Abstract
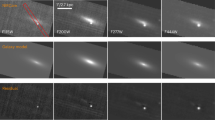
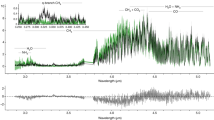
The final chapter in the long-standing mystery of the γ-ray bursts (GRBs) centres on the origin of the short-hard class of bursts, which are suspected on theoretical grounds to result from the coalescence of neutron-star or black-hole binary systems. Numerous searches for the afterglows of short-hard bursts have been made, galvanized by the revolution in our understanding of long-duration GRBs that followed the discovery in 1997 of their broadband (X-ray, optical and radio) afterglow emission. Here we present the discovery of the X-ray afterglow of a short-hard burst, GRB 050709, whose accurate position allows us to associate it unambiguously with a star-forming galaxy at redshift z = 0.160, and whose optical lightcurve definitively excludes a supernova association. Together with results from three other recent short-hard bursts, this suggests that short-hard bursts release much less energy than the long-duration GRBs. Models requiring young stellar populations, such as magnetars and collapsars, are ruled out, while coalescing degenerate binaries remain the most promising progenitor candidates.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang, B. & Meszaros, P. Gamma-ray bursts: progress, problems & prospects. Int. J. Mod. Phys. A19, 2385–2472 (2004)
Kouveliotou, C. et al. Identification of two classes of gamma-ray bursts. Astrophys. J. 413, L101–L104 (1993)
Hurley, K. et al. Afterglow upper limits for four short-duration, hard spectrum gamma-ray bursts. Astrophys. J. 567, 447–453 (2002)
Kulkarni, S. R. et al. Supernova and low-velocity ejecta constraints for the short-hand γ-ray burst GRB 050509B. Nature (submitted)
Bloom, J. S. et al. Closing in on a short-hard burst progenitor: constraints from early-time optical imaging and spectroscopy of a possible host galaxy of GRB 050509b. Astrophys. J (submitted)
Gehrels, N. et al. A short γ-ray burst apparently associated with an elliptical galaxy at redshift z = 0.225. Nature doi:10.1038/nature04142 (this issue)
Schmidt, M. Luminosities and space densities of short gamma-ray bursts. Astrophys. J. 559, L79–L82 (2001)
Eichler, D., Livio, M., Piran, T. & Schramm, D. N. Nucleosynthesis, neutrino bursts and gamma-rays from coalescing neutron stars. Nature 340, 126–128 (1989)
Guetta, D. & Piran, T. The luminosity and redshift distributions of short-duration GRBs. Astron. Astrophys. 435, 421–426 (2005)
Villasenor, J. et al. Discovery of the short γ-ray burst GRB 050709. Nature doi:10.1038/nature04213 (this issue)
Garmire, G. P., Bautz, M. W., Ford, P. G., Nousek, J. A. & Ricker, G. R. in X-Ray and Gamma-Ray Telescopes and Instruments for Astronomy (eds Truemper, J. E. & Tananbaum, H. D.) Proc. SPIE. 4851, 28–44 (2003).
Condon, J. J. et al. The NRAO VLA Sky Survey. Astron. J. 115, 1693–1716 (1998)
Fox, D. B., Frail, D. A., Cameron, P. B. & Cenko, S. B. GRB050709: candidate X-ray afterglow. GRB Circ. Netw. 3585 (2004)
Burrows, D. N. et al. Bright X-ray flares in gamma-ray burst afterglows. Science 150, 1–5 (2005)
Jensen, B. L. et al. GRB 050709: Chandra source optical counterpart. GRB Circ. Netw. 3589 (2005)
Hjorth, J. et al. The optical afterglow of the short γ-ray burst GRB 050709. Nature doi:10.1038/nature04174 (this issue)
Sirianni, M. et al. The photometric performance and calibration of the HST advanced camera for surveys. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pacif. (in the press); preprint at http://arxiv.org/astro-ph/0507614 (2005)
Bloom, J. S., Kulkarni, S. R. & Djorgovski, S. G. The observed offset distribution of gamma-ray bursts from their host galaxies: A robust clue to the nature of the progenitors. Astron. J. 123, 1111–1148 (2002)
Frail, D. A. et al. Beaming in gamma-ray bursts: evidence for a standard energy reservoir. Astrophys. J. 562, L55–L58 (2001)
Rhoads, J. E. The dynamics and light curves of beamed gamma-ray burst afterglows. Astrophys. J. 525, 737–749 (1999)
Berger, E. et al. A merger origin for short gamma-ray bursts inferred from the afterglow and host galaxy of GRB 050724. Nature (submitted); preprint at http://arXiv.org/astro-ph/0508115 (2005)
Kumar, P. The distribution of burst energy and shock parameters for gamma-ray bursts. Astrophys. J. 538, L125–L128 (2000)
Berger, E., Kulkarni, S. R. & Frail, D. A. A standard kinetic energy reservoir in gamma-ray burst afterglows. Astrophys. J. 590, 379–385 (2003)
Janka, H.-T. & Ruffert, M. Stellar Collisions, Mergers and their Consequences 333–358 (ASP Conf. Ser. 263, Astronomical Society of the Pacific, San Francisco, 2002)
