article is cited by
-
Metal-to-insulator transitions in 3d-band correlated oxides containing Fe compositions
International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy and Materials (2024)
-
Giant uniaxial negative thermal expansion in FeZr2 alloy over a wide temperature range
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Structural and Magneto-Elastic Properties of the Quadruple Perovskites CaCu3B2Os2O12 (B = Mn-Ni): The Heisenberg Model and DFT Study
Journal of Electronic Materials (2023)
-
Physical realization of topological Roman surface by spin-induced ferroelectric polarization in cubic lattice
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Giant multiple caloric effects in charge transition ferrimagnet
Scientific Reports (2021)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.