Abstract
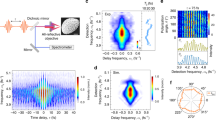
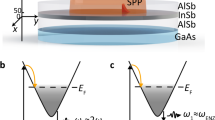
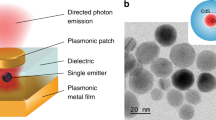
Control over the interaction between single photons and individual optical emitters is an outstanding problem in quantum science and engineering. It is of interest for ultimate control over light quanta1, as well as for potential applications such as efficient photon collection2, single-photon switching3 and transistors4, and long-range optical coupling of quantum bits5,6. Recently, substantial advances have been made towards these goals, based on modifying photon fields around an emitter using high-finesse optical cavities2,3,5,6,7,8. Here we demonstrate a cavity-free, broadband approach for engineering photon–emitter interactions4,9 via subwavelength confinement of optical fields near metallic nanostructures10,11,12,13. When a single CdSe quantum dot is optically excited in close proximity to a silver nanowire, emission from the quantum dot couples directly to guided surface plasmons in the nanowire, causing the wire’s ends to light up. Non-classical photon correlations between the emission from the quantum dot and the ends of the nanowire demonstrate that the latter stems from the generation of single, quantized plasmons. Results from a large number of devices show that efficient coupling is accompanied by more than 2.5-fold enhancement of the quantum dot spontaneous emission, in good agreement with theoretical predictions.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haroche, S. & Raimond, J.-M. Exploring the Quantum: Atoms, Cavities, Photons. (Oxford Univ. Press, New York, 2006)
Englund, D. et al. Controlling the spontaneous emission rate of single quantum in a two-dimensional photonic crystal. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 013904 (2005)
Birnbaum, K. M. et al. Photon blockade in an optical cavity with one trapped atom. Nature 436, 87–90 (2005)
Chang, D. E., Sørensen, A. S., Demler, E. A. & Lukin, M. D. A single-photon transistor using nano-scale surface plasmons. Nature Phys. advance online publication doi: 10.1038/nphys708 (26 August 2007)
Cirac, J. I., Zoller, P., Kimble, H. J. & Mabuchi, H. Quantum state transfer and entanglement distribution among distant nodes in a quantum network. Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 3221–3224 (1997)
Imamoğlu, A. et al. Quantum information processing using quantum dot spins and cavity QED. Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 4204–4207 (1999)
Hennessy, K. et al. Quantum nature of a strongly coupled single quantum dot–cavity system. Nature 445, 896–899 (2007)
Wilk, T., Webster, S. C., Kuhn, A. & Rempe, G. Single-atom single-photon quantum interface. Science 317, 488–490 (2007)
Chang, D. E., Sørensen, A. S., Hemmer, P. R. & Lukin, M. D. Quantum optics with surface plasmons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 053002 (2006)
Atwater, H. A. The promise of plasmonics. Sci. Am. 296, 56–63 (2007)
Genet, C. & Ebbesen, T. W. Light in tiny holes. Nature 445, 39–46 (2007)
Sanders, A. W. et al. Observation of plasmon propagation, redirection, and fan-out in silver nanowires. Nano Lett. 6, 1822–1826 (2006)
Ditlbacher, H. et al. Silver nanowires as surface plasmon resonators. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 257403 (2005)
Nayak, K. P. et al. Optical nanofiber as an efficient tool for manipulating and probing atomic fluorescence. Opt. Express 15, 5431–5438 (2007)
Takahara, J., Yamagishi, S., Taki, H., Morimoto, A. & Kobayashi, T. Guiding of a one-dimensional optical beam with nanometer diameter. Opt. Lett. 22, 475–477 (1997)
Chang, D. E., Sørensen, A. S., Hemmer, P. R. & Lukin, M. D. Strong coupling of single emitters to surface plasmons. Phys. Rev. B 76, 035420 (2007)
Chance, R. R., Prock, A. & Silbey, R. Molecular fluorescence and energy transfer near interfaces. Adv. Chem. Phys. 37, 1–65 (1978)
