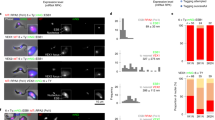
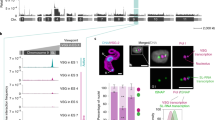
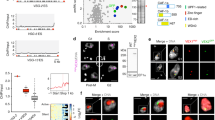
Abstract
Giardia lamblia (also called Giardia intestinalis) is one of the most common intestinal parasites of humans. To evade the host’s immune response, Giardia undergoes antigenic variation—a process that allows the parasite to develop chronic and recurrent infections. From a repertoire of ∼190 variant-specific surface protein (VSP)-coding genes, Giardia expresses only one VSP on the surface of each parasite at a particular time, but spontaneously switches to a different VSP by unknown mechanisms. Here we show that regulation of VSP expression involves a system comprising RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, Dicer and Argonaute, known components of the RNA interference machinery. Clones expressing a single surface antigen efficiently transcribe several VSP genes but only accumulate transcripts encoding the VSP to be expressed. Detection of antisense RNAs corresponding to the silenced VSP genes and small RNAs from the silenced but not for the expressed vsp implicate the RNA interference pathway in antigenic variation. Remarkably, silencing of Dicer and RNA-dependent RNA polymerase leads to a change from single to multiple VSP expression in individual parasites.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deitsch, K. W., Moxon, E. R. & Wellems, T. E. Shared themes of antigenic variation and virulence in bacterial, protozoal, and fungal infections. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 61, 281–293 (1997)
Adam, R. D. Biology of Giardia lamblia. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 14, 447–475 (2001)
Nash, T. E. Antigenic variation in Giardia lamblia and the host’s immune response. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 352, 1369–1375 (1997)
Morrison, H. G. et al. Genomic minimalism in the early diverging intestinal parasite Giardia lamblia. Science 317, 1921–1926 (2007)
Adam, R. D. et al. Antigenic variation of a cysteine-rich protein in Giardia lamblia. J. Exp. Med. 167, 109–118 (1988)
Nash, T. E., Mowatt, M. R. & Conrad, J. T. Variant-specific surface protein switching in Giardia lamblia. Infect. Immun. 69, 1922–1923 (2001)
Nash, T. E., Alling, D. W., Merritt, J. W. & Conrad, J. T. Frequency of variant antigens in Giardia lamblia. Exp. Parasitol. 71, 415–421 (1990)
Kulakova, L. S., Conrad, J. T. & Nash, T. E. Epigenetic mechanisms are involved in the control of Giardia lamblia antigenic variation. Mol. Microbiol. 61, 1533–1542 (2006)
Cogoni, C. & Macino, G. Homology-dependent gene silencing in plants and fungi: a number of variations on the same theme. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2, 657–662 (1999)
Fagard, M., Boutet, S., Morel, J. B., Bellini, C. & Vaucheret, H. AGO1, QDE-2, and RDE-1 are related proteins required for post-transcriptional gene silencing in plants, quelling in fungi, and RNA interference in animals. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 97, 11650–11654 (2000)
Elmendorf, H. G., Singer, S. M. & Nash, T. E. The abundance of sterile transcripts in Giardia lamblia. Nucleic Acids Res. 29, 4674–4683 (2001)
Hutvágner, G. & Zamore, P. D. RNAi: nature abhors a double-strand. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 12, 225–232 (2002)
Pak, J. F. et al. Distinct populations of primary and secondary effectors during RNAi in C. elegans. Science 315, 241–244 (2007)
Dougherty, W. G. P. Transgenes and gene suppression: telling us something new? Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 7, 399–405 (1995)
Zamore, P. D. Ancient pathways programmed by small RNAs. Science 296, 1265–1269 (2002)
White, T. C. & Wang, C. C. RNA dependent RNA polymerase activity associated with the double-stranded RNA virus of Giardia lamblia. Nucleic Acids Res. 18, 553–559 (1990)
Green-Willms, N. S., Fox, T. D. & Costanzo, M. C. Functional interactions between yeast mitochondrial ribosomes and mRNA 5′ untranslated leaders. Mol. Cell. Biol. 18, 1826–1834 (1998)
Bernstein, E., Caudy, A. A., Hammond, S. M. & Hannon, G. J. Role for a bidentate ribonuclease in the initiation step of RNA interference. Nature 409, 363–366 (2001)
Macrae, I. J. et al. Structural basis for double-stranded RNA processing by Dicer. Science 311, 195–198 (2006)
Nykanen, A., Haley, B. & Zamore, P. D. ATP requirements and small interfering RNA structure in the RNA interference pathway. Cell 107, 309–321 (2001)
Höck, J. M. The Argonaute protein family. Genome Biol. 9, 210 (2008)
Pal-Bhadra, M., Bhadra, U. & Birchler, J. A. RNAi related mechanisms affect both transcriptional and posttranscriptional transgene silencing in Drosophila. Mol. Cell 9, 315–327 (2002)
Touz, M. C., Gottig, N., Nash, T. E. & Lujan, H. D. Identification and characterization of a novel secretory granule calcium-binding protein from the early branching eukaryote Giardia lamblia. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 50557–50563 (2002)
