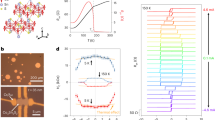
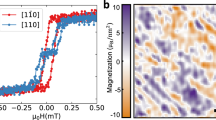
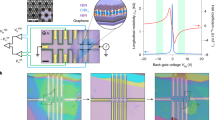
Abstract
The role of magnetic domains (and the walls between domains) in determining the electrical properties of ferromagnetic materials1 has been investigated in great detail for many years, not least because control over domains offers a means of manipulating electron spin to control charge transport in ‘spintronic’ devices2. In contrast, much less attention has been paid to the effects of domains and domain walls on the electrical properties of antiferromagnets: antiferromagnetic domains show no net external magnetic moment, and so are difficult to manipulate or probe. Here we describe electrical measurements on chromium—a simple metal and quintessential spin density wave antiferromagnet3—that show behaviour directly related to spin density wave formation and the presence of antiferromagnetic domains. Two types of thermal hysteresis are seen in both longitudinal and Hall resistivity: the first can be explained by the quantization of spin density waves due to the finite film thickness (confirmed by X-ray diffraction measurements) and the second by domain-wall scattering of electrons4,5. We also observe the striking influence of the electrical lead configuration (a mesoscopic effect) on the resistivity of macroscopic samples in the spin density wave state. Our results are potentially of practical importance, in that they reveal tunable electrical effects of film thickness and domain walls that are as large as the highest seen for ferromagnets6,7.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Marrows, C. H. Spin-polarised currents and magnetic domain walls. Adv. Phys. 54, 585–713 (2005)
Zutic, I., Fabian, J. & Das Sarma, S. Spintronics: Fundamentals and applications. Rev. Mod. Phys. 76, 323–410 (2004)
Fawcett, E. Spin-density-wave antiferromagnetism in chromium. Rev. Mod. Phys. 60, 209–283 (1988)
Jaramillo, R. et al. Microscopic and macroscopic signatures of antiferromagnetic domain walls. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 117206 (2007)
Shpyrko, O. G. et al. Direct measurement of antiferromagnetic domain fluctuations. Nature 447, 68–71 (2007)
Marrows, C. H. & Dalton, B. C. Spin mixing and spin-current asymmetry measured by domain wall magnetoresistance. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 097206 (2004)
Ebels, U. et al. Spin accumulation and domain wall magnetoresistance in 35 nm Co wires. Phys. Rev. Lett. 84, 983–986 (2000)
Baibich, M. N. et al. Giant magnetoresistance of (001)Fe/(001) Cr magnetic superlattices. Phys. Rev. Lett. 61, 2472–2475 (1988)
Evans, P. G. et al. X-ray microdiffraction images of antiferromagnetic domain evolution in chromium. Science 295, 1042–1045 (2002)
Bode, M. et al. Atomic spin structure of antiferromagnetic domain walls. Nature Mater. 5, 477–481 (2006)
Yeh, A. et al. Quantum phase transition in a common metal. Nature 419, 459–462 (2002)
Lee, M., Husmann, A., Rosenbaum, T. F. & Aeppli, G. High resolution study of magnetic ordering at absolute zero. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 187201 (2004)
Lomer, W. M. Electronic structure of chromium group metals. Proc. Phys. Soc. Lond. 80, 489–496 (1962)
Rotenberg, E. et al. Electron states and the spin density wave phase diagram in Cr(110) films. N. J. Phys. 10.1088/1367–2630/7/1/114 (2005)
Norman, M. R., Si, Q. M., Bazaliy, Y. B. & Ramazashvili, R. Hall effect in nested antiferromagnets near the quantum critical point. Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 116601 (2003)
Bazaliy, Y. B., Ramazashvili, R., Si, Q. & Norman, M. R. Magnetotransport near a quantum critical point in a simple metal. Phys. Rev. B 69, 144423 (2004)
Takeda, M. et al. Spin density wave in epitaxial Cr(001)/Sn and Cr(001)/Au multilayers with nonmagnetic spacer layers. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 69, 1590–1593 (2000)
Sonntag, P. et al. Magnetic phase diagram for spin-density waves in thin epitaxial Cr(001) films. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 183, 5–18 (1998)
Bodeker, P. et al. Reorientation of spin density waves in Cr(001) films induced by Fe(001) cap layers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 914–917 (1998)
Shi, Z. P. & Fishman, R. S. Interplay between spin density wave and proximity magnetic layers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 1351–1354 (1997)
Niklasson, A. M. N., Johansson, B. & Nordstrom, L. Spin density waves in thin chromium films. Phys. Rev. Lett. 82, 4544–4547 (1999)
Werner, S. A., Arrott, A. & Kendrick, H. Temperature and magnetic-field dependence of antiferromagnetism in pure chromium. Phys. Rev. 155, 528–539 (1967)
Mibu, K. et al. Discrete change of spin-density-wave modulation in Cr(100)/Sn multilayers as a function of Cr layer thickness. Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 287202 (2002)
Fullerton, E. E. et al. Hysteretic spin-density-wave ordering in confined geometries. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 237201 (2003)
Hill, J. P., Helgesen, G. & Gibbs, D. X-ray scattering study of charge and spin-density-waves in chromium. Phys. Rev. B 51, 10336–10344 (1995)
Fishman, R. S. & Shi, Z. P. Collinear spin-density-wave ordering in Fe Cr multilayers and wedges. Phys. Rev. B 59, 13849–13860 (1999)
Muir, W. B. & Stromols, J. O. Electrical resistance of single-crystal single-domain chromium from 77 to 325 degrees K. Phys. Rev. B 4, 988–991 (1971)
Arko, A. J., Marcus, J. A. & Reed, W. A. High-field galvanomagnetic effects in antiferromagnetic chromium. Phys. Rev. 1, 671–683 (1968)
Ziman, J. M. Electrons and Phonons. (Oxford Univ. Press, Oxford, 1960)
Michel, R. P. et al. Electrical-noise measurements on chromium films. Phys. Rev. B 44, 7413–7425 (1991)
Furuya, Y. Temperature and magnetic-field dependence of Hall-coefficient on antiferromagnetic chromium. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 40, 490–497 (1976)
Laurent, D. G., Callaway, J., Fry, J. L. & Brener, N. E. Band-structure, Fermi-surface, Compton profile, and optical conductivity of paramagnetic chromium. Phys. Rev. B 23, 4977–4987 (1981)
Acknowledgements
We thank the Burke foundation for their generous support of the project, J. Karapetrova, Z. Islam and J. Lang at Argonne National Laboratory and M. Vaudin at NIST for assisting the X-ray measurements, and the Rockefeller Foundation for the Bellagio Residency where this manuscript was completed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Methods
This file contains Supplementary Methods describing additional details of the measurements and some calculations. (PDF 47 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kummamuru, R., Soh, YA. Electrical effects of spin density wave quantization and magnetic domain walls in chromium. Nature 452, 859–863 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06826
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06826
This article is cited by
-
Atomic-scale thermopower in charge density wave states
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Nanoscale mechanics of antiferromagnetic domain walls
Nature Physics (2021)
-
Femtosecond control of phonon dynamics near a magnetic order critical point
Nature Communications (2021)
-
Dimensionality Effects in FeGe2 Nanowires: Enhanced Anisotropic Magnetization and Anomalous Electrical Transport
Scientific Reports (2017)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.