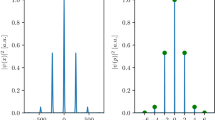
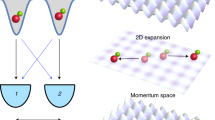
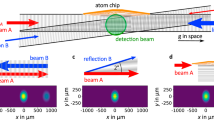
Abstract
The collision of two ultracold atoms results in a quantum mechanical superposition of the two possible outcomes: each atom continues without scattering, and each atom scatters as an outgoing spherical wave with an s-wave phase shift. The magnitude of the s-wave phase shift depends very sensitively on the interaction between the atoms. Quantum scattering and the underlying phase shifts are vitally important in many areas of contemporary atomic physics, including Bose–Einstein condensates1,2,3,4,5, degenerate Fermi gases6,7,8,9, frequency shifts in atomic clocks10,11,12 and magnetically tuned Feshbach resonances13. Precise experimental measurements of quantum scattering phase shifts have not been possible because the number of scattered atoms depends on the s-wave phase shifts as well as the atomic density, which cannot be measured precisely. Here we demonstrate a scattering experiment in which the quantum scattering phase shifts of individual atoms are detected using a novel atom interferometer. By performing an atomic clock measurement using only the scattered part of each atom’s wavefunction, we precisely measure the difference of the s-wave phase shifts for the two clock states in a density-independent manner. Our method will enable direct and precise measurements of ultracold atom–atom interactions, and may be used to place stringent limits on the time variations of fundamental constants14.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hall, D. S., Matthews, M. R., Ensher, J. R., Wieman, C. E. & Cornell, E. A. Dynamics of component separation in a binary mixture of Bose-Einstein condensates. Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 1539–1542 (1998)
Stenger, J. et al. Spin domains in ground-state Bose–Einstein condensates. Nature 396, 345–348 (1998)
Khaykovich, L. et al. Formation of a matter-wave bright soliton. Science 296, 1290–1293 (2002)
Strecker, K. E., Partridge, G. B., Truscott, A. G. & Hulet, R. G. Formation and propagation of matter-wave soliton trains. Nature 417, 150–153 (2002)
Widera, A. et al. Precision measurement of spin-dependent interaction strengths for spin-1 and spin-2 87Rb atoms. New J. Phys. 8, 152 (2006)
DeMarco, B. & Jin, D. S. Onset of Fermi degeneracy in a trapped atomic gas. Science 285, 1703–1706 (1999)
Modugno, G. et al. Collapse of a degenerate Fermi gas. Science 297, 2240–2243 (2002)
O’Hara, K. M., Hemmer, S. L., Gehm, M. E., Granade, S. R. & Thomas, J. E. Observation of a strongly interacting degenerate Fermi gas of atoms. Science 298, 2179–2182 (2002)
Gupta, S. et al. Radio-frequency spectroscopy of ultracold fermions. Science 300, 1723–1726 (2003)
Gibble, K. & Chu, S. Laser-cooled Cs frequency standard and a measurement of the frequency shift due to ultracold collisions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 70, 1771–1774 (1993)
Fertig, C. & Gibble, K. Measurement and cancellation of the cold collision shift in an 87Rb fountain clock. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 1622–1625 (2000)
Wynands, R. & Weyers, S. Atomic fountain clocks. Metrologia 42, S64–S79 (2005)
Inouye, S. et al. Observation of Feshbach resonances in a Bose–Einstein condensate. Nature 392, 151–154 (1998)
Chin, C. & Flambaum, V. V. Enhanced sensitivity to fundamental constants in ultracold atomic and molecular systems near Feshbach resonances. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 230801 (2006)
Legere, R. & Gibble, K. Quantum scattering in a juggling atomic fountain. Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 5780–5783 (1998)
Kasevich, M. et al. Atomic velocity selection using stimulated Raman transitions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 66, 2297–2300 (1991)
Gibble, K., Chang, S. & Legere, R. Direct observation of s-wave atomic collisions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 75, 2666–2669 (1995)
Legere, R. J. Quantum Scattering in a Juggling Atomic Fountain. PhD thesis, Yale Univ. (1999)
Kokkelmans, S. J. J. M. F. Interacting Atoms in Clocks and Condensates. PhD thesis, Univ. Eindhoven. (2000)
Monroe, C. R., Cornell, E. A., Sackett, C. A., Myatt, C. J. & Wieman, C. E. Measurement of Cs-Cs elastic scattering at T = 30 μK. Phys. Rev. Lett. 70, 414–417 (1993)
Myatt, C. J., Burt, E. A., Ghrist, R. W., Cornell, E. A. & Wieman, C. E. Production of two overlapping Bose-Einstein condensates by sympathetic cooling. Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 586–589 (1997)
Ensher, J. R., Jin, D. S., Matthews, M. R., Wieman, C. E. & Cornell, E. A. Bose-Einstein condensation in a dilute gas: Measurement of energy and ground-state occupation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 4984–4987 (1996)
DePue, M. T., McCormick, C., Winoto, S. L., Oliver, S. & Weiss, D. S. Unity occupation of sites in a 3D optical lattice. Phys. Rev. Lett. 82, 2262–2265 (1999)
Chin, C., Vuletic, V., Kerman, A. J. & Chu, S. High resolution Feshbach spectroscopy of cesium. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 2717–2720 (2000)
Chin, C. et al. Precision Feshbach spectroscopy of ultracold Cs2 . Phys. Rev. A 70, 032701 (2004)
Thomas, N. R., Kjærgaard, N., Julienne, P. S. & Wilson, A. C. Imaging of s and d partial-wave interference in quantum scattering of identical bosonic atoms. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 173201 (2004)
Buggle, Léonard, J., von Klitzing, W. & Walraven, J. T. M. Interferometric determination of the s and d-wave scattering amplitudes in 87Rb. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 173202 (2004)
Hamann, S. E. et al. Resolved-sideband Raman cooling to the ground state of an optical lattice. Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 4149–4152 (1998)
Treutlein, P., Chung, K. Y. & Chu, S. High-brightness atom source for atomic fountains. Phys. Rev. A 63, 051401(R) (2001)
Levitt, M. H. Composite pulses. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 18, 61–122 (1986)
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge discussions with B. Verhaar and S. Kokkelmans and contributions from R. Li. This work was supported by NASA, NSF, ONR and Penn State University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Reprints and permissions information is available at www.nature.com/reprints. The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hart, R., Xu, X., Legere, R. et al. A quantum scattering interferometer. Nature 446, 892–895 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05680
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05680
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.