Sun, Y., Gates, B., Mayers, B. & Xia, Y. Crystalline silver nanowires by soft solution processing. Nano Lett. 2, 165–168 (2002)
Chung, I., Witkoskie, J. B., Cao, J. & Bawendi, M. G. Description of the fluorescence intensity time trace of collections of CdSe nanocrystal quantum dots based on single quantum dot fluorescence blinking statistics. Phys. Rev. E 73, 011106 (2006)
Tao, A. et al. Langmuir-Blodgett silver nanowire monolayers for molecular sensing using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Nano Lett. 3, 1229–1233 (2003)
Lounis, B., Bechtel, H. A., Gerion, D., Alivisatos, P. & Moerner, W. E. Photon antibunching in single CdSe/ZnS quantum dot fluorescence. Chem. Phys. Lett. 329, 399–404 (2000)
Dickson, R. M. & Lyon, L. A. Unidirectional plasmon propagation in metallic nanowires. J. Phys. Chem. B 104, 6095–6098 (2000)
Hochberg, M., Baehr-Jones, T., Walker, C. & Scherer, A. Integrated plasmon and dielectric waveguides. Opt. Express 12, 5481–5486 (2004)
Biteen, J. S., Lewis, N. S. & Atwater, H. A. Spectral tuning of plasmon-enhanced silicon quantum dot luminescence. Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 131109 (2006)
Zhang, J., Ye, Y.-H., Wang, X., Rochon, P. & Xiao, M. Coupling between semiconductor quantum dots and two-dimensional surface plasmons. Phys. Rev. B 72, 201306(R) (2005)
Mertens, H., Biteen, J. S., Atwater, H. A. & Polman, A. Polarization-selective plasmon-enhanced silicon quantum-dot luminescence. Nano Lett. 6, 2622–2625 (2006)
Bellessa, J., Bonnand, C. & Plenet, J. C. Strong coupling between surface plasmons and excitons in an organic semiconductor. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 036404 (2004)
Dintinger, J., Klein, S., Bustos, F., Barnes, W. L. & Ebbesen, T. W. Strong coupling between surface plasmon-polaritons and organic molecules in subwavelength hole arrays. Phys. Rev. B 71, 035424 (2005)
Klimov, V. V., Ducloy, M. & Letokhov, V. S. A model of an apertureless scanning microscope with a prolate nanospheroid as a tip and an excited molecule as an object. Chem. Phys. Lett. 358, 192–198 (2002)
Smolyaninov, I. I., Elliott, J., Zayats, A. & Davis, C. C. Far-field optical microscopy with a nanometer-scale resolution based on the in-plane magnification by surface plasmon polaritons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 057401 (2005)
Sagué, G., Vetsch, E., Alt, W., Meschede, D. & Rauschenbeutel, A. Cold atom physics using ultra-thin optical fibers: light-induced dipole forces and surface interactions. Preprint at 〈http://arxiv.org/quant-ph/0701167〉 (2007)
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge discussions with M. Loncar, J. Doyle, A. Sørensen and M.-H. Yoon, and support from the NSF, DARPA, Harvard-MIT CUA, Harvard CNS, the DTO, the Packard Foundation and Samsung Electronics.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
The file contains Supplementary Notes with Supplementary Figures S1-S12 and additional references. (PDF 2677 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akimov, A., Mukherjee, A., Yu, C. et al. Generation of single optical plasmons in metallic nanowires coupled to quantum dots. Nature 450, 402–406 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06230
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06230
This article is cited by
-
Ultrafast photoluminescence and multiscale light amplification in nanoplasmonic cavity glass
Nature Communications (2024)
-
Nonlinear optical response in multiple-mode coupling nanomechanical system
Nonlinear Dynamics (2024)
-
Recent progress of exciton transport in two-dimensional semiconductors
Nano Convergence (2023)
-
Emission enhancement of erbium in a reverse nanofocusing waveguide
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Reshaping plasmon modes by film interference
Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy (2023)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.