Elmendorf, H. G. et al. Initiator and upstream elements in the α2-tubulin promoter of Giardia lamblia. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 113, 157–169 (2001)
Ullu, E. L., Lujan, H. D. & Tschudi, C. Small sense and antisense RNAs derived from a telomeric retroposon family in Giardia intestinalis. Euk. Cell 4, 1155–1157 (2005)
Tam, O. H. et al. Pseudogene-derived small interfering RNAs regulate gene expression in mouse oocytes. Nature 453, 534–543 (2008)
Watanabe, T. et al. Endogenous siRNAs from naturally formed dsRNAs regulate transcripts in mouse oocytes. Nature 453, 544–547 (2008)
von Allmen, N., Bienz, M., Hemphill, A. & Muller, N. Quantitative assessment of sense and antisense transcripts from genes involved in antigenic variation (vsp genes) and encystation (cwp 1 gene) of Giardia lamblia clone GS/M-83–H7. Parasitology 130, 389–396 (2005)
Lujan, H. D., Mowatt, M. R. & Nash, T. E. Molecular mechanisms of Giardia lamblia differentiation into cysts. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 61, 294–304 (1997)
Kloc, M. et al. RNA localization and germ cell determination in Xenopus. Int. Rev. Cytol. 203, 63–91 (2001)
Jambhekar, A. D. et al. Cis-acting determinants of asymmetric, cytoplasmic RNA transport. RNA 13, 625–642 (2007)
Nash, T. E., Aggarwal, A., Adam, R. D., Conrad, J. T. & Merritt, J. W. Antigenic variation in Giardia lamblia. J. Immunol. 141, 636–641 (1988)
Lujan, H. D., Mowatt, M. R., Conrad, J. T., Bowers, B. & Nash, T. E. Identification of a novel Giardia lamblia cyst wall protein with leucine-rich repeats. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 29307–29313 (1995)
Yee, J., Mowatt, M. R., Dennis, P. P. & Nash, T. E. Transcriptional analysis of the glutamate dehydrogenase gene in the primitive eukaryote, Giardia lamblia. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 11432–11439 (2000)
Hutvagner, G., Mlynarova, L. & Nap, J. P. Detailed characterization of the posttranscriptional gene-silencing-related small RNA in a GUS gene-silenced tobacco. RNA 6, 1445–1454 (2000)
Ngo, H., Tschudi, C., Gull, K. & Ullu, E. Double-stranded RNA induces mRNA degradation in Trypanosoma brucei. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 14687–14692 (1998)
Singer, S. M., Yee, J. & Nash, T. E. Episomal and integrated maintenance of foreign DNA in Giardia lamblia. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 92, 59–69 (1998)
Yee, J. & Nash, T. E. Transient transfection and expression of firefly luciferase in Giardia lamblia. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 92, 5615–5619 (1995)
Acknowledgements
We thank N. Gottig and M. E. Alvarez for technical support. This work was supported by grants from the Agencia Nacional para la Promoción de la Ciencia y la Tecnología (ANPCYT), the Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas (CONICET), the Universidad Católica de Córdoba (UCC), the Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI), and the European Union CONTENT project. H.D.L. is an HHMI International Research Scholar and a Member of the Scientific Investigator’s Career of the CONICET.
Author Contributions C.G.P. knocked down the expression of AGO and VSP9B10, expressed VSPH7 in WB strain trophozoites, performed confocal immunofluorescence assays, northern blots and quantitative RT–PCRs, and cloned and sequenced small RNAs; I.S. knocked down the expression of Dicer and RdRP, performed nuclear run-on and Dicer activity experiments, and cloned and sequenced RdRP, Dicer and VSP genes; R.Q. performed immunofluorescence assays, quantitative RT–PCRs and flow cytometry experiments; P.G.C. performed DNA methylation experiments; and F.D.R., E.V.E. and A.S. generated different monoclonal antibodies and performed immunofluorescence and immunoblotting assays. C.G.P., I.S. and H.D.L wrote this manuscript. H.D.L. conceived and coordinated the project. All authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
This file contains Supplementary Figures 1-10 with Legends, Supplementary Table 1, Supplementary Methods and Supplementary References (PDF 3257 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prucca, C., Slavin, I., Quiroga, R. et al. Antigenic variation in Giardia lamblia is regulated by RNA interference. Nature 456, 750–754 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07585
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07585
This article is cited by
-
Decoding the impact of nuclear organization on antigenic variation in parasites
Nature Microbiology (2023)
-
Antibodies to variable surface antigens induce antigenic variation in the intestinal parasite Giardia lamblia
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Liquid Biopsy for Promising Non-invasive Diagnostic Biomarkers in Parasitic Infections
Acta Parasitologica (2022)
-
MicroRNA profiling of Neospora caninum tachyzoites (NC-1) using a high-throughput approach
Parasitology Research (2021)
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitors induce expression of chromosomally tagged variant-specific surface protein genes in Giardia lamblia
BMC Research Notes (2020)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.