Abstract
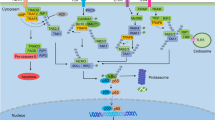
Nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) transcription factors and the signalling pathways that activate them are central coordinators of innate and adaptive immune responses. More recently, it has become clear that NF-κB signalling also has a critical role in cancer development and progression. NF-κB provides a mechanistic link between inflammation and cancer, and is a major factor controlling the ability of both pre-neoplastic and malignant cells to resist apoptosis-based tumour-surveillance mechanisms. NF-κB might also regulate tumour angiogenesis and invasiveness, and the signalling pathways that mediate its activation provide attractive targets for new chemopreventive and chemotherapeutic approaches.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balkwill, F. & Mantovani, A. Inflammation and cancer: back to Virchow? Lancet 357, 539–545 (2001).
Coussens, L. M. & Werb, Z. Inflammation and cancer. Nature 420, 860–867 (2002).
Kuper, H., Adami, H. O. & Trichopoulos, D. Infections as a major preventable cause of human cancer. J. Intern. Med. 248, 171–183 (2000).
Roder, D. M. The epidemiology of gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer 5 (Suppl. 1), 5–11 (2002).
Ekbom, A. Risk of cancer in ulcerative colitis. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2, 312–313 (1998).
Dhala, A., Pinsker, K. & Prezant, D. J. Respiratory health consequences of environmental tobacco smoke. Med. Clin. North Am. 88, 1535–1552, xi (2004).
Greten, F. R. & Karin, M. NF-κB: linking inflammation and immunity to cancer development and progression. Nature Rev. Immunol. 5, 749–759 (2005).
Balkwill, F., Charles, K. A. & Mantovani, A. Smoldering and polarized inflammation in the initiation and promotion of malignant disease. Cancer Cell 7, 211–217 (2005).
Hanahan, D. & Weinberg, R. A. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 100, 57–70 (2000).
Li, Q., Withoff, S. & Verma, I. M. Inflammation-associated cancer: NF-κB is the lynchpin. Trends Immunol. 26, 318–325 (2005).
Karin, M., Cao, Y., Greten, F. R. & Li, Z. W. NF-κB in cancer: from innocent bystander to major culprit. Nature Rev. Cancer 2, 301–310 (2002).
Gilmore, T. D. The Re1/NF-κB/IκB signal transduction pathway and cancer. Cancer Treat. Res. 115, 241–265 (2003).
Medzhitov, R. Toll-like receptors and innate immunity. Nature Rev. Immunol. 1, 135–145 (2001).
Akira, S., Uematsu, S. & Takeuchi, O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell 124, 783–801 (2006).
Nizet, V., Lawrence, T. & Karin, M. Innate immunity gone awry: mechanisms linking microbial infections to chronic inflammatory disorders and cancer. Cell 124, 823–835 (2006).
Li, Q. & Verma, I. M. NF-κB regulation in the immune system. Nature Rev. Immunol. 2, 725–734 (2002).
Sun, J. et al. Sequence variants in Toll-like receptor gene cluster (TLR6–TLR1–TLR10) and prostate cancer risk. J. Natl Cancer Inst. 97, 525–532 (2005).
El-Omar, E. M. et al. Interleukin-1 polymorphisms associated with increased risk of gastric cancer. Nature 404, 398–402 (2000).
Arnott, C. H. et al. Tumour-necrosis factor-α mediates tumour promotion via a PKCα- and AP-1-dependent pathway. Oncogene 21, 4728–4738 (2002).
Lind, M. H. et al. Tumor necrosis factor receptor 1-mediated signaling is required for skin cancer development induced by NF-κB inhibition. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 101, 4972–4977 (2004).
Pikarsky, E. et al. NF-κB functions as a tumour promoter in inflammation-associated cancer. Nature 431, 461–466 (2004).
Balkwill, F. Tumor necrosis factor or tumor promoting factor? Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 13, 135–141 (2002).
Oshima, M., Oshima, H., Matsunaga, A. & Taketo, M. M. Hyperplastic gastric tumors with spasmolytic polypeptide-expressing metaplasia caused by tumor necrosis factor-α-dependent inflammation in cyclooxygenase-2/microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 transgenic mice. Cancer Res. 65, 9147–9151 (2005).
Liu, Z. -G., Hu, H., Goeddel, D. V. & Karin, M. Dissection of TNF receptor 1 effector functions: JNK activation is not linked to apoptosis, while NF-κB activation prevents cell death. Cell 87, 565–576 (1996).
Beg, A. A. & Baltimore, D. An essential role for NF-κB in preventing TNF-α induced cell death. Science 274, 782–784 (1996).
