Abstract
Arising from: J. A. Byrne et al. Nature 450, doi: 10.1038/nature06357 (2007)
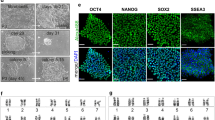
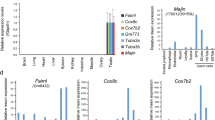
Somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT) into enucleated oocytes has emerged as a technique that can be used to derive mouse embryonic stem cell lines with defined genotypes. In this issue Byrne et al.1 report the derivation of two SCNT Rhesus macaca male stem cell lines designated CRES-1 and CRES-2. Molecular studies detailed in their paper provides supporting evidence that the chromosome complement of CRES-1 and CRES-2 was genetically identical to the male cell donor nucleus and that the mitochondrial DNA originated from different recipient oocytes. In this validation paper, we independently confirm that both stem cell lines were indeed derived by SCNT.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Byrne, J. A. et al. Producing primate embryonic stem cells by somatic cell nuclear transfer. Nature (this issue). 10.1038/nature06357 (2007)
Kim, K. et al. Histocompatible embryonic stem cells by parthenogenesis. Science 315, 482–486 (2007)
Raveendran, M. et al. Designing new microsatellite markers for linkage and population genetic analyses in rhesus macaques and other nonhuman primates. Genomics 88, 706–710 (2006)
Budowle, B. et al. Twelve short tandem repeat loci Y chromosome haplotypes: genetic analysis on populations residing in North America. Forensic Sci. Int. 150, 1–15 (2005)
Rogers, J. et al. An initial genetic linkage map of the rhesus macaque (Macaca mulatta) genome using human microsatellite loci. Genomics 87, 30–38 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cram, D., Song, B. & Trounson, A. Genotyping of Rhesus SCNT pluripotent stem cell lines. Nature 450, E12–E14 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06456
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06456
This article is cited by
-
Research integrity: Cell-induced stress
Nature (2014)
-
Stem-cell cloner acknowledges errors in groundbreaking paper
Nature (2013)
-
Progress and prospects: techniques for site-directed mutagenesis in animal models
Gene Therapy (2009)
-
Erratum: Genotyping of Rhesus SCNT pluripotent stem cell lines
Nature (2008)
-
Breathtaking advances in stem cell biology
Nature Clinical Practice Neurology (2008)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.