Li, L. & Paczyński, B. Transient events from neutron star mergers. Astrophys. J. 507, L59–L62 (1998)
Totani, T. Probing the cosmic star formation history by the brightness distribution of gamma-ray bursts. Astrophys. J. 511, 41–55 (1999)
Balázs, L. G., Bagoly, Z., Horváth, I., Mészáros, A. & Mészáros, P. On the difference between the short and long gamma-ray bursts. Astron. Astrophys. 401, 129–140 (2003)
Katz, J. I. & Canel, L. M. The long and the short of gamma-ray bursts. Astrophys. J 471, 915–920 (1996)
Piran, T. Compact Stars in Binaries 489–500 (IAU Symp. 165, Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, 1996)
Eisenstein, D. J., Hogg, D. W. & Padmanabhan, N. GRB050509b, SDSS pre-burst observations. GRB Circ. Netw. 3418 (2005)
Mannucci, F. et al. The supernova rate per unit mass. Astron. Astrophys. 433, 807–814 (2005)
Kulkarni, S. R. et al. Radio emission from the unusual supernova 1998bw and its association with the gamma-ray burst of 25 April 1998. Nature 395, 663–669 (1998)
Galama, T. J. et al. An unusual supernova in the error box of the gamma-ray burst of 25 April 1998. Nature 395, 670–672 (1998)
Hjorth, J. et al. A very energetic supernova associated with the γ-ray burst of 29 March 2003. Nature 423, 847–850 (2003)
Stanek, K. Z. et al. Spectroscopic discovery of the supernova 2003dh associated with GRB 030329. Astrophys. J. 591, L17–L20 (2003)
Hjorth, J. et al. GRB 050509B: constraints on short gamma-ray burst models. Astrophys. J. Lett. 630, 117–120 (2005)
Narayan, R., Paczynski, B. & Piran, T. Gamma-ray bursts as the death throes of massive binary stars. Astrophys. J. 395, L83–L86 (1992)
Morgan, A. et al. GRB 050709: Swift UVOT and XRT observations. CGN Circ. 3577 (2005)
Schlegel, D. J., Finkbeiner, D. P. & Davis, M. Maps of dust infrared emission for use in estimation of reddening and cosmic microwave background radiation foregrounds. Astrophys. J. 500, 525–553 (1998)
Motohara, K. et al. CISCO: cooled infrared spectrograph and camera for OHS on the Subaru telescope. Proc. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 54, 315–325 (2002)
Fruchter, A. S. & Hook, R. N. Drizzle: a method for the linear reconstruction of undersampled images. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pacif. 114, 144–152 (2002)
Covino, S. et al. GRB 050724: a short-burst detected by Swift. GCN Circ. 3665 (2005)
Peng, C. Y., Ho, L. C., Impey, C. D. & Rix, H.-W. Detailed structural decomposition of galaxy images. Astron. J. 124, 266–293 (2002)
Berger, E. et al. A common origin for cosmic explosions inferred from calorimetry of GRB030329. Nature 426, 154–157 (2003)
Friedman, A. S. & Bloom, J. S. Toward a more standardized candle using gamma-ray burst energetics and spectra. Astrophys. J. 627, 1–25 (2005)
Berger, E. et al. The afterglows, redshifts, and properties of Swift gamma-ray bursts. Astrophys. J. (submitted); preprint at http://arXiv.org/astro-ph/0505107 (2005)
Acknowledgements
Our GRB research is supported in part by funds from NSF, NASA, the Australian Research Council, and the Ministry of Education, Science, Culture, Sports, and Technology in Japan. The VLA is operated by the National Radio Astronomy Observatory, a facility of the NSF operated under cooperative agreement by Associated Universities, Inc. The Gemini Observatory is operated by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy (AURA), Inc., under a cooperative agreement with the NSF on behalf of the Gemini partnership. This work is based in part on data collected at Subaru Telescope, which is operated by the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Reprints and permissions information is available at npg.nature.com/reprintsandpermissions. The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fox, D., Frail, D., Price, P. et al. The afterglow of GRB 050709 and the nature of the short-hard γ-ray bursts. Nature 437, 845–850 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04189
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04189
This article is cited by
-
The Gravitational-wave physics II: Progress
Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy (2021)
-
Detection of short high-energy transients in the local universe with SVOM/ECLAIRs
Astrophysics and Space Science (2020)
-
Kilonovae
Living Reviews in Relativity (2017)
-
The Macronova in GRB 050709 and the GRB-macronova connection
Nature Communications (2016)
-
Gamma-Ray Burst Progenitors
Space Science Reviews (2016)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.