Van Antwerp, D. J., Martin, S. J., Kafri, T., Green, D. R. & Verma, I. M. Suppression of TNFα-induced apoptosis by NF-κB. Science 274, 787–789 (1996).
Wang, C.-Y., Mayo, M. W. & Baldwin, A. S. Jr. TNF-α and cancer therapy-induced apoptosis: potentiation by inhibition of NF-κB. Science 274, 784–787 (1996).
Makris, C. et al. Female mice heterozygous for IKKγ/NEMO deficiencies develop a dermatopathy similar to the human X-linked disorder incontinentia pigmenti. Mol. Cell 5, 969–979 (2000).
Micheau, O., Lens, S., Gaide, O., Alevizopoulos, K. & Tschopp, J. NF-κB signals induce the expression of c-FLIP. Mol. Cell. Biol. 21, 5299–5305 (2001).
Karin, M. & Lin, A. NF-κB at the crossroads of life and death. Nature Immunol. 3, 221–227 (2002).
Danial, N. N. & Korsmeyer, S. J. Cell death: critical control points. Cell 116, 205–219 (2004).
Lavon, I. et al. High susceptibility to bacterial infection, but no liver dysfunction, in mice compromised for hepatocyte NF-κB activation. Nature Med. 6, 573–577 (2000).
Chen, L. W. et al. The two faces of IKK and NF-κB inhibition: prevention of systemic inflammation but increased local injury following intestinal ischemia–reperfusion. Nature Med. 9, 575–581 (2003).
Okayasu, I., Ohkusa, T., Kajiura, K., Kanno, J. & Sakamoto, S. Promotion of colorectal neoplasia in experimental murine ulcerative colitis. Gut 39, 87–92 (1996).
Greten, F. R. et al. IKKβ links inflammation and tumorigenesis in a mouse model of colitis-associated cancer. Cell 118, 285–296 (2004).
Becker, C. et al. TGF-β suppresses tumor progression in colon cancer by inhibition of IL-6 trans-signaling. Immunity 21, 491–501 (2004).
Mauad, T. H. et al. Mice with homozygous disruption of the mdr2 P-glycoprotein gene. A novel animal model for studies of nonsuppurative inflammatory cholangitis and hepatocarcinogenesis. Am. J. Pathol. 145, 1237–1245 (1994).
Zucca, E., Bertoni, F., Roggero, E. & Cavalli, F. The gastric marginal zone B-cell lymphoma of MALT type. Blood 96, 410–419 (2000).
Ruland, J. et al. Bcl10 is a positive regulator of antigen receptor-induced activation of NF-κB and neural tube closure. Cell 104, 33–42 (2001).
Lucas, P. C. et al. Bcl10 and MALT1, independent targets of chromosomal translocation in malt lymphoma, cooperate in a novel NF-κB signaling pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 19012–19019 (2001).
Thome, M. CARMA1, BCL-10 and MALT1 in lymphocyte development and activation. Nature Rev. Immunol. 4, 348–359 (2004).
van Hogerlinden, M., Rozell, B. L., Ahrlund-Richter, L. & Toftgard, R. Squamous cell carcinomas and increased apoptosis in skin with inhibited Rel/nuclear factor-κB signaling. Cancer Res. 59, 3299–3303 (1999).
van Hogerlinden, M., Auer, G. & Toftgard, R. Inhibition of Rel/nuclear factor-κB signaling in skin results in defective DNA damage-induced cell cycle arrest and Ha-ras- and p53-independent tumor development. Oncogene 21, 4969–4977 (2002).
Dajee, M. et al. NF-κB blockade and oncogenic Ras trigger invasive human epidermal neoplasia. Nature 421, 639–643 (2003).
Zhang, J. Y., Green, C. L., Tao, S. & Khavari, P. A. NF-κB RelA opposes epidermal proliferation driven by TNFR1 and JNK. Genes Dev. 18, 17–22 (2004).
Karin, M. The regulation of AP-1 activity by mitogen-activated protein kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 16483–16486 (1995).
Kamata, H. et al. Reactive oxygen species promote TNFα-induced death and sustained JNK activation by inhibiting MAP kinase phosphatases. Cell 120, 649–661 (2005).
Pham, C. G. et al. Ferritin heavy chain upregulation by NF-κB inhibits TNFα-induced apoptosis by suppressing reactive oxygen species. Cell 119, 529–542 (2004).
Maeda, S., Kamata, H., Luo, J. L., Leffert, H. & Karin, M. IKKβ couples hepatocyte death to cytokine-driven compensatory proliferation that promotes chemical hepatocarcinogenesis. Cell 121, 977–990 (2005).
Chang, L. et al. The E3 ubiquitin ligase itch couples JNK activation to TNFα-induced cell death by inducing c-FLIP(L) turnover. Cell 124, 601–613 (2006).
Park, J. S. et al. Involvement of toll-like receptors 2 and 4 in cellular activation by high mobility group box 1 protein. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 7370–7377 (2004).
Holla, V. R. et al. Prostaglandin E2 regulates the complement inhibitor CD55/decay-accelerating factor in colorectal cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 476–483 (2005).
Sparmann, A. & Bar-Sagi, D. Ras-induced interleukin-8 expression plays a critical role in tumor growth and angiogenesis. Cancer Cell 6, 447–458 (2004).
Garkavtsev, I. et al. The candidate tumour suppressor protein ING4 regulates brain tumour growth and angiogenesis. Nature 428, 328–332 (2004).
Joyce, D. et al. NF-κB and cell-cycle regulation: the cyclin connection. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 12, 73–90 (2001).
Cao, Y. et al. IKKα provides an essential link between RANK signaling and cyclin D1 expression during mammary gland development. Cell 107, 763–775 (2001).
Luo, J. L., Maeda, S., Hsu, L. C., Yagita, H. & Karin, M. Inhibition of NF-κB in cancer cells converts inflammation- induced tumor growth mediated by TNFα to TRAIL-mediated tumor regression. Cancer Cell 6, 297–305 (2004).
Karin, M., Yamamoto, Y. & Wang, Q. M. The IKK NF-κB system: a treasure trove for drug development. Nature Rev. Drug Discov. 3, 17–26 (2004).
Ghosh, S. & Karin, M. Missing pieces in the NF-κB puzzle. Cell 109 (suppl.), S81–S96 (2002).
Gilmore, T. D. The Rel/NF-κB signal transduction pathway: introduction. Oncogene 18, 6842–6844 (1999).
Rothwarf, D. M. & Karin, M. The NF-κB activation pathway: a paradigm in information transfer from membrane to nucleus. Sci. STKE 1999, RE1 (1999).
Karin, M. & Ben-Neriah, Y. Phosphorylation meets ubiquitination: the control of NF-κB activity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 18, 621–663 (2000).
Werner, S. L., Barken, D. & Hoffmann, A. Stimulus specificity of gene expression programs determined by temporal control of IKK activity. Science 309, 1857–1861 (2005).
Park, J. M. et al. Signaling pathways and genes that inhibit pathogen-induced macrophage apoptosis — CREB and NF-κB as key regulators. Immunity 23, 319–329 (2005).
Covert, M. W., Leung, T. H., Gaston, J. E. & Baltimore, D. Achieving stability of lipopolysaccharide-induced NF-κB activation. Science 309, 1854–1857 (2005).
Bonizzi, G. & Karin, M. The two NF-κB activation pathways and their role in innate and adaptive immunity. Trends Immunol. 25, 280–288 (2004).
Senftleben, U. et al. Activation by IKKα of a second, evolutionary conserved, NF-κB signaling pathway. Science 293, 1495–1499 (2001).
Neri, A. et al. B-cell lymphoma-associated chromosomal translocation involves candidate oncogene lyt-10, homologous to NF-κB p50. Cell 67, 1075–1087 (1991).
Demicco, E. G. et al. RelB/p52 NF-κB complexes rescue an early delay in mammary gland development in transgenic mice with targeted superrepressor IκB-α expression and promote carcinogenesis of the mammary gland. Mol. Cell. Biol. 25, 10136–10147 (2005).
Kato, T. Jr., Delhase, M., Hoffmann, A. & Karin, M. CK2 Is a c-terminal IκB kinase responsible for NF-κB activation during the UV response. Mol. Cell 12, 829–839 (2003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The author declares no competing financial interests.
Additional information
Author Information Reprints and permissions information is available at npg.nature.com/reprintsandpermissions.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karin, M. Nuclear factor-κB in cancer development and progression. Nature 441, 431–436 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04870
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04870
This article is cited by
-
PLOD3 facilitated T cell activation in the colorectal tumor microenvironment and liver metastasis by the TNF-α/ NF-κB pathway
Journal of Translational Medicine (2024)
-
HPV E6/E7: insights into their regulatory role and mechanism in signaling pathways in HPV-associated tumor
Cancer Gene Therapy (2024)
-
Something still missing in molecular imaging: CXCR2 axis in prostate cancer
European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (2024)
-
Sterile inflammation via TRPM8 RNA-dependent TLR3-NF-kB/IRF3 activation promotes antitumor immunity in prostate cancer
The EMBO Journal (2024)
-
The linear ANRIL transcript P14AS regulates the NF-κB signaling to promote colon cancer progression
Molecular Medicine (2